Abstract
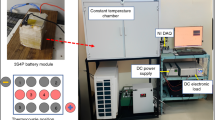
In this work, an experimental study was conducted to investigate the thermal performance of a heat pipe thermal management system for electric vehicle lithium-ion batteries. The battery cells were represented by two proxy cells with a heat source ranging from 10 to 35 W/cell. The evaporator of the heat pipes was in close contact with the battery cell surface, and the condenser was subjected to the forced convection of circulating water. The performance was characterized by the maximum surface temperature, temperature difference, total thermal resistance and Nusselt number at the condenser side. The effects of heat inputs, length of the condenser and water flowrate were also investigated. A condenser length in the range of 100–150 mm and water flowrate showed insignificant effects on the battery surface temperature and the total thermal resistance. Heat pipes were also observed to be able to reduce the battery surface temperature by 39.1% on average. They are also capable of maintaining the surface temperature below 50 °C and temperature differential below 5 °C if the heat generation of the battery cell is less than 20 W.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BTMS:
-
Battery thermal management system
- EV:
-
Electric vehicle
- HEV:
-
Hybrid electric vehicle
- NCC:
-
Naturally cooled condenser
- PCM:
-
Phase-change material
- TMS:
-
Thermal management system
- WCC:
-
Water-cooled condenser
- δ :
-
Thickness (m)
- ṁ :
-
Mass flowrate (kg/s)
- η :
-
Thermal efficiency of heat pipe
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- A s :
-
Surface area of the heat pipe that is exposed to the water (m2)
- c p :
-
Specific heat capacity (J/kg K)
- d :
-
Diameter (m)
- e h :
-
Uncertainty for convection coefficient
- e loss :
-
Uncertainty for the heat loss
- e Nu :
-
Uncertainty for Nusselt number
- e Q :
-
Uncertainty for heat input
- e R :
-
Uncertainty for thermal resistance
- h :
-
Convection heat transfer coefficient (W/m K)
- I :
-
Electrical current (A)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity of the surrounding fluid at the condenser side (W/m2 K)
- L :
-
Length (m)
- Q cond :
-
Heat removed from the condenser section (W)
- R t :
-
Total thermal resistance of the system (K/W)
- T p :
-
Average surface temperature of the proxy battery cell (°C)
- T f :
-
Temperature of the surrounding fluid (water) on the condenser side (°C)
- T in :
-
Water temperature at the entrance of the water tank (°C)
- T out :
-
Water temperature at the exit of the water tank (°C)
- T pipe :
-
Condenser surface temperature (°C)
- V :
-
Voltage (V)
- c:
-
Condenser
- e:
-
Evaporator
- i:
-
Inner
- o:
-
Outer
- w:
-
Wick outer region
References
Frieske, B.; Kloetzke, M.; Mauser, F.: Trends in vehicle concept and key technology development for hybrid and battery electric vehicles. In: 2013 World Electric Vehicle Symposium and Exhibition, Barcelona, Spain, pp. 1–12 (2013)
Sato, N.: Thermal behavior analysis of lithium-ion batteries for electric and hybrid vehicles. J. Power Sources 99, 70–77 (2001)
Rao, Z.; Wang, S.: A review of power battery thermal energy management. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 15, 4554–4571 (2011)
Khateeb, S.A.; Amiruddin, S.; Farid, M.; Selman, J.R.; Al-Hallaj, S.: Thermal management of Li-ion battery with phase change material for electric scooters: experimental validation. J. Power Sources 142, 345–353 (2005)
Pesaran, A.A.: Battery thermal models for hybrid vehicle simulations. J. Power Sources 110, 377–382 (2002)
Tran, T.-H.; Harmand, S.; Sahut, B.: Experimental investigation on heat pipe cooling for hybrid electric vehicle and electric vehicle lithium-ion battery. J. Power Sources 265, 262–272 (2014)
Karimi, G.; Li, X.: Thermal management of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles. Int. J. Energy Res. 37, 13–24 (2013)
Sabbah, R.; Kizilel, R.; Selman, J.R.; Al-Hallaj, S.: Active (air-cooled) vs. passive (phase change material) thermal management of high power lithium-ion packs: limitation of temperature rise and uniformity of temperature distribution. J. Power Sources 182, 630–638 (2008)
Pesaran, A.: Battery Thermal Management in EVs and HEVs : Issues and Solutions. In: Advanced Automotive Batteries Conference, Las Vegas, Nevada, p. 10 (2001)
Rao, Z.; Huo, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, G.: Experimental investigation of battery thermal management system for electric vehicle based on paraffin/copper foam. J. Energy Inst. 88, 241–246 (2015)
Kizilel, R.; Sabbah, R.; Selman, J.R.; Al-Hallaj, S.: An alternative cooling system to enhance the safety of Li-ion battery packs. J. Power Sources 194, 1105–1112 (2009)
Liu, R.; Chen, J.; Xun, J.; Jiao, K.; Du, Q.: Numerical investigation of thermal behaviors in lithium-ion battery stack discharge. Appