Abstract
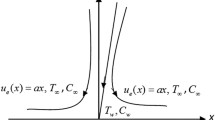
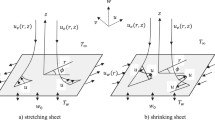
The stagnation-point flow towards a permeable linearly stretching/shrinking wall immersed in copper/water nanofluids is treated numerically using Runge–Kutta–Fehlberg Method (RKF45). A realistic contemporary nanofluids model is employed to modify the involved thermo-physical properties including viscosity and thermal conductivity. This new model enables us to specifically explore the effects of nano particles size and heat transfer direction (say cooling or heating) on the evolution of velocity and temperature profiles as well as on the main quantities of engineering interest. In this respect, it is shown how these effects play significant roles in the evolution of skin friction coefficient and convective heat transfer coefficient. It should be pointed out that these effects are obscure respecting the classic modeling of nanofluids. It is also found that dual solutions (say upper and lower) appear and a stability analysis revealed that the solutions associated with the lower branch are not likely to reside in the actual physics.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \( \rho \) :
-
Density
- \( \phi \) :
-
Volumetric concentration
- \( C_{\text{p}} \) :
-
Specific heat capacity
- \( k \) :
-
Thermal conductivity
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number
- T :
-
Temperature
- \( N_{\text{A}} \) :
-
Avogadro number
- \( T_{\text{fr}} \) :
-
The freeing point temperature
- \( k_{\text{Bo}} \) :
-
Boltzmann constant
- \( \mu \) :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- d :
-
Diameter
- M :
-
Molecular weight
- \( \rho_{\text{bfo}} \) :
-
Density of the base fluid
- \( \upsilon \) :
-
Kinematic viscosity
References
Schlichting, H.; Gersten, K.: Boundary Layer Theory. Springer, New York (2000)
White, F.M.: Viscous Fluid Flow. McGraw-Hill, New York (2006)
Pop, I.; Ingham, D.B.: Convective Heat Transfer: Mathematical and Computational Modeling of Viscous Fluids and Porous Media. Pergamon, Oxford (2001)
Bejan, A.: Convection Heat Transfer, 4th edn. Wiley, New York (2013)
Crane, L.J.: Flow past a stretching plate. J. Appl. Math. Phys. (ZAMP) 21, 645–647 (1970)
Bachok, N.; Ishak, A.: Similarity solutions for the stagnation-point flow and heat transfer over a nonlinearly stretching/shrinking sheet. Sains Malays. 40(11), 1297–1300 (2011)
Kolomenskiy, D.; Moffatt, H.K.: Similarity solutions for unsteady stagnation point flow. J. Fluid Mech. 711, 394–410 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2012.39
Seddighi Chaharborj, S.; Ismail, F.; Gheisari, Y.; Seddighi Chaharborj, R.; Abu Bakar, M.R.; Abdul Majid, Z.: Lie group analysis and similarity solutions for mixed convection boundary layers in the stagnation-point flow toward a stretching vertical sheet. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2013, 269420 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/269420
Farooq, M.; ul ainAnzar, Q.; Hayat, T.; Ijaz Khan, M.; Anjum, A.: Local similar solution of MHD stagnation point flow in Carreau fluid over a non-linear stretched surface with double stratified medium. Results Phys. 7, 3078–3089 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2017.08.019
Subba, R.; Gorla, R.; Dakappagari, V.; Pop, I.: Boundary layer flow at a three-dimensional stagnation point in power-law non-Newtonian fluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 14, 408–412 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0142-727X(93)90015-F
Ahmad, M.; Sajid, M.; Hayat, T.; Ahmad, I.: On numerical and approximate solutions for stagnation point flow involving third order fluid. AIP Adv. 5, 067138 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4922878
Bhattacharyya, K.: Boundary layer stagnation-point flow of casson fluid and heat transfer towards a shrinking/stretching sheet. Front. Heat Mass Transf. (FHMT) 4, 023003 (2013)
Hayat, T.; Farooq, M.; Alsaedi, A.; Iqbal, Z.: Melting heat transfer in the stagnation point flow of Powell–Eyring fluid. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 27(4), 761–766 (2013)
Yasin, M.H.M.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I.: MHD stagnation-point flow and heat transfer with effects of viscous dissipation, Joule heating and partial velocity slip. Sci. Rep. 5, 17848 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17848
Buongiorno, J.: Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 128, 240–250 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2150834
