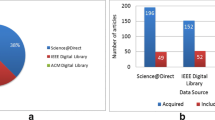
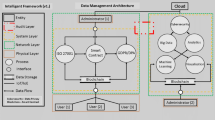
Abstract
For the growth of an economy, the satisfactory and steady availability of energy supplies is necessary. A developing country (like Pakistan) encounters perpetual issues of power losses. This paper explores the challenges faced by the power economy in Pakistan. Furthermore, technologies to prevent power losses are studied and analyzed. Based on the blockchain technology, this paper proposes a power loss preventing solution by using Ethereum smart contracts. These contracts handle both sides of the power economy (the consumer and the grid) by ensuring the integrity and security of data. For the evaluation of our proposed solution, we implement the contracts and the results show that our solution is effective in reducing the line losses. The proposed solution is location independent and can be applied to economies facing similar issues.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jamil, F.; Ahmad, E.: An empirical study of electricity theft from electricity distribution companies in Pakistan. Pakistan Dev. Rev. 53(3), 239–254 (2014)
Bhattacharyya, S.C.: Energy Economics: Concepts, Issues, Markets and Governance. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Smith, T.B.: Electricity theft: a comparative analysis. Energy Policy 32(18), 2067–2076 (2004)
Dal Bó, E.; Rossi, M.A.: Corruption and inefficiency: theory and evidence from electric utilities. J. Public Econ. 91(5–6), 939–962 (2007)
Lewis, F.B.: Costly ‘throw-ups’: electricity theft and power disruptions. Electr. J. 28(7), 118–135 (2015)
Zaman, R.; Brudermann, T.: Energy governance in the context of energy service security: a qualitative assessment of the electricity system in Bangladesh. Appl. Energy 223, 443–456 (2018)
Gaur, V.; Gupta, E.: The determinants of electricity theft: an empirical analysis of indian states. Energy Policy 93, 127–136 (2016)
Jokar, P.; Arianpoo, N.; Leung, V.C.M.: Electricity theft detection in ami using customers’ consumption patterns. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 7(1), 216–226 (2015)
McDaniel, P.; McLaughlin, S.: Security and privacy challenges in the smart grid. IEEE Secur. Priv. 7(3), 75–77 (2009)
Irfan, M.; Iqbal, J.; Iqbal, A.; Iqbal, Z.; Riaz, R.A.; Mehmood, A.: Opportunities and challenges in control of smart grids—Pakistani perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 71, 652–674 (2017)
Khalil, H.B.; Abas, N.: Smart grids: an approach to integrate the renewable energies and efficiently manage the energy system of Pakistan. In: Fifth International Conference on Computing, Communications and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), pp 1–7 (2014)
Ahmad, M: Pakistan lost rs90 billion in electricity theft, line losses. The News, Pakistan
Mustafa, K: Rs59.174b power theft in 9 discos in 9 months. The International News
Cachin, C; Vukolić, M: Blockchain consensus protocols in the wild. arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.01873, (2017)
Baliga, A.: Understanding blockchain consensus models. https://www.persistent.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/WP-Understanding-Blockchain-Consensus-Models.pdfs (2017)
Tschorsch, F.; Scheuermann, B.: Bitcoin and beyond: a technical survey on decentralized digital currencies. IEEE Commun. Surveys Tutor. 18(3), 2084–2123 (2016)
Nakamoto, S. et al: Bitcoin: a peer-to-peer electronic cash system. (2008)
Suliman, A.; Husain, Z.; Abououf, M.; Alblooshi, M.; Salah, K.: Monetization of IoT data using smart contracts. IET Netw. 8(1), 32–37 (2019)
Chaer, A; Salah, K; Lima, C; Ray, P; Sheltami, T: Blockchain for 5g: opportunities and challenges. 12 (2019)
Salah, K.; Rehman, M.H.U.; Nizamuddin, N.; Al-Fuqaha, A.: Blockchain for ai: review and open research challenges. IEEE Access 7, 10127–10149 (2019)
Collectif. OECD digital economy outlook 2017 - en. OECD, 2017, (2017)
Hasan, H.R.; Salah, K.: Blockchain-based proof of delivery of physical assets with single and multiple transporters. IEEE Access 6, 46781–46793 (2018)
Hasan, H. R..; Salah, K.: Blockchain-based solution for proof of delivery of physical assets. In: Shiping, C.; Harry, W.; Liang-Jie, Z. (eds.) Blockchain, ICBC 2018, pp. 39–152. Cham, Springer (2018)
Clarke, G.R.G.; Xu, L. C.: Privatization, competition and corruption: how characteristics of bribe takers and payers after bribe payments to utilities. Technical report, Nota di Lavoro, Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei (2002)
