Abstract
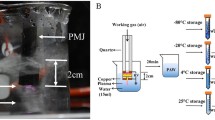
In this study, nonthermal atmospheric pressure plasma (NTAPP) method was performed for the sterilization of natural rose water which has a great potential as drug and food additive. NTAPP is applied to rose water containing mesophilic aerobic bacteria, mold and yeast. Experiments were carried out at a voltage of 500 V, a rotating speed of 500 rpm and a plasma power of 100 W. The effect of various plasma treatment times (15, 30 and 45 s) on the inactivation of total viable (aerobic count), mold and yeast was evaluated. Scanning electron microscopy images showed that the microorganism population in rose water was reduced after plasma treatment for 45 s. After 45 s of plasma treatment, inactivation of mesophilic aerobic bacteria, mold and yeast cells are decreased ~ 70%. This sterilization effect may be associated with cell death, which may be attributed to oxidative stress and other damage effects caused by the applied plasma. After sterilization process, the composition of volatile oils obtained from rose water samples was detected using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. The chemical composition of rose water before and after plasma sterilization was evaluated by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marsit, N.M.; Sidney, L.E.; Branch, M.J.; Wilson, S.L.; Hopkinson, A.: Terminal sterilization: conventional methods versus emerging cold atmospheric pressure plasma technology for non-viable biological tissues. Plasma Process Polym. 14(1600134), 1–17 (2017)
Zhang, Q.; Ma, R.; Tian, Y.; Su, B.; Wang, K.; Yu, S.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J.: Sterilization efficiency of a novel electrochemical disinfectant against Staphylococcus aureus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50(6), 3184–3192 (2016)
Rutala, W.A.; Weber, D.J.: Disinfection and sterilization in health care facilities: an overview and current issues. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 30, 609–637 (2016)
Colagar, A.H.; Alavi, O.; Motallebi, S.; Sohbatzadeh, E.: Decontamination of Streptococcus pyogenes and Escherichia coli from solid surfaces by singlet and triplet atmospheric pressure plasma jet arrays. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 41, 2139–2145 (2016)
Akishev, Y.; Grushin, M.; Karalnik, V.; Trushkin, N.; Kholodenko, V.; Chugunov, V.; Kobzev, E.; Zhirkova, N.; Irkhina, I.; Kireev, G.: Atmospheric-pressure, nonthermal plasma sterilization of microorganisms in liquids and on surfaces. Pure Appl. Chem. 80, 1953–1969 (2008)
Kulaga, E.; Ploux, L.; Roucoules, V.: Effect of ageing and sterilization on plasma multilayer system. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 116, 1–13 (2015)
Gucker, S.M.N.: Plasma discharges in gas bubbles in liquid water: breakdown mechanisms and resultant chemistry (Ph.D. Thesis). The University of Michigan, Nuclear Engineering and Radiological Sciences, USA, pp. 271 (2015)
Gils, C.A.J.; Hofmann, S.; Boekema, B.K.H.L.; Brandenburg, R.; Bruggeman, P.J.: Mechanisms of bacterial inactivation in the liquid phase induced by a remote RF cold atmospheric pressure plasma jet. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 46(175203), 1–14 (2013)
Scholtz, V.; Pazlarova, J.; Souskova, H.; Khun, J.; Julak, J.: Nonthermal plasma—a tool for decontamination and disinfection. Biotechnol. Adv. 33, 1108–1119 (2015)
Liao, X.; Liu, D.; Xiang, Q.; Ahn, J.; Chen, S.; Ye, X.; Ding, T.: Inactivation mechanisms of non-thermal plasma on microbes: a review. Food Control 75, 83–91 (2017)
Moreau, M.; Orange, N.; Feuilloley, M.G.J.: Non-thermal plasma technologies: new tools for bio-decontamination. Biotechnol. Adv. 26, 610–617 (2008)
Locke, B.R.; Sato, M.; Sunka, P.; Hoffmann, M.R.; Chang, J.S.: Electrohydraulic discharge and nonthermal plasma for water treatment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 45, 882–905 (2006)
