Abstract
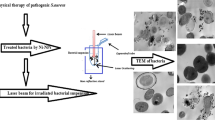
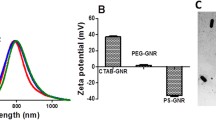
Nowadays, implant-related infections are considered as one of the major dangers for human health, and a novel method to ablate the related pathogens is therefore crucial. In this paper, potentials of PEGylated gold nanoparticles to load methylene blue and consequently enhance its effectiveness in photodynamic inactivation of Staphylococcus epidermidis (PTCC1114) were investigated. According to our experimental results, it was shown that PEGylated gold nanoparticles have the ability to load and preserve optical properties of methylene blue. Our studies demonstrated that photodynamic inactivation of the bacteria in an in vitro model using a red laser (630 nm and 100 mW/cm2) and methylene blue or methylene blue-PEGylated gold nanoparticles showed a superiority for the PEGylated gold nanoparticles conjugated with methylene blue. In fact, conjugation of MB with the PEGylated gold nanoparticles avoids dimer formation through preventing direct contact between MB and cellular or plasma components. Based on the results of this paper, PEGylated gold nanoparticles are proposed to improve the photodynamic inactivation of implant-related infections.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoci Jr., V.; Adams, C.S.; Parvizi, J.; Davidson, H.M.; Composto, R.J.; Freeman, T.A.; Wickstrom, E.; Ducheyne, P.; Jungkind, D.; Shapiro, I.M.; Hickok, N.J.: The inhibition of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation by vancomycin-modified titanium alloy and implications for the treatment of periprosthetic infection. Biomaterials 29(35), 4684–4690 (2008)
Turcheniuk, K.; Hage, C.H.; Spadavecchia, J.; Serrano, A.Y.; Larroulet, I.; Pesquera, A.; Zurutuza, A.; Pisfil, M.G.; Heliot, L.; Boukaert, J.; Boukherroub, R.: Plasmonic photothermal destruction of uropathogenic E. coli with reduced graphene oxide and core/shell nanocomposites of gold nanorods/reduced graphene oxide. J. Mater. Chem. B 3(3), 375–386 (2015)
Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R.: Antibacterial activity of graphene-based materials. J. Mater. Chem. B 4(43), 6892–6912 (2016)
Jijie, R.; Dumych, T.; Chengnan, L.; Bouckaert, J.; Turcheniuk, K.; Hage, C.H.; Heliot, L.; Cudennec, B.; Dumitrascu, N.; Boukherroub, R.; Szunerits, S.: Particle-based photodynamic therapy based on indocyanine green modified plasmonic nanostructures for inactivation of a Crohn’s disease-associated Escherichia coli strain. J. Mater. Chem. B 4(15), 2598–2605 (2016)
Jori, G.; Fabris, C.; Soncin, M.; Ferro, S.; Coppellotti, O.; Dei, D.; Fantetti, L.; Chiti, G.; Roncucci, G.: Photodynamic therapy in the treatment of microbial infections: basic principles and perspective applications. Lasers Surg. Med.: Off. J. Am. Soc. Laser Med. Surg. 38(5), 468–481 (2006)
Amini, B.; Kamali, M.; Salouti, M.; Yaghmaei, P.: Spectrophotometric colorimetric and visually detection of Pseudomonas aerugenosa ETA gene based gold nanoparticles DNA probe and endonuclease enzyme. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 199, 421–429 (2018)
Amini, A.; Kamali, M.; Amini, B.; Najafi, A.: Enhanced antibacterial activity of imipenem immobilized on surface of spherical and rod gold nanoparticles. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aaef4d
Amini, A.; Kamali, M.; Amini, B.; Njafi, A.; Narmani, A.; Hasani, L.; Rashidiani, J.; Kooshki, H.; Elahi, N.: Bio-barcode technology for detection of Staphylococcus aureus protein A based on gold and iron nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 124, 1256–1263 (2019)
Shahbazi, R.; Salouti, M.; Amini, B.; Jalilvand, A.; Naderlou, E.; Amini, A.; Shams, A.: Highly selective and sensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus with gold nanoparticle-based core–shell nano biosensor. Mol. Cell. Probes 41, 8–13 (2018)
Narmani, A.; Rezvani, M.; Farhood, B.; Darkhor, P.; Mohammadnejad, J.; Amini, B.; Refahi, S.; Abdi Goushbolagh, N.: Folic acid functionalized nanoparticles as pharmaceutical carrier in drug delivery systems. Drug Deliv. Res. 80, 404–424 (2019)
Roper, D.K.; Ahn, W.; Hoepfner, M.: Microscale heat transfer transduced by surface plasmon resonant gold nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 111(9), 3636–3641 (2007)
