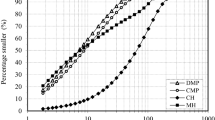
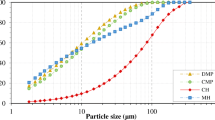
Abstract
The recycling of waste marble powder (MP) for soil stabilization is still under research for geotechnical engineers, with the aim of improving poor soil properties. This paper investigated the effect of calcitic marble powder (CMP) and dolomitic marble powder (DMP) on the geotechnical properties of fine-grained soils. Consistency limits, linear shrinkage, expansion index, and one-dimensional consolidation tests were performed on non-stabilized and stabilized samples with 5, 10, 20, 30, and 50% of waste CMP and DMP to determine the efficiency of using waste marble powders in soil stabilization. The marble powder ratio which gave the best results was determined as 50% for both MH samples and CH samples. The laboratory test results showed that the waste marble powders were effective in soil stabilization by reducing the plasticity index from 49 to 26 for the CH samples and from 21 to 9 for the MH sample, expansion index from 45 to 20 for the CH sample and from 32 to 7 for the MH sample, swelling index from 0.0030 to 0.0012 for the MH sample, compression index from 0.013 to 0.010 for the MH sample, and linear shrinkage from 16.2 to 10.5 for the CH sample. The waste MP content and fine-grained soil type need to be taken into consideration in soil stabilization based on volume change.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lim, S.M.; Wijeyesekera, D.C.; Lim, A.J.M.S.; Bakar, I.B.H.: Critical review of innovative soil road stabilization techniques. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 3(5), 204–211 (2014)
Sabzi, Z.: Environmental friendly soil stabilization materials available in Iran. JEFM 2(1), 33–39 (2018)
Gupta, C.; Sharma, R.K.: Influence of marble dust, fly ash and beas sand on sub grade characteristics of expansive soil. In: International Conference on Advances in Engineering & Technology, IOSR-JMCE, pp. 13–18 (2014)
Zhang, T.; Cai, G.; Liu, S.; Puppala, A.J.: Engineering properties and microstructural characteristics of foundation silt stabilized by lignin-based industrial by-product. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 20(7), 2725–2736 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-016-1325-4
Yilmaz, F.; Yurdakul, M.: Evaluation of marble dust for soil stabilization. Acta Phys. Pol. 132(3), 710–711 (2017). https://doi.org/10.12693/APhysPolA.132.710
Al-Bared, M.A.M.; Marto, A.; Latifi, N.: Utilization of recycled tiles and tyres in stabilization of soils and production of construction materials—a state-of-the-art review. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 22(10), 3860–3874 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-018-1532-2
Ziani, H.; Abbèche, K.; Messaoudene, I.; Pais, A.L.J.: Treatment of collapsible soils by additions of granulated slag and natural pozzolan. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 23(3), 1028–1042 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-019-0051-0
Oncu, S.; Bilsel, H.: Ageing effect on swell, shrinkage and flexural strength of sand and waste marble powder stabilized expansive soil. E3S Web Conf. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/20160913003
Balkis, A.P.: The effects of waste marble dust and polypropylene fiber contents on mechanical properties of gypsum stabilized earthen. Constr. Build. Mater. 134, 556–562 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.12.172
Senol, A.; Edil, T.B.; Bin-Shafique, M.S.; Acosta, H.A.; Benson, C.H.: Soft subgrades’ stabilization by using various fly ashes. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 46(4), 365–376 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2005.08.005
Başer, O.: Stabilization of expansive soils using waste marble dust. MSc Thesis in Civil Engineering, Middle East Technical University, Ankara (2009)
Cetin, B.; Aydilek, A.H.; Guney, Y.: Stabilization of recycled base materials with high carbon fly ash. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 54(11), 878–892 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2010.01.007