Najib, N.; Bachok, N.; Arifin, N.M.; Ali, F.M.: Stability analysis of stagnation-point flow in a nanofluid over a stretching/shrinking sheet with second-order slip, Soret and Dufour effects: a revised model. Appl. Sci. 8, 642 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/app8040642
Jafarimoghaddam, A.: Closed form analytic solutions to heat and mass transfer characteristics of wall jet flow of nanofluids. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 4, 175–184 (2017)
Hamad, M.A.A.; Ferdows, M.: Similarity solution of boundary layer stagnation-point flow towards a heated porous stretching sheet saturated with a nanofluid with heat absorption/generation and suction/blowing: a Lie group analysis. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 17, 132–140 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2011.02.024
Mustafa, M.; Hayat, T.; Pop, I.; Asghar, S.; Obaidat, S.: Stagnation-point flow of a nanofluid towards a stretching sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 54, 5588–5594 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2011.07.021
Hayat, T.; Ijaz, M.; Qayyum, S.; Ayub, M.; Alsaedi, A.: Mixed convective stagnation point flow of nanofluid with Darcy–Fochheimer relation and partial slip. Results Phys. 9, 771–778 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2018.02.073
Mabood, F.; Pochai, N.; Shateyi, S.: “Stagnation point flow of nanofluid over a moving plate with convective boundary condition and magnetohydrodynamics. J. Eng. 2016, 5874864 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5874864
Shafie, S.; Kasim, A.R.M.; Salleh, M.Z.: Radiation effect on MHD stagnation-point flow of a nanofluid over a nonlinear stretching sheet with convective boundary condition. J. Mol. Liq. 221, 1097–1103 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1615/heattransres.2016007840
Abdollahzadeh, M.; Sedighi, A.A.; Esmailpour, M.: Stagnation point flow of nanofluids towards stretching sheet through a porous medium with heat generation. J. Nanofluids 7, 149–155 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1166/jon.2018.1431
Sharma, B.; Kumar, S.; Paswan, M.: Numerical investigation of MHD stagnation-point flow and heat transfer of sodium alginate non-Newtonian nanofluid. Nonlinear Eng. 8, 179–192 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1515/nleng-2018-0044
Roşca, A.V.; Roşca, N.C.; Pop, I.: Stagnation point flow of a nanofluid past a non-aligned stretching/shrinking sheet with a second-order slip velocity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 29(2), 738–762 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1108/HFF-05-2018-0201
Abbas, N.; Saleem, S.; Nadeem, S.; Alderremy, A.A.; Khan, A.U.: On stagnation point flow of a micro polar nanofluid past a circular cylinder with velocity and thermal slip. Results Phys. 9, 1224–1232 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2018.04.017
Pop, I.; Roşca, N.C.; Roşca, A.V.: MHD stagnation-point flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid over a stretching/shrinking sheet with melting, convective heat transfer and second-order slip. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 28(9), 2089–2110 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1108/HFF-12-2017-0488
Jusoh, R.; Nazar, M.R.: MHD stagnation point flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid over a permeable nonlinear stretching/shrinking sheet with viscous dissipation effect. AIP Conf. Proc. 1940, 020125 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5028040
Mahatha, B.K.; Nandkeolyar, R.; Nagaraju, G.; Das, M.: MHD stagnation point flow of a nanofluid with velocity slip, non-linear radiation and Newtonian heating. Procedia Eng. 127, 1010–1017 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2015.11.450
Mabood, F.; Shateyi, S.; Rashidi, M.M.; Momoniat, E.; Freidoonimehr, N.: MHD stagnation point flow heat and mass transfer of nanofluids in porous medium with radiation, viscous dissipation and chemical reaction. Adv. Powder Technol. 27, 742–749 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2016.02.033
Zaib, A.; Bhattacharyya, K.; Urooj, S.A.; Shafie, S.: Dual solutions of an unsteady magnetohydrodynamic stagnation-point flow of a nanofluid with heat and mass transfer in the presence of thermophoresis. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process. Mech. Eng. 232, 155–164 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954408916686626
Rauf, A.; Shehzad, S.A.; Hayat, T.; Meraj, M.A.; Alsaedi, A.: MHD stagnation point flow of micro nanofluid towards a shrinking sheet with convective and zero mass flux conditions. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 65, 155–162 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1515/bpasts-2017-0019