Norman, R.S.; Stone, J.W.; Gole, A.; Murphy, C.J.; Sabo-Attwood, T.L.: Targeted photothermal lysis of the pathogenic bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, with gold nanorods. Nano Lett. 8(1), 302–306 (2008)
Wang, S.; Singh, A.K.; Senapati, D.; Neely, A.; Yu, H.; Ray, P.C.: Rapid colorimetric identification and targeted photothermal lysis of Salmonella bacteria by using bioconjugated oval-shaped gold nanoparticles. Chem. Eur. J. 16(19), 5600–5606 (2010)
Hu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Saran, A.; Hou, S.; Wen, T.; Liu, W.; Ji, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wu, X.: Gold nanorods core/AgPt alloy nanodots shell: a novel potent antibacterial nanostructure. Nano Res. 6(11), 822–835 (2013)
Meeker, D.G.; Jenkins, S.V.; Miller, E.K.; Beenken, K.E.; Loughran, A.J.; Powless, A.; Muldoon, T.J.; Galanzha, E.I.; Zharov, V.P.; Smeltzer, M.S.; Chen, J.: Synergistic photothermal and antibiotic killing of biofilm-associated Staphylococcus aureus using targeted antibiotic-loaded gold nanoconstructs. ACS Infect. Dis. 2(4), 241–250 (2016)
Khlebtsov, B.N.; Tuchina, E.S.; Khanadeev, V.A.; Panfilova, E.V.; Petrov, P.O.; Tuchin, V.V.; Khlebtsov, N.G.: Enhanced photoinactivation of Staphylococcus aureus with nanocomposites containing plasmonic particles and hematoporphyrin. J. Biophotonics 6(4), 338–351 (2013)
Orth, K.; Beck, G.; Genze, F.; Ruck, A.: Methylene blue mediated photodynamic therapy in experimental colorectal tumors in mice. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 57(2–3), 186–192 (2000)
Kariminezhad, H.; Habibi, M.; Mirzababayi, N.: Nanosized ZSM-5 will improve photodynamic therapy using methylene blue. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 148, 107–112 (2015)
Harrison, E.; Hamilton, J.W.; Macias-Montero, M.; Dixon, D.: Peptide functionalized gold nanoparticles: the influence of pH on binding efficiency. Nanotechnology 28(29), 29560 (2017)
Hsiao, P.F.; Peng, S.; Tang, T.C.; Lin, S.Y.; Tsai, H.C.: Enhancing the in vivo transdermal delivery of gold nanoparticles using poly (ethylene glycol) and its oleylamine conjugate. Int. J. Nanomed. 11, 1867 (2016)
Zou, X.; Ying, E.; Dong, S.: Seed-mediated synthesis of branched gold nanoparticles with the assistance of citrate and their surface-enhanced Raman scattering properties. Nanotechnology 17(18), 4758 (2006)
Brewer, S.H.; Glomm, W.R.; Johnson, M.C.; Knag, M.K.; Franzen, S.: Probing BSA binding to citrate-coated gold nanoparticles and surfaces. Langmuir 21(20), 9303–9307 (2005)
Kumar, V.; Sharma, N.; Maitra, S.S.: In vitro and in vivo toxicity assessment of nanoparticles. Int. Nano Lett. 7(4), 243–256 (2017)
Pourali, P.; Badiee, S.H.; Manafi, S.; Noorani, T.; Rezaei, A.; Yahyaei, B.: Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by two bacterial and fungal strains, Bacillus cereus and Fusarium oxysporum, and assessment and comparison of their nanotoxicity in vitro by direct and indirect assays. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 29, 86–93 (2017)
Mohamed, M.M.; Fouad, S.A.; Elshoky, H.A.; Mohammed, G.M.; Salaheldin, T.A.: Antibacterial effect of gold nanoparticles against Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 5(1), 23–29 (2017)
Ergaieg, K.; Seux, R.: A comparative study of the photoinactivation of bacteria by meso-substituted cationic porphyrin, rose Bengal and methylene blue. Desalination 246(1–3), 353–362 (2009)
Kariminezhad, H.; Amani, H.; Khanbabaie, R.; Biglarnia, M.: Photodynamic inactivation of E. coli PTCC 1276 using light emitting diodes: application of Rose Bengal and methylene blue as two simple models. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 182(3), 967–977 (2017)
Souza, R.C.; Junqueira, J.C.; Rossoni, R.D.; Pereira, C.A.; Munin, E.; Jorge, A.O.: Comparison of the photodynamic fungicidal efficacy of methylene blue, toluidine blue, malachite green and low-power laser irradiation alone against Candida albicans. Lasers Med. Sci. 25(3), 385–389 (2010)
Tardivo, J.P.; Del Giglio, A.; de Oliveira, C.S.; Gabrielli, D.S.; Junqueira, H.C.; Tada, D.B.; Severino, D.; de Fatima Turchiello, R.; Baptista, M.S.: Methylene blue in photodynamic therapy: from basic mechanisms to clinical applications. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2(3), 175–191 (2005)