Bhavsar, S.N.; Patel, A.J.: Behavior of black cotton soil after stabilization with marble powder. Int. J. Sci. Res. (IJSR) 3(12), 769 (2014)
Yazdandoust, F.; Yasrobi, S.S.: Effect of cyclic wetting and drying on swelling behavior of polymer-stabilized expansive clays. Appl. Clay Sci. 50(4), 461–468 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2010.09.006
Sabat, A.K.: Stabilization of expansive soil using waste ceramic dust. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 17, 3915–3926 (2012)
James, J.; Pandian, P.K.: Soil stabilization as an avenue for reuse of solid wastes: a review. Acta Tech. Napocensis 58(1), 50–76 (2015)
Öncü, Ş.; Bilsel, H.: Utilization of waste marble to enhance volume change and strength characteristics of sand-stabilized expansive soil. Environ. Earth Sci. 77(12), 461 (2018)
Sivrikaya, O.; Kıyıldı, K.R.; Karaca, Z.: Recycling waste from natural stone processing plants to stabilise clayey soil. Environ. Earth Sci. 71(10), 4397–4407 (2014)
RTMEN: Republic of Turkey Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources (2019). www.enerji.gov.tr. Accessed 10 Mar 2020
MTA: Mineral Research & Exploration General Directorate reports (2019). www.mta.gov.tr. Accessed 10 Mar 2020
Celik, M.Y.; Sabah, E.: Geological and technical characterisation of Iscehisar (Afyon-Turkey) marble deposits and the impact of marble waste on environmental pollution. J. Environ. Manag. 87(1), 106–116 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.01.004
Ersoy, B.: Description of flocculants used in cleaning of waste water of marble processing plant. In: Proceedings of 4th National Marble Symposium, Afyon (Turkey), pp. 449–462 (2003)
El-Sayed, H.A.; Farag, A.B.; Kandeel, A.M.; Younes, A.A.; Yousef, M.M.: Characteristics of the marble processing powder waste at Shaq El-Thoaban industrial area, Egypt, and its suitability for cement manufacture. HBRC J. 14(2), 171–179 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hbrcj.2016.06.002
Çelik, M.Y.: Recycling of waste marble. MSc Thesis in Mining Engineering, Afyon Kocatepe University, Afyonkarahisar (1996)
Akbulut, H.; Gürer, C.: The environmental effects of waste marble and possibilities of utilization and waste minimization by using in the road layers. In: Proceeding of the Fourth National Marble Symposium, Afyonkarahisar, December, pp. 371–378 (2003)
Pilkington, A.; Maclaren, W.; Searl, A.; Davis, J.M.G.; Hurley, J.E.; Soutar, C.A.; Pairon, J.C.; Bignon, J.: Scientific opinion on the health effects of airborne crystalline silica. IOM report TM/95/08. Edinburgh, Institute of Occupational Medicine. Ref Type: Report (1996)
Tjoe-Nij, E.; Burdoff, A.; Parker, J.; Attfield, M.; Van Duivenbooden, C.; Heederik, D.: Radiographic abnormalities among construction workers exposed to quartz containing dust. Occup. Environ. Med. 60(6), 410–417 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.60.6.410
Parks, C.G.; Conrad, K.; Cooper, G.S.: Occupational exposure to crystalline silica and autoimmune disease. Environ. Health Perspect. 107, 793–802 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.99107s5793
Steenland, K.; Sanderson, W.T.: Lung cancer among industrial sand workers exposed to crystalline silica. Am. J. Epidemiol. 153(7), 695–703 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/153.7.695
Hnizdo, E.; Vallyathan, V.: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease due to occupational exposure to silica dust: a review of epidemiological and pathological evidence. Occup. Environ. Med. 60, 237–243 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.60.4.237
Raju, B.; Rom, W.N.: Silica, Some Silicates, Coal Dust and Para-Aramid Fibrils: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, vol. 68. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon (1998)