Razavi, R.; Gharipour, A.; Fleury, M.; Akpan, I.J.: A practical feature-engineering framework for electricity theft detection in smart grids. Appl. Energy 238, 481–494 (2019)
Ahmad, T.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.: Review of various modeling techniques for the detection of electricity theft in smart grid environment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 82, 2916–2933 (2018)
Yip, S.C.; Wong, K.; Hew, W.P.; Gan, M.T.; Phan, R.C.W.; Tan, S.W.: Detection of energy theft and defective smart meters in smart grids using linear regression. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 91, 230–240 (2017)
Yip, S.-C.; Tan, W.-N.; Tan, C.K.; Gan, M.-T.; Wong, K.S.: An anomaly detection framework for identifying energy theft and defective meters in smart grids. Int. J.Electr. Power Energy Syst. 101, 189–203 (2018)
Pasdar, A.; Mirzakuchaki, S.: A solution to remote detecting of illegal electricity usage based on smart metering. In: 2007 2nd International Workshop on Soft Computing Applications, pp. 163–167. IEEE, (2007)
Monedero, Í; Biscarri, F; León, C; Biscarri, J; Millán, : Midas: detection of non-technical losses in electrical consumption using neural networks and statistical techniques. In: International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications, pp. 725–734. Springer, (2006)
Nagi, J.; Yap, K. S.; Nagi, F.; Tiong, S. K.; Koh, SP; Ahmed, S. K.: NTL detection of electricity theft and abnormalities for large power consumers in TNB Malaysia. In: 2010 IEEE Student Conference on Research and Development (SCOReD), pp. 202–206. IEEE, (2010)
Cabral, J. E.; Pinto, J. O.; Martins, E. M.; Pinto, A. M.: Fraud detection in high voltage electricity consumers using data mining. In: 2008 IEEE/PES Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exposition, pp. 1–5. IEEE, (2008)
Sreenadh Reddy Depuru, S.S.; Wang, L.; Devabhaktuni, V.; Gudi, N.: Smart meters for power grid: challenges, issues, advantages and status. AGRIS 15(18), 2736–2742 (2015)
Chamberlin, B.: Ibm blockchain trend report 2017 (2017)
Conoscenti, M.; Vetro, A.; De Martin, J. C.: Blockchain for the internet of things: a systematic literature review. In: 2016 IEEE/ACS 13th International Conference of Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), pp. 1–6. IEEE, (2016)
Biswas, K.; Muthukkumarasamy, V. : Securing smart cities using blockchain technology. In: 2016 IEEE 18th international conference on high performance computing and communications; IEEE 14th International Conference on Smart City; IEEE 2nd International Conference on Data Science And Systems (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS), pp. 1392–1393. IEEE, (2016)
Boudguiga, A.; Bouzerna, N.; Granboulan, L.; Olivereau, A.; Quesnel, F.; Roger, A.; Sirdey, R.: Towards better availability and accountability for iot updates by means of a blockchain. In: 2017 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy Workshops (EuroS&PW), pp. 50–58. IEEE, (017)
Lee, B.; Lee, J.-H.: Blockchain-based secure firmware update for embedded devices in an internet of things environment. J. Supercomput 73(3), 1152–1167 (2017)
Casado-Vara, R.; Prieto, J.; Corchado, J. M.: How blockchain could improve fraud detection in power distribution grid. In: The 13th International Conference on Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications, pp. 67–76. Springer, (2018)
Guan, Z.; Si, G.; Zhang, X.; Longfei, W.; Guizani, N.; Xiaojiang, D.; Ma, Y.: Privacy-preserving and efficient aggregation based on blockchain for power grid communications in smart communities. IEEE Commun. Mag. 56(7), 82–88 (2018)
Fan, Mochan; Zhang, Xiaohong: Consortium blockchain based data aggregation and regulation mechanism for smart grid. IEEE Access 7, 35929–35940 (2019)
Imbault, F.; Swiatek, M.; de Beaufort, R.; Plana, R.: The green blockchain: managing decentralized energy production and consumption. pp. 1–5, 06 (2017)
Kshetri, N.; Voas, J.: Blockchain in developing countries. IT Prof. 3, 11–14 (2018)
De Angelis, Stefano; Aniello, Leonardo; Lombardi, Federico; Margheri, Andrea; Sassone, V.: PBFT vs proof-of-authority: applying the CAP theorem to permissioned blockchain. 01 (2017)
Hu kenneth. Developing ethereum dapps with truffle, ganache and metamask. coinmarks, (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalid, S., Maqbool, A., Rana, T. et al. A Blockchain-Based Solution to Control Power Losses in Pakistan. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 6051–6061 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04464-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04464-z