Abstract
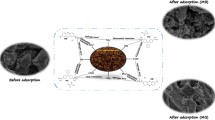
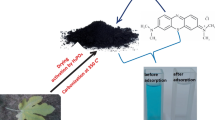
In this study, jojoba seeds residues are investigated for the removal of anionic dyes (Eriochrome black T and Congo red) from aqueous phase after extraction of oil and defatting (washing with n-hexane) from them. The fatted (F-JR) and defatted (DF-JR) jojoba residues were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron spectroscopy, thermogravimetric and BET analyzer. The results indicated that the surface of F-JR and DF-JR exhibited abundant oxygen functionalities (O–H, C–O, C=O, C–O–C) with highly porous surface morphology. The adsorption results showed that the removal of EBT and CR was significantly affected by solution pH and maximum removal of both dyes (EBT and CR) was obtained at pH 2 and 6, respectively, with equilibrium reached at 600 min. The kinetic results were best fitted with pseudo-second-order model. The Freundlich isotherm model well described the EBT adsorption, whereas CR adsorption better matches the Langmuir isotherm model for both F-JR and DF-JR. The maximum adsorption of EBT and CR was found to be 88.96 and 24.64 and 113.50 and 58.82 mg/g onto F-JR and DF-JR, respectively. The adsorption mechanism of EBT and CR mainly involved electrostatic attraction, chemical reactions, pi-pi interactions and development of hydrophobic forces. The adsorbent showed better removal performance of dyes, when compared to other agriculture residues, indicating potential and beneficial utilization of jojoba residues for effective decontamination of dye-contaminated wastewater.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rawat, D.; Sharma, R.S.; Karmakar, S.; Arora, L.S.; Mishra, V.: Ecotoxic potential of a presumably non-toxic azo dye. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 148, 528–537 (2018)
Wang, K.; Fu, J.; Wang, S.; Gao, M.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Q.: Polydopamine-coated magnetic nanochains as efficient dye adsorbent with good recyclability and magnetic separability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 516, 263–273 (2018)
Khumalo, N.; Nthunya, L.; De Canck, E.; Derese, S.; Verliefde, A.; Kuvarega, A.; Mamba, B.; Mhlanga, S.; Dlamini, D.: Congo red dye removal by direct membrane distillation using PVDF/PTFE membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 211, 578–586 (2019)
Van Tran, T.T.; Kumar, S.R.; Lue, S.J.: Separation mechanisms of binary dye mixtures using a PVDF ultrafiltration membrane: donnan effect and intermolecular interaction. J. Membr. Sci. 575, 38–49 (2019)
Allen, T.R.; Smith, C.; Charanda, T.: Ozone process for color removal. (Google Patents) (2019)
Azner, A.C.Z.; Fahmi, M.R.; Ong, S.A.; Haqi, I.A.; Nasuha, S.S.; Aqilah, R.N.: Study of O3/S2O82-advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for removal of dye industrial effluents. In: MATEC Web of Conferences, vol. 255. (EDP Sciences), p. 03003 (2019)
dos Santos, A.J.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Sirés, I.; Brillas, E.: Use of Pt and boron-doped diamond anodes in the electrochemical advanced oxidation of ponceau SS diazo dye in acidic sulfate medium. ChemElectroChem 5, 685–693 (2018)
Beluci, N.D.C.L.; Mateus, G.A.P.; Miyashiro, C.S.; Homem, N.C.; Gomes, R.G.; Fagundes-Klen, M.R.; Bergamasco, R.; Vieira, A.M.S.: Hybrid treatment of coagulation/flocculation process followed by ultrafiltration in TIO2-modified membranes to improve the removal of reactive black 5 dye. Sci. Total Environ. 664, 222–229 (2019)
Fu, J.; Xin, Q.; Wu, X.; Chen, Z.; Yan, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Xu, Q.: Selective adsorption and separation of organic dyes from aqueous solution on polydopamine microspheres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 461, 292–304 (2016)