Singh, P.S.; Yadav, R.K.: Effect of marble dust on index properties of black cotton soil. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. 3, 158–163 (2014)
Sabat, A.K.; Nanda, R.P.: Effect of marble dust on strength and durability of rice husk ash stabilised expansive soil. Int. J. Civ. Struct. Eng. 1(4), 939–948 (2011)
Saygili, A.: Use of waste marble dust for stabilization of clayey soil. Mater. Sci. 21(4), 601–606 (2015). https://doi.org/10.5755/j01.ms.21.4.11966
Deboucha, S.; Sail, Y.; Ziani, H.: Effects of ceramic waste, marble dust, and cement in pavement sub-base layer. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 38, 3331–3340 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-020-01211-x
Gourley, C.S.; Newill, D.; Shreiner, H.D.: Expansive soils: TRL’s research strategy. In: Proceedings of 1st International Symposium on Engineering Characteristics of Arid Soils, 6–7 July, London, pp. 247–260, Balkema, Rotterdam (1994)
Estabragh, A.R.; Moghadas, M.; Javadi, A.A.: Effect of different types of wetting fluids on the behaviour of expansive soil during wetting and drying. Soils Found. 53(5), 617–627 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2013.08.001
Mokhtari, M.; Dehghani, M.: Swell–shrink behavior of expansive soils, damage and control. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 17, 2673–2682 (2012)
Day, R.W.: Foundation Engineering Handbook. ASCE Press, The McGraw-Hill Companies, New York (2006)
Giraldez, J.V.; Sposito, G.: A general soil volume change equation: II. Effect of load pressure. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 47(3), 422–425 (1983). https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1983.03615995004700030006x
Braudeau, E.; Costantini, J.M.; Bellier, G.; Colleuille, H.: New device and method for soil shrinkage curve measurement and characterization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 63(3), 525–535 (1999). https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1999.03615995006300030015x
Boivin, P.; Garnier, P.; Tessier, D.: Relationship between clay content, clay type, and shrinkage properties of soil samples. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 68(4), 1145–1153 (2004)
Al-Mukhtar, M.; Lasledj, A.; Alcover, J.F.: Behavior and mineralogy changes in lime treated expansive soil at 50 °C. Appl. Clay Sci. 50(2), 199–203 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2010.07.022
Tang, C.S.; Shi, B.; Liu, C.; Suo, W.B.; Gao, L.: Experimental characterization of shrinkage and desiccation cracking in thin clay layer. Appl. Clay Sci. 52(1), 69–77 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2011.01.032
Khazaei, J.; Moayedi, H.: Soft expansive soil improvement by eco-friendly waste and quick lime. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2590-3
Khemissa, M.; Mahamedi, A.: Cement and lime mixture stabilization of an expansive overconsolidated clay. Appl. Clay Sci. 95, 104–110 (2014)
Lindenmaier, F.; Zehe, E.; Helms, M.; Evdakov, O.; Ihringer, J.: Effect of soil shrinkage on runoff generation in micro and mesoscale catchments. In: Predictions in Ungauged Basins: Promise and Progress (Proceedings of Symposium S7 Held During the Seventh IAHS Scientific Assembly at Foz do Iguaçu, Brazil, April 2005), pp. 305–317 (2006)
Ross, G.J.: Relationships of specific surface area and clay content to shrink–swell potential of soils having different clay mineralogical compositions. Can. J. Soil Sci. 58(2), 159–166 (1978)
Mitchell, J.K.; Soga, K.: Fundamentals of Soil Behavior. Wiley, New York (2005)
Achmad, F.; Nazmi, W.M.; Fauzi, U.J.: California bearing ratio (CBR) improvement of Kuantan clay subgrade by using reused material as stabilizer. In: 9th National Conference of the Indonesia Road Development Association (IRDA), Jakarta (2011)
ASTM D 2487-00: Standard practice for classification of soils for engineering purposes (Unified Soil Classification System). West Conshohocken, PA, USA (2013)
Nalbantoğlu, Z.: Effectiveness of class C fly ash as an expansive soil stabilizer. Constr. Build. Mater. 18(6), 377–381 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2004.03.011