Yu, J.; Hsu, C.H.; Huang, C.C.; Chang, P.Y.: Development of therapeutic Au–methylene blue nanoparticles for targeted photodynamic therapy of cervical cancer cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7(1), 432–441 (2014)
Khan, S.; Alam, F.; Azam, A.; Khan, A.U.: Gold nanoparticles enhance methylene blue-induced photodynamic therapy: a novel therapeutic approach to inhibit Candida albicans biofilm. Int. J. Nanomed. 7, 3245 (2012)
Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Xu, H.; Tang, W.; Kopelman, R.; Philbert, M.A.; Xi, C.: Eradication of bacteria in suspension and biofilms using methylene blue-loaded dynamic nanoplatforms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53(7), 3042–3048 (2009)
Tuite, E.M.; Kelly, J.M.: New trends in photobiology: photochemical interactions of methylene blue and analogues with DNA and other biological substrates. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 21(2–3), 103–124 (1993)
Usacheva, M.N.; Teichert, M.C.; Biel, M.A.: Comparison of the methylene blue and toluidine blue photobactericidal efficacy against gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. Lasers Surg. Med.: Off. J. Am. Soc. Laser Med. Surg. 29(2), 165–173 (2001)
Daniel, M.C.; Astruc, D.: Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 104(1), 293–346 (2004)
Wang, C.; Singh, P.; Kim, Y.J.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Myagmarjav, D.; Wang, D.; Jin, C.G.; Yang, D.C.: Characterization and antimicrobial application of biosynthesized gold and silver nanoparticles by using Microbacterium resistens. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 44(7), 1714–1721 (2016)
Lipovsky, A.; Nitzan, Y.; Gedanken, A.; Lubart, R.: Visible light-induced killing of bacteria as a function of wavelength: implication for wound healing. Lasers Surg. Med. 42(6), 467–472 (2010)
Usacheva, M.N.; Teichert, M.C.; Biel, M.A.: The role of the methylene blue and toluidine blue monomers and dimers in the photoinactivation of bacteria. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 71(1–3), 87–98 (2003)
Tang, W.; Xu, H.; Park, E.J.; Philbert, M.A.; Kopelman, R.: Encapsulation of methylene blue in polyacrylamide nanoparticle platforms protects its photodynamic effectiveness. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 369(2), 579–583 (2008)
Allesen-Holm, M.; Barken, K.B.; Yang, L.; Klausen, M.; Webb, J.S.; Kjelleberg, S.; Molin, S.; Givskov, M.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.: A characterization of DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures and biofilms. Mol. Microbiol. 59(4), 1114–1128 (2006)
de Bentzmann, S.; Aurouze, M.; Ball, G.; Filloux, A.: FppA, a novel Pseudomonas aeruginosa prepilin peptidase involved in assembly of type IVb pili. J. Bacteriol. 188(13), 4851–4860 (2006)
Giltner, C.L.; van Schaik, E.J.; Audette, G.F.; Kao, D.; Hodges, R.S.; Hassett, D.J.; Irvin, R.T.: The Pseudomonas aeruginosa type IV pilin receptor binding domain functions as an adhesin for both biotic and abiotic surfaces. Mol. Microbiol. 59(4), 1083–1096 (2006)
Jenkins, A.T.A.; Buckling, A.; McGhee, M.; Ffrench-Constant, R.H.: Surface plasmon resonance shows that type IV pili are important in surface attachment by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. R. Soc. Interface 2(3), 255–259 (2005)
Hamblin, M.R.; Zahra, T.; Contag, C.H.; McManus, A.T.; Hasan, T.: Optical monitoring and treatment of potentially lethal wound infections in vivo. J. Infect. Dis. 187(11), 1717–1726 (2003)
Lambrechts, S.A.G.; Demidova, T.N.; Aalders, M.C.; Hasan, T.; Hamblin, M.R.: Photodynamic therapy for Staphylococcus aureus infected burn wounds in mice. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 4(7), 503–509 (2005)
Zolfaghari, P.S.; Packer, S.; Singer, M.; Nair, S.P.; Bennett, J.; Street, C.; Wilson, M.: In vivo killing of Staphylococcus aureus using a light-activated antimicrobial agent. BMC Microbiol. 9(1), 27 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Babol Noshirvani University of Technology [Grant No. BNUT/370542/97]. Also, authors thank Armina Company for their supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kariminezhad, H., Mousapour, M., Khorram, S. et al. Photodynamic Inactivation of Staphylococcus epidermidis: Application of PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 71–79 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04248-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04248-0