Abstract
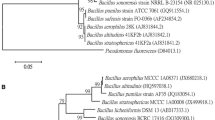
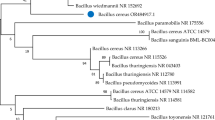
In agriculture, Bacillus species are widely used to stimulate plant growth and act as an efficient and ecologically sound tool for protecting the plant from pathogens and other environmental stresses. This study reveals the plant growth-promoting (PGP) ability of bacteria isolated from the rhizosphere soil of the tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum). The isolates were identified as Bacillus species based on a 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. Among the PGP attributes, the isolates were found to be positive for indole acetic acid (IAA) production, phosphate solubilization, siderophore production, ammonia production, and nitrogen fixation. The isolates were found negative for zinc and potassium solubilization. The quantitative estimation of IAA production ranged from 10.28 to 25.81 µg/ml, solubilization of inorganic phosphorous ranged from 0.12 to 13.83 μg/ml, and siderophore production ranged from 1.39 to 78.79%. The isolates also had the ability to produce lytic enzymes such as amylase, cellulase, lipase, protease, and pectinase and biocontrol activity against Fusarium oxysporum. The inoculation PGP Bacillus improved germination rate, seedling vigor index, and a range of growth parameters in the tomato (L. esculentum) compared to uninoculated control plants. These findings give an insight into the ways to use PGP bacteria as an alternative to chemicals and pesticides.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qiao, J.-Q.; Wu, H.-J.; Huo, R.; Gao, X.-W.; Borriss, R.: Stimulation of plant growth and biocontrol by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum FZB42 engineered for improved action. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 1, 1–14 (2014)
Kloepper, J.W.; Leong, J.; Teintze, M.; Schroth, M.N.: Enhanced plant growth by siderophores produced by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Nature 286, 885–886 (1980)
Qiao, J.; Yu, X.; Liang, X.; Liu, Y.; Borriss, R.; Liu, Y.: Addition of plant-growth-promoting Bacillus subtilis PTS-394 on tomato rhizosphere has no durable impact on composition of root microbiome. BMC Microbiol. 17, 131 (2017)
Bhattacharyya, P.N.; Jha, D.K.: Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): emergence in agriculture. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 28, 1327–1350 (2012)
Fravel, D.R.: Commercialization and implementation of biocontrol. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 43, 337–359 (2005)
Xu, D.; Cote, J.C.: Phylogenetic relationships between Bacillus species and related genera inferred from comparison of 3′ end 16 S rDNA and 5′ end 16S-23 S ITS nucleotide sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 53, 695–704 (2003)
Niu, D.D.; Liu, H.X.; Jiang, C.H.; Wang, Y.P.; Wang, Q.Y.; Jin, H.L.; Guo, J.H.: The plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Bacillus cereus AR156 induces systemic resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana by simultaneously activating salicylate- and jasmonate/ethylene-dependent signaling pathways. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 24, 533–542 (2011)
McSpadden Gardener, B.E.: Ecology of Bacillus and Paenibacillus spp. in agricultural systems. Phytopathology 9411, 1252–1258 (2004)
Kumar, A.; Prakash, A.; Johri, B.N.: Bacteria in agrobiology: crop ecosystems. In: Maheshwari, D.K. (ed.) Bacillus as PGPR in Crop Ecosystem, pp. 37–59. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Stein, T.: Bacillus subtilis antibiotics: structures, synthesis and specifics functions. Mol. Microbiol. 56, 845–847 (2005)
Senthilkumar, M.; Swarnlakshmi, K.; Govindasamy, V.; Lee, Y.K.; Annapurna, K.: Biocontrol potential of soybean bacterial endophytes against charcoal rot fungus Rhizoctonia bataticola. Curr. Microbiol. 58, 288–293 (2009)