Ibrahim, W.; Makinde, O.D.: magnetohydrodynamic stagnation point flow and heat transfer of casson nanofluid past a stretching sheet with slip and convective boundary condition. J. Aerosp. Eng. 29, 04015037 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)AS.1943-5525.0000529
Hamid, R.A.; Nazar, R.; Pop, I.: Non-alignment stagnation point flow of a nanofluid past a permeable stretching/shrinking sheet: Buongiorno’s model. Sci. Rep. 5, 14640 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14640
Corcione, M.: Empirical correlating equations for predicting the effective thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of nanofluids. Energy Convers. Manag. 52, 789–793 (2011)
Li, Q.; Xuan, Y.: Convective heat transfer and flow characteristics of Cu-water nanofluid. Sci. China Ser. E-Technol. Sci. 45, 408 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1360/02ye9047
Khoshvaght-Aliabadi, M.; Hormozi, F.; Zamzamian, A.: Self-similar analysis of fluid flow, heat, and mass transfer at orthogonal nanofluid impingement onto a flat surface. Heat Mass Transf. 51, 423 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-014-1422-1
El-Maghlany, W.M.; Hanafy, A.A.; Hassan, A.A.; El-Magid, M.A.: Experimental study of Cu–water nanofluid heat transfer and pressure drop in a horizontal double-tube heat exchanger. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 78, 100–111 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2016.05.015
Khoshvaght-Aliabadi, M.; Alizadeh, A.: An experimental study of Cu–water nanofluid flow inside serpentine tubes with variable straight-section lengths. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 61, 1–11 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2014.09.014
Myers, T.G.; Ribera, H.; Cregan, V.: Does mathematics contribute to the nanofluid debate? Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 111, 279–288 (2017)
Jafarimoghaddam, A.; Aberoumand, H.; Aberoumand, S.; Abbasian Arani, A.A.; Habibollahzade, A.: MHD wedge flow of nanofluids with an analytic solution to an especial case by Lambert W-function and homotopy perturbation method. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 20, 1515–1530 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2017.11.002
Das, R.; Mishra, S.C.; Ajith, M.; Uppaluri, R.: An inverse analysis of a transient 2-D conduction–radiation problem using the lattice Boltzmann method and the finite volume method coupled with the genetic algorithm. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 109, 2060–2077 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jqsrt.2008.01.011
Das, R.: Feasibility study of different materials for attaining similar temperature distributions in a fin with variable properties. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process. Mech. Eng. 230, 292–303 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954408914548742
Das, R.: A simulated annealing-based inverse computational fluid dynamics model for unknown parameter estimation in fluid flow problem. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 26(9–10), 499–513 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1080/10618562.2011.632375
Jafarimoghaddam, A.: The magnetohydrodynamic wall jets: techniques for rendering similar and perturbative non-similar solutions. Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 75, 44–57 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechflu.2018.12.007
Jafarimoghaddam, A.; Pop, I.: Numerical modeling of Glauert type exponentially decaying wall jet flows of nanofluids using Tiwari and Das’ nanofluid model. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 29(3), 1010–1038 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1108/HFF-08-2018-0437
Jafarimoghaddam, A.; Shafizadeh, F.: Numerical modeling and spatial stability analysis of the wall jet flow of nanofluids with thermophoresis and brownian effects. Propul. Power Res. 8(3), 210–220 (2019)
Funding
No funding was received for this submission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no competing interest of any kind within this submission.
Additional information
Previously at the Department of Aerospace Engineering, K.N. Toosi University of Technology, Tehran, Iran.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jafarimoghaddam, A. Numerical Analysis of the Nanofluids Flow Near the Stagnation Point over a Permeable Stretching/Shrinking Wall: A New Modeling. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 1001–1015 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04205-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04205-x