Guimin, X.; Guanjun, Z.; Xingmin, S.; Yue, M.; Ning, W.; Yuan, L.: Bacteria inactivation using DBD plasma jet in atmospheric pressure argon. Plasma Sci. Technol. 11, 83–88 (2009)
Lee, J.; Jo, K.; Lim, Y.; Jeon, H.J.; Choe, J.H.; Jo, C.; Jung, S.: The use of atmospheric pressure plasma as a curing process for canned ground ham. Food Chem. 240, 430–436 (2018)
Laroussi, M.: Sterilization of contaminated matter with an atmospheric pressure plasma. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 24, 1188–1191 (1996)
Chandana, L.; Sangeetha, C.J.; Shashidhar, T.; Subrahmanyam, Ch: Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma jet for the bacterial inactivation in an aqueous medium. Sci. Total Environ. 640–641, 493–500 (2018)
Korachi, M.; Gurol, C.; Aslan, N.: Atmospheric plasma discharge sterilization effects on whole cell fatty acid profiles of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Electrostat. 68, 508–512 (2010)
Xu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Ma, R.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.: Effect of plasma activated water on the postharvest quality of button mushrooms, Agaricus bisporus. Food Chem. 197, 436–444 (2016)
Liu, F.; Sun, P.; Bai, N.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wei, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, W.; Becker, K.; Fang, J.: Inactivation of bacteria in an aqueous environment by a direct-current, cold-atmospheric-pressure air plasma microjet. Plasma Process. Polym. 7, 231–236 (2010)
Zahid, K.; Ahmed, M.; Khan, F.: Phytochemical screening, antioxidant activity, total phenolic and total flavonoid contents of seven local varieties of Rosa indica L. Nat. Prod. Res. 32, 1239–1243 (2018)
Agarwal, S.G.; Aruna, G.; Kapahi, B.K.; Baleshwar, M.; Thappa, R.K.; Suri, O.P.: Chemical composition of rose water volatiles. J. Essent. Oil Res. 17, 265–267 (2005)
Mahboubifar, M.; Shahabipour, S.; Javidnia, K.: Evaluation of the valuable oxygenated components in Iranian rose water. Int. J. Chemtech Res. 6, 4782–4788 (2014)
Haj, Ammar A.; Lebrihi, A.; Mathieu, F.; Romdhane, M.; Zagrouba, F.: Chemical composition and in vitro antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Citrus aurantium L. flowers essential oil (Neroli oil). Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 15, 1034–1040 (2012)
Ercisli, S.: Rose (Rosa spp.) germplasm resources of Turkey. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 52, 787–795 (2005)
Shimizu, S.; Barczyk, S.; Rettberg, P.; Shimizu, T.; Klaempfl, T.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Hoeschen, T.; Linsmeier, C.; Weber, P.; Morfill, G.E.; Thomas, H.M.: Cold atmospheric plasma—a new technology for spacecraft component decontamination. Planet. Space Sci. 90, 60–71 (2014)
Baydar, H.; Kuleasan, H.; Kara, N.; Secilmis-Canbay, H.; Kineci, S.: The effects of pasteurization, ultraviolet radiation and chemiclal preservatives on microbial spoilage and scent composition of rose water. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 16, 151–160 (2013)
Seçilmiş-Canbay, H.: Effectiveness of liquid–liquid extraction, solid phase extraction, and headspace technique for determination of some volatile water-soluble compounds of rose aromatic water. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 1–7 (2017)
Ryu, Y.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Shim, G.B.; Uhm, H.S.; Park, G.; Choi, E.H.: Effects of background fluid on the efficiency of inactivating yeast with non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma. Plos One 8(6), e66231 (2013)
Han, L.; Patil, S.; Boehm, D.; Milosavljevic, V.; Cullen, P.J.; Bourke, P.: Mechanisms of inactivation by high-voltage atmospheric cold plasma differ for Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 82, 450–458 (2016)
