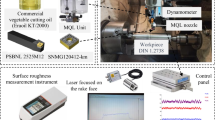
Abstract
To comply with the remarkable demand of bio-implants at a reasonable cost, selection of appropriate material, efficient manufacturing processes and associated parameters play a vital role. Particularly, benign of green manufacturing is gaining huge attention in bio-implants manufacturing to comply with environmental concerns. The present work is an effort to exhibit the viability of green manufacturing during dry turning of bio-implant steel (AISI 316L) using coated carbide cutting tool. Cutting speed, feed rate, depth of cut and tool nose radius are considered as input variables, whereas main cutting force, tool flank wear and centreline mean surface roughness are taken as output responses. Range of the input variables has been decided on the bases of pilot studies. Using the design of experiment strategy, experimentation has been carried out on a computerized numerically controlled lathe machine in a dry environment. Significant input variables affecting the responses have been identified through the analysis of variance and response surface methodology. Further, mathematical regression models have also been derived. Desirability factor-based multi-response optimization analysis has been implemented and found the optimum main cutting force: 113.6 N, flank wear: 0.14 mm and mean surface roughness: 1.27 µm, at cutting speed: 125 m/min, feed: 0.05 mm/rev., depth of cut: 0.75 mm and tool nose radius: 0.4 mm.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, Q.; Thouas, G.A.: Metallic implant biomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 87, 1–57 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2014.10.001
Watari, F.; Yokoyama, A.; Omori, M.; Hirai, T.; Kondo, H.: Biocompatibility of materials and development to functionally graded implant for bio-medical application. Compos. Sci. Technol. 64, 893–908 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2003.09.005
Lai, J.J.; Lin, Y.S.; Chang, C.H.; Wei, T.Y.; Huang, J.C.; Liao, Z.X.; et al.: Applied Surface Science Promising Ta-Ti-Zr-Si metallic glass coating without cytotoxic elements for bio-implant applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 427, 485–495 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.08.065
Jin, S.; Ren, L.; Yang, K.: Bio-functional Cu containing biomaterials: a new way to enhance bio-adaption of biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 32, 835–839 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2016.06.022
Zaman, H.A.; Sharif, S.; Idris, M.H.; Kamarudin, A.: Metallic biomaterials for medical implant applications: a review. Appl. Mech. Mater. 735, 19–25 (2015). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.735.19
Mudali, U.K.; Sridhar, T.M.; Raj, B.: Corrosion of bio implants. Sadhana—Acad. Proc. Eng. Sci. 28, 601–637 (2003)
Su, Y.; Luo, C.; Zhang, Z.; Hermawan, H.; Zhu, D.; Huang, J.; et al.: Bioinspired surface functionalization of metallic biomaterials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 77, 90–105 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2017.08.035
Dixit, U.S.; Sarma, D.K.; Davim, J.P.: Environmentally Friendly Machining. Springer, New York (2012)
Davim, J.P.: Green Manufacturing Processes and Systems. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Saptaji, K.: Machining of biocompatible materials: a review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 97, 2255–2292 (2018)
Karimi, S.; Nickchi, T.; Alfantazi, A.M.: Applied surface science long-term corrosion investigation of AISI 316L, Co–28Cr–6Mo, and Ti–6Al–4V alloys in simulated body solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 6087–6096 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.03.008
Polishetty A, Alabdullah M, Littlefair G.: A preliminary study on machinability of super austenitic stainless steel. In: Proceedings of 2015 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition IMECE 2015 November 13–19, 2015, Houston, Texas, USA (2015). doi:10.1115/IMECE2015-50224
Endrino, J.L.; Fox-rabinovich, G.S.; Gey, C.: Hard AlTiN, AlCrN PVD coatings for machining of austenitic stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 200, 6840–6845 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2005.10.030
Jagtap, K.A.; Pawade, R.S.: Experimental investigation on surface roughness of face turned Co–Cr–Mo biocompatible alloy followed by polishing. J Mater. Sci. Eng. 5, 585–592 (2017)
Rao, K.; Kumar, M.C.A.; Rashmi, S.; Shrikantha, L.M.; Herbert, M.A.: Machinability study of austenitic stainless steel under wet and cryogenic treatment in face milling. J. Mater. Sci. Surf. Eng. 5(6), 653–656 (2018)
Sinha, M.K.; Madarkar, R.; Ghosh, S.; Rao, P.V.: Application of eco-friendly nano fluids during grinding of Inconel 718 through small quantity lubrication. J. Clean. Prod. 141, 1359–1375 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.09.212
Bagaber, S.A.; Yusoff, A.R.: Multi-responses optimization in dry turning of a stainless steel as a key factor in minimum energy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 96, 1109–1122 (2018)
Ramu, I., Srinivas, P., Vekatash, K.: Taguchi based grey relational analysis for optimization of machining parameters of CNC Taguchi based grey relational analysis for optimization of machining parameters of CNC turning steel 316. In: International Conference on Mechanical, Materials and Renewable Energy (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/377/1/012078.