Tilak, B.R.; Reddy, B.S.: Bacillus cereus and B. circulans—novel inoculants for crops. Curr. Sci. 90(5), 642–644 (2006)
Handelsman, J.; Raffel, S.; Mester, E.H.; Wunderlich, L.; Grau, C.R.: Biological control of damping-off of alfalfa seedlings with Bacillus cereus UW85. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56, 713–718 (1990)
Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. (eds.): Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York (2001)
Berg, G.; Krechel, A.; Ditz, M.; Sikora, R.A.; Ulrich, A.; Hallmann, J.: Endophytic and ectophytic potato-associated bacterial communities differ in structure and antagonistic function against plant pathogenic fungi. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 51, 215–229 (2005)
Cappuccino, J.G.; Sherman, N. (eds.): Biochemical Activities of Microorganisms. Microbiology, a Laboratory Manual, pp. 105–300, 1st edn. The Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co, California (1992)
Gordon, S.A.; Weber, R.P.: Colorimetric estimation of indole acetic acid. Plant Physiol. 26, 192–195 (1951)
Schwyn, B.; Neilands, J.B.: Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal. Biochem. 160, 47–56 (1987)
Alexander, D.B.; Zuberer, D.A.: Use of Chrome Azurol S reagents to evaluate siderophore production by rhizosphere bacteria. Biol. Fertil. Soils 12, 39–45 (1991)
Payne, S.M.: Iron acquisition in microbial pathogenesis. Trends Microbiol. 1, 66–69 (1993)
Jensen, H.L.: Nitrogen fixation in leguminous plants II. Is symbiotic nitrogen fixation influenced by Azotobacter? Proc. Linn. Soc. N.S.W. 57, 205–212 (1942)
Zucconi, F.; Pera, A.; Forte, M.; de Bertoldi, M.: Evaluating toxicity of immature compost. BioCycle 22, 54–57 (1981)
Medawar, G.; Srour, G.; El Azzi, D.: Comparison of chlorophyll content in greenhouse tomato and cucumber leaves after HBED-Fe and EDDHA-Fe applications. Front. Life. Sci. 9, 182–189 (2016)
Arnon, I.: Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 24, 1–15 (1949)
Cao, Y.; Pi, H.; Chandrangsu, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xiong, H.; Helmann, J.D.; Cai, Y.: Antagonism of two plant-growth promoting Bacillus velezensis isolates against Ralstonia solanacearum and Fusarium oxysporum. Sci. Rep. 8, 4360 (2018)
Costacurta, A.; Vanderleyden, J.: Synthesis of phytohormones by plant-associated bacteria. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 21, 1–18 (1995)
Kamnev, A.; Shchelochkov, A.; Perfiliev, Y.D.; Tarantilis, P.A.; Polissiou, M.G.: Spectroscopic investigation of indole-3-acetic acid interaction with iron (III). J. Mol. Struct. 563, 565–572 (2001)
Ribeiro, V.P.; Marriel, I.E.; de Sousa, S.M.; de Paula Lana, U.G.; Mattos, B.B.; de Oliveira, C.A.; Gomes, E.A.: Endophytic Bacillus strains enhance pearl millet growth and nutrient uptake under low-P. Braz. J. Microbiol. 49, 40–46 (2018)
Verma, J.P.; Jaiswal, D.K.; Krishna, R.; Prakash, S.; Yadav, J.; Singh, V.: Characterization and screening of thermophilic Bacillus strains for developing plant growth promoting consortium from hot spring of Leh and Ladakh Region of India. Front. Microbiol. 9, 1293 (2018)
Sridevi, M.; Mallaiah, K.V.: Bioproduction of indole acetic acid by Rhizobium strains isolated from root nodules of green manure crop, Sesbania sesban (L.). Merr. Iran. J. Biotechnol. 5, 178–182 (2007)
Verma, J.P.; Yadav, J.; Tiwari, K.N.; Lavakush,; Singh, V.: The impact of Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on crop production. Int. J. Agric. Res. 5, 954–983 (2010)
Kuan, K.B.; Othman, R.; Rahim, K.A.; Shamsuddin, Z.H.: Plant growth-promoting Rhizobacteria inoculation to enhance vegetative growth, nitrogen fixation and nitrogen remobilisation of maize under greenhouse conditions. PLoS ONE 11, 1–19 (2016)