Yao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, K.; Yan, Z.; Cai, S.; Yang, C.; Sand, W.; Dai, Y.; Yang, H.: Study on inactivation of Escherichia coli by double dielectric barrier discharge. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/tps.2018.2837640
Lee, M.H.; Park, B.J.; Jin, S.C.; Kim, D.; Han, I.; Kim, J.; Hyun, S.O.; Chung, K.H.; Par, J.C.: Removal and sterilization of biofilms and planktonic bacteria by microwave-induced argon plasma at atmospheric pressure. New J. Phys. 11(115022), 1–11 (2009)
Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wandell, R.; Bresch, S.; Wang, H.; Locke, B.R.; Tang, Y.: Synergistic 1,4-dioxane removal by non-thermal plasma followed by biodegradation. Chem. Eng. J. 361, 519–527 (2019)
Fukuda, S., Kawasaki, Y., Izawa, S.: Ferrous chloride and ferrous sulfate improve the fungicidal efficacy of cold atmospheric argon plasma on melanized Aureobasidium pullulans. J. Biosci. Bioeng. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2018.12.008
Chandana, L.; Sangeetha, C.J.; Shashidhar, T.; Subrahmanyam, Ch: Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma jet for the bacterial inactivation in an aqueous medium. Sci. Total Environ. 640–641, 493–500 (2018)
Maniruzzaman, M.: Investigation of plasma-treated water for plant growth. Deakin University, Doctor Thesis of Philosophy (2018)
Dai, X.J.; Corr, C.S.; Ponraj, S.B.; Maniruzzaman, M.; Ambujakshan, A.T.; Chen, Z.; Kviz, L.; Lovett, R.; Rajmohan, G.D.; de Celis, D.R.; Wright, M.L.; Lamb, P.R.; Krasik, Y.E.; Graves, D.B.; Graham, W.G.; d’Agostino, R.; Wang, X.: Efficient and selectable production of reactive species using a nanosecond pulsed discharge in gas bubbles in liquid. Plasma Process. Polym. 13, 306–310 (2016)
Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Gao, J.: Low temperature argon plasma sterilization effect on Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its mechanisms. J. Electrostat. 67, 646–651 (2009)
Boudam, M.K.; Moisan, M.; Saoudi, B.; Popovici, C.; Gherardi, N.; Massines, F.: Bacterial spore inactivation by atmospheric-pressure plasmas in the presence or absence of UV photons as obtained with the same gas mixture. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 39, 3494–3507 (2006)
Pérez-López, A.J.; Saura, D.; Lorente, J.; Carbonell-Barrachina, A.A.: Limonene, linalool, α-terpineol, and terpinen-4-ol as quality control parameters in mandarin juice processing. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 222, 281–285 (2006)
Alves Filho, E.G.; Rodrigues, T.H.S.; Fernandes, F.A.N.; de Brito, E.S.; Cullen, P.J.; Frias, J.M.; Bourke, P.; Cavalcante, R.S.; Almeida, F.D.L.; Rodrigues, S.: An untargeted chemometric evaluation of plasma and ozone processing effect on volatile compounds in orange juice. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2017.10.001
Bayrak, A.; Akgül, A.: Volatile oil composition of Turkish rose (Rosa damascena). J. Sci. Food Agric. 64, 441–448 (1994)
Canbay, H.S.; Bardakçı, B.: Determination of fatty acid, C, H, N and trace element composition in grape seed by GC/MS, FTIR, elemental analyzer and ICP/OES. SDU J. Sci. (E-Journal) 6(2), 140–148 (2011)
Haghighi, B.; Tabrizi, M.A.: Green-synthesis of reduced graphene oxide nanosheets using rose water and a survey on their characteristics and applications. RSC Adv. 3, 13365–13371 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Suleyman Demirel University Scientific Research Project Coordination Unit (Project No: 4765-YL2-16) for their financial support of this study. We would also like to thank the outstanding service in the plasma system provided by PlazmaTek Company (Isparta, Turkey).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dogan, C., Uygun Oksuz, A., Nohut Maslakci, N. et al. Sterilization of Natural Rose Water with Nonthermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma. Arab J Sci Eng 44, 6403–6410 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-03921-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-03921-8