Fu, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Han, R.; Xu, Q.: Adsorption of methylene blue by a high-efficiency adsorbent (polydopamine microspheres): kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and mechanism analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 259, 53–61 (2015)
Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Fu, J.: Large-scale fabrication of N-doped porous carbon nanosheets for dye adsorption and supercapacitor applications. Nanoscale 11, 8785–8797 (2019)
Mahmoodi, N.M.; Oveisi, M.; Bakhtiari, M.; Hayati, B.; Shekarchi, A.A.; Bagheri, A.; Rahimi, S.: Environmentally friendly ultrasound-assisted synthesis of magnetic zeolitic imidazolate framework—graphene oxide nanocomposites and pollutant removal from water. J. Mol. Liq. 282, 115–130 (2019)
Wang, Y.; Lin, C.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Fu, J.: Magnetic hollow poly(cyclotriphosphazene-co-4,4′-sulfonyldiphenol)-Fe3O4 hybrid nanocapsules for adsorbing Safranine T and catalytic oxidation of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 556, 278–291 (2019)
Fu, J.; Chen, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Q.: Hollow poly(cyclotriphosphazene-co-phloroglucinol) microspheres: an effective and selective adsorbent for the removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 281, 42–52 (2015)
Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Han, R.; Xu, Q.: Adsorption of methylene blue onto poly(cyclotriphosphazene-co-4,4′-sulfonyldiphenol) nanotubes: kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 273, 263–271 (2014)
Li, P.; Chen, X.; Zeng, X.; Zeng, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Xie, T.; Zhang, Y.: Utilization of waste biomass (kitchen waste) hydrolysis residue as adsorbent for dye removal: kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 185, 971–985 (2018)
Baysal, M.; Bilge, K.; Yılmaz, B.; Papila, M.; Yürüm, Y.: Preparation of high surface area activated carbon from waste-biomass of sunflower piths: kinetics and equilibrium studies on the dye removal. J. Envir. Chem. Eng. 6, 1702–1713 (2018)
Ahmed, M.J.: Application of agricultural based activated carbons by microwave and conventional activations for basic dye adsorption: review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 4, 89–99 (2016)
Marković, S.; Stanković, A.; Lopičić, Z.; Lazarević, S.; Stojanović, M.; Uskoković, D.: Application of raw peach shell particles for removal of methylene blue. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 3, 716–724 (2015)
Namasivayam, C.; Kavitha, D.: Removal of Congo Red from water by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from coir pith, an agricultural solid waste. Dyes Pigments 54, 47–58 (2002)
Sharma, A.; Siddiqui, Z.M.; Dhar, S.; Mehta, P.; Pathania, D.: Adsorptive removal of congo red dye (CR) from aqueous solution by Cornulaca monacantha stem and biomass-based activated carbon: isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics. Sep. Sci. Technol. 54, 916–929 (2019)
Al-Anber, Z.A.; Al-Anber, M.A.; Matouq, M.; Al-Ayed, O.; Omari, N.M.: Defatted Jojoba for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution: thermodynamic and kinetic studies. Desalination 276, 169–174 (2011)
Ahmad, R.; Kumar, R.: Adsorptive removal of congo red dye from aqueous solution using bael shell carbon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 1628–1633 (2010)
Attia, A.A.M.; Shouman, M.A.H.; Khedr, S.A.A.; Hassan, N.A.: Fixed-bed column studies for the removal of Congo red using Simmondsia chinesis (jojoba) and coated with Chitosan. Indones. J. Chem. 18, 294–305 (2018)
Allawzi, M.; Abu-Arabi, M.K.; Al-Zoubi, H.S.; Tamimi, A.: Physicochemical characteristics and thermal stability of Jordanian jojoba oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 75, 57–62 (1998)