Mahamuni, S.V.; Wani, P.V.; Patil, A.S.: Isolation of phosphate solubilizing fungi from rhizosphere of sugarcane & sugar beet using TCP & RP solubilization. Asian J. Biomed. Pharm. Sci. 2, 237–244 (2012)
Kim, Y.H.; Bae, B.; Choung, Y.K.: Optimization of biological phosphorus removal from contaminated sediments with phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 1, 23–29 (2005)
Nenwani, V.; Doshi, P.; Saha, T.; Rajkumar, S.: Isolation and characterization of a fungal isolate for phosphate solubilization and plant growth promoting activity. J. Yeast Fungal Res. 1, 9–14 (2010)
Banerjee, S.; Palit, R.; Sengupta, Ch; Standing, D.: Stress induces phosphate solubilisation by Arthrobacter sp. and Bacillus sp. isolated from tomato rhizosphere. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 4, 378–383 (2010)
Louden, B.C.; Haarmann, D.; Lynne, A.: Use of blue agar CAS assay for siderophore detection. J. Microbiol. Biol. Educ. 12, 51–53 (2011)
Rahi, P.; Vyas, P.; Sharma, S.; Gulati, A.: Plant growth promoting potential of the fungus Discosia sp. FIHB 571 from tea rhizosphere tested on chickpea, maize and pea. Indian J Microbiol. 49(2), 128–133 (2009)
Lin, T.X.; Xu, C.H.; Tang, M.; Guan, Q.L.; Gong, M.F.: Siderophore producing by endophytic bacterial strain YBS106 with antifungal activity against Fusarium oxysporum. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 7, 2091–2096 (2013)
Yu, X.; Ai, C.; Xin, L.; Zhou, G.: The siderophore producing bacterium, Bacillus subtilis CAS15, has a biocontrol effect on Fusarium wilt and promotes the growth of pepper. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 47, 138–145 (2011)
Passari, A.K.; Upadhyaya, K.; Singh, G.; Abdel-Azeem, A.M.; Thankappan, S.; Uthandi,; et al.: Enhancement of disease resistance, growth potential, and photosynthesis in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) by inoculation with an endophytic actinobacterium, Streptomyces thermocarboxydus strain BPSAC147. PLoS ONE 14(7), e0219014 (2019)
Koh, R.-H.; Song, H.-G.: Effects of application of Rhodopseudomonas sp. on seed germination and growth of tomato under axenic conditions. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 17(11), 1805–1810 (2007)
Hassen, A.I.; Labuschagne, N.: Root colonization and growth enhancement in wheat and tomato by rhizobacteria isolated from the rhizoplane of grasses. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 26, 1837–1846 (2010)
Babu, A.N.; Jogaiah, S.; Ito, S.-I.; Nagaraj, A.K.; Tran, L.-S.P.: Improvement of growth, fruit weight and early blight disease protection of tomato plants by rhizosphere bacteria is correlated with their beneficial traits and induced biosynthesis of antioxidant peroxidase and polyphenol oxidase. Plant Sci. 231, 62–73 (2015)
Dias, M.P.; Bastos, M.S.; Xavier, V.B.; Cassel, E.; Astarita, L.V.; Santarém, E.R.: Plant growth and resistance promoted by Streptomyces spp. in tomato. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 118, 479–493 (2017)
Deivanai, S.; Bindusara, A.S.; Prabhakaran, G.; Bhore, S.J.: Culturable bacterial endophytes isolated from Mangrove tree (Rhizophora apiculata Blume) enhance seedling growth in Rice. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 5(2), 437–444 (2014)
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge UTU management for their constant support and providing necessary facilities to carry out the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, R., Amaresan, N., Patel, P. et al. Isolation and Characterization of Bacillus spp. Endowed with Multifarious Plant Growth-Promoting Traits and Their Potential Effect on Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) Seedlings. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 4579–4587 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04543-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04543-1