Nur, R.; Noordin, M.Y.; Izman, S.; Kurniawan, D.: Machining parameters effect in dry turning of AISI 316L stainless steel using coated carbide tools. Proc. I Mech. E Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954408915624861
Gupta, A.K.; Guntuku, S.C.: Optimisation of turning parameters by integrating genetic algorithm with support vector regression and artificial neural networks. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 77, 331–339 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6282-9
Bedi, S.S.; Behera, G.C.; Datta, S.: Effects of cutting speed on MQL machining performance of AISI 304 stainless steel using uncoated carbide insert: application potential of coconut oil and rice bran oil as cutting fluids. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 1–17 (2020)
Mishra, S.K.; Ghosh, S.; Aravindan, S.: Machining performance evaluation of Ti6Al4V alloy with laser textured tools under MQL and nano-MQL environments. J. Manuf. Process. 53, 174–189 (2020)
Rahman, M.A.; Rahman, M.; Mia, M.; Gupta, M.K.; Sen, B.; Ahmed, A.: Investigation of the specific cutting energy and its effect in shearing dominant precision micro cutting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 283, 116688 (2020)
Mia, M.; Dhar, N.R.: Modeling of surface roughness using RSM, FL and SA in dry hard turning. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43, 1125–1136 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2754-1
Alharthi, N.H.; Bingol, S.; Abbas, A.T.; Ragab, A.E.; Aly, M.F.; Alharbi, H.F.: Prediction of cutting conditions in turning AZ61 and parameters optimization using regression analysis and artificial neural network. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 1–10 (2018)
Gupta, M.K.; Sood, P.K.; Sharma, V.S.: Machining parameters optimization of titanium alloy using response surface methodology and particle swarm optimization under minimum-quantity lubrication environment. Mater. Manuf. Process. 31, 1671–1682 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1117632
Rao, K.V.; Murthy, B.S.N.; Rao, N.M.: Prediction of cutting tool wear, surface roughness and vibration of work piece in boring of AISI 316 steel with artificial neural network. Measurement 51, 63–70 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2014.01.024
Susanto, T.A.; Nur, R.: Performance evaluation of Titanium nitride coated tool in turning of mild steel. IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/330/1/012078
Chauhan, P.K.S.R.: Machinability study on finish turning of AISI H13 hot working die tool steel with cubic boron nitride (CBN) cutting tool inserts using response surface methodology (RSM). Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 40, 1471–1485 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1606-0
Makadia, A.J.; Nanavati, J.I.: Optimisation of machining parameters for turning operations based on response surface methodology. Measurement 46, 1521–1529 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2012.11.026
El-Hossainy, T.M.; El-Zoghby, A.A.; Badr, M.A.; Maalawi, K.Y.; Nasr, M.F.: Cutting parameter optimization when machining different materials. Mater. Manuf. Process. 25, 1101–1114 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2010.480998
Qian, L.; Hossan, M.R.: Effect on cutting force in turning hardened tool steels with cubic boron nitride inserts. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 191, 274–278 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.03.022
Philip Selvaraj, D.; Chandramohan, P.; Mohanraj, M.: Optimization of surface roughness, cutting force and tool wear of nitrogen alloyed duplex stainless steel in a dry turning process using Taguchi method. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 49, 205–215 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2013.11.037
Sinha, M.K.; Madarkar, R.; Ghosh, S.: Some investigations in grindability improvement of Inconel 718 under ecological grinding. J. Eng. Manuf. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405417752513
Dasgupta, S.; Mukherjee, S.: Effects of machining parameters on tool life and its optimization in turning mild steel with brazed carbide cutting tool. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/149/1/012005
Byers, J.P.: Metalworking Fluids, 2nd edn. Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton (2006)
Debnath, S.; Reddy, M.M.; Yi, Q.S.: Influence of cutting fluid conditions and cutting parameters on surface roughness and tool wear in turning process using Taguchi method. Measurement 78, 111–119 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2015.09.011
Zaharudin, A.M.; Budin, S.: Influence of cutting speed on coated TiCN cutting tool during turning of AISI 316L stainless steel in dry turning process. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 505, 012044 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/505/1/012044
Adarsha Kumar, K.; Ratnam, C.; Venkata Rao, K.; Murthy, B.S.N.: Experimental studies of machining parameters on surface roughness, flank wear, cutting forces and work piece vibration in boring of AISI 4340 steels: modelling and optimization approach. SN Appl. Sci. 1, 1–12 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-018-0026-7
Zerti, A.: Modeling and multi-objective optimization for minimizing surface roughness, cutting force, and power, and maximizing productivity for tempered stainless steel AISI 420 in turning operations. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 102, 135–157 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A., Sinha, M.K. Multi-Response Optimization During Dry Turning of Bio-implant Steel (AISI 316L) Using Coated Carbide Inserts. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 9397–9411 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04717-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04717-x