Allawzi, M.; Kandah, M.I.: Parametric study of biodiesel production from used soybean oil. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 110, 760–767 (2008)
Tawalbeh, M.; Allawzi, M.; Kandah, M.I.: Production of activated carbon from jojoba seed residue by chemical activation residue using a static bed reactor. J. Appl. Sci. 5, 482–487 (2005)
Abu-Arabi, M.K.; Allawzi, M.A.; Al-Zoubi, A.S.: Adsorption of phenol from aqueous solutions on jojoba nuts residue. Chem. Eng. Technol. Ind. Chem.-Plant Equip.-Process Eng.-Biotechnol. 30, 493–500 (2007)
Allawzi, M.; Al-Asheh, S.; Allaboun, H.; Borini, O.: Assessment of the natural jojoba residues as adsorbent for removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions. Desalin. Water Treat. 21, 60–65 (2010)
Abu-Arabi, M.K.; Allawzi, M.A.; Al-Zoubi, A.S.: Adsorption of phenol from aqueous solutions on jojoba nuts residue. Chem. Eng. Technol. 30, 493–500 (2007)
Al-Anber, M.A.; Al-Anber, Z.A.; Al-Momani, I.; Al-Momani, F.; Abu-Salem, Q.: The performance of defatted jojoba seeds for the removal of toxic high concentration of the aqueous ferric ion. Desalin. Water Treat. 52, 293–304 (2014)
Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G.: Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 34, 451–465 (1999)
Moon, H.; Kook Lee, W.: Intraparticle diffusion in liquid-phase adsorption of phenols with activated carbon in finite batch adsorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 96, 162–171 (1983)
Jarrah, N.; Mu’azu, N.D.; Zubair, M.; Al-Harthi, M.: Enhanced adsorptive performance of Cr(VI) onto layered double hydroxide-bentonite composite: isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Sep. Sci. Technol. 54, 1–13 (2019)
Sheindorf, C.; Rebhun, M.; Sheintuch, M.: A Freundlich-type multicomponent isotherm. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 79, 136–142 (1981)
Ojo, T.A.; Ojedokun, A.T.; Bello, O.S.: Functionalization of powdered walnut shell with orthophosphoric acid for Congo red dye removal. Part. Sci. Technol. 37, 74–85 (2019)
Kaur, S.; Rani, S.; Mahajan, R.K.: Adsorption kinetics for the removal of hazardous dye congo red by biowaste materials as adsorbents. J. Chem. 2013, 1–12 (2012)
Al-Harthi, M.A.; Zubair, M.: Effect of modified graphene and microwave irradiation on the mechanical and thermal properties of P (S-co-MMA)/graphene nanocomposites. (Google Patents) (2016)
Blaisi, N.I.; Zubair, M.; Ali, S.; Kazeem, T.S.; Manzar, M.S.; Al-Kutti, W.; Al Harthi, M.A.: Date palm ash-MgAl-layered double hydroxide composite: sustainable adsorbent for effective removal of methyl orange and eriochrome black-T from aqueous phase. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25, 34319–34331 (2018)
Mu’azu, N.D.; Jarrah, N.; Kazeem, T.S.; Zubair, M.; Al-Harthi, M.: Bentonite-layered double hydroxide composite for enhanced aqueous adsorption of Eriochrome Black T. Appl. Clay Sci. 161, 23–34 (2018)
Fu, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yan, R.; Xu, Q.: Highly-efficient and selective adsorption of anionic dyes onto hollow polymer microcapsules having a high surface-density of amino groups: isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics and mechanism. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 542, 123–135 (2019)
Aly-Eldeen, M.A.; El-Sayed, A.A.M.; Salem, D.M.S.A.; El Zokm, G.M.: The uptake of Eriochrome Black T dye from aqueous solutions utilizing waste activated sludge: adsorption process optimization using factorial design. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 44, 179–186 (2018)
Zubair, M.; Jarrah, N.; Manzar, M.S.; Al-Harthi, M.; Daud, M.; Mu’azu, N.D.; Haladu, S.A.: Adsorption of eriochrome black T from aqueous phase on MgAl-, CoAl- and NiFe- calcined layered double hydroxides: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J. Mol. Liq. 230, 344–352 (2017)