Fırat, S.; Yılmaz, G.; Cömert, A.T.; Sümer, M.: Utilization of marble dust, fly ash and waste sand (silt–quartz) in road subbase filling materials. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 16(7), 1143–1151 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-012-1526-4
James, J.; Lakshmi, S.V.; Pandian, P.K.: Strength and index properties of phosphogypsum stabilized expansive soil. Int. J. Appl. Environ. Sci. 5(1), 2721–2731 (2014)
ASTM D 854: Standard test methods for specific gravity of soil solids by water pycnometer. West Conshohocken, PA, USA (2013)
ASTM D 4318: Standard test methods for liquid limit, plastic limit, and plasticity index of soils. West Conshohocken, PA, USA (2013)
ASTM D 698-07: Standard test methods for laboratory compaction characteristics of soil using standard effort. West Conshohocken, PA, USA (2013)
BS 1377-2: Methods of test for soils for civil engineering purposes. Part 2: classification tests, BSI (1990)
ASTM D 4546-14: Standard test methods for one-dimensional swell or collapse of soils. West Conshohocken, PA, USA (2014)
ASTM D 2435-00: Standard test methods for one-dimensional consolidation properties of soils using incremental loading. West Conshohocken, PA, USA (2013)
Holtz, R.D.; Kovacs, W.D.: An Introduction to Geotechnical Engineering. Prentice Hall Inc., New Jersey (1981)
Gürü, M.; Tekeli, S.; Akin, E.: Manufacturing of polymer matrix composite material using marble dust and fly ash. Key Eng. Mater. 336, 1353–1356 (2007). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.336-338.1353
Ramadas, T.L.; Kumar N.D.; Aparna, G.: Swelling and strength characteristics of expansive soil treated with stone dust and fly Ash. In: Indian Geotechnical Conference-2010, GEOtrendz, 16–18 December, Bombay, pp. 557–560 (2010)
Agrawal, V.; Gupta, M.: Expansive soils stabilization using marble dust. Int. J. Earth Sci. Eng. 4, 59–62 (2011)
Devarajan, D.; Sasikumar, A.: Evaluation of geotechnical properties of marble dust treated clayey soil. IJARTET 1, 17–22 (2014)
Bhavsar, S.N.; Patel, A.J.: Effect of waste material on swelling and shrinkage properties of clayey soil. IJAIEM 3, 200–206 (2014)
Chen, J.A.; Idusuyi, F.O.: Effect of waste ceramic dust (WCD) on index and engineering properties of shrink–swell soils. Int. J. Educ. Med. Technol. 1(8), 52–62 (2015)
Batman, A.: Investigation of the effect of crushed quartz sand on clay strength properties. PhD Thesis in Civil Engineering, Atatürk University, Erzurum (2015)
Hasan, H.A.: Effect of fly ash on geotechnical properties of expansive soil. JEAD 16(2), 306–316 (2012)
Bhavsar, S.N.; Patel, A.J.: Analysis of swelling and shrinkage properties of expansive soil using brick dust as a stabilizer. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 4(12), 303–308 (2014)
Day, R.W.: Expansion potential according to the uniform building code. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 119(6), 1067–1071 (1993)
Abdulla, R.S.; Majeed, N.N.: Some physical properties treatment of expansive soil using marble waste powder. IJERT 3(1), 591–600 (2014)
Zorluer, I.; Muratoglu, I.: Effect of marble dust on consolidation characteristics of clay soils. In: International Symposium on Sustainable Development, pp. 514–517 (2010)
Acknowledgements
This paper is partly produced from the FEB 2017/10-11-YULTEP Project of Niğde Ömer Halisdemir University, Scientific Research Projects Unit. The authors also thank Niğde NİDAŞ Company for giving permission for the use of their laser diffraction device.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sivrikaya, O., Uysal, F., Yorulmaz, A. et al. The Efficiency of Waste Marble Powder in the Stabilization of Fine-Grained Soils in Terms of Volume Changes. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 8561–8576 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04768-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04768-0