Lafi, R.; Montasser, I.; Hafiane, A.: Adsorption of congo red dye from aqueous solutions by prepared activated carbon with oxygen-containing functional groups and its regeneration. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 37, 160–181 (2019)
Saleh, T.A.; Muhammad, A.M.; Ali, S.A.: Synthesis of hydrophobic cross-linked polyzwitterionic acid for simultaneous sorption of Eriochrome black T and chromium ions from binary hazardous waters. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 468, 324–333 (2016)
Ali, S.A.; Rachman, I.B.; Saleh, T.A.: Simultaneous trapping of Cr(III) and organic dyes by a pH-responsive resin containing zwitterionic aminomethylphosphonate ligands and hydrophobic pendants. Chem. Eng. J. 330, 663–674 (2017)
Moeinpour, F.; Alimoradi, A.; Kazemi, M.: Efficient removal of Eriochrome black-T from aqueous solution using NiFe 2 O 4 magnetic nanoparticles. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 12, 112 (2014)
Khalid, A.; Zubair, M.: A comparative study on the adsorption of Eriochrome Black T dye from aqueous solution on graphene and acid-modified graphene. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43, 2167–2179 (2018)
Lei, C.; Pi, M.; Xu, D.; Jiang, C.; Cheng, B.: Fabrication of hierarchical porous ZnO–Al2O3 microspheres with enhanced adsorption performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 426, 360–368 (2017)
Bao, Y.; Qin, M.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H.: Facile fabrication of porous NiCo2O4 nanosheets with high adsorption performance toward Congo red. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 124, 289–295 (2019)
Lei, C.; Zhu, X.; Le, Y.; Zhu, B.; Yu, J.; Ho, W.: Hierarchically porous NiO–Al2O3 nanocomposite with enhanced Congo red adsorption in water. RSC Adv. 6, 10272–10279 (2016)
Yasin, Y.; Malek, A.H.A.; Sumari, S.M.: Adsorption of eriochrome black dye from aqueous solution onto anionic layered double hydroxides. Orient. J. Chem. 26, 1293 (2010)
Zheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Cheng, B.; You, W.; Ho, W.; Tang, H.: Hierarchical porous Al2O3@ ZnO core-shell microfibres with excellent adsorption affinity for Congo red molecule. Appl. Surf. Sci. 473, 251–260 (2019)
Manzar, M.S.; Waheed, A.; Qazi, I.W.; Blaisi, N.I.; Ullah, N.: Synthesis of a novel epibromohydrin modified crosslinked polyamine resin for highly efficient removal of methyl orange and eriochrome black T. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 97, 424–432 (2019)
Lei, C.; Pi, M.; Jiang, C.; Cheng, B.; Yu, J.: Synthesis of hierarchical porous zinc oxide (ZnO) microspheres with highly efficient adsorption of Congo red. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 490, 242–251 (2017)
Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.: Different dye removal mechanisms between monodispersed and uniform hexagonal thin plate-like MgAl–CO32–LDH and its calcined product in efficient removal of Congo red from water. J. Alloys Compd. 673, 265–271 (2016)
Zhu, H.-Y.; Jiang, R.; Fu, Y.-Q.; Li, R.-R.; Yao, J.; Jiang, S.-T.: Novel multifunctional NiFe2O4/ZnO hybrids for dye removal by adsorption, photocatalysis and magnetic separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 369, 1–10 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University for funding our project titled ‘Production of Biodiesel from jojoba oil as a future alternative for renewable energy using nanoparticles metal oxide catalyst’ with Project No. of 2017-149-ENG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Zoubi, H., Zubair, M., Manzar, M.S. et al. Comparative Adsorption of Anionic Dyes (Eriochrome Black T and Congo Red) onto Jojoba Residues: Isotherm, Kinetics and Thermodynamic Studies. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 7275–7287 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04418-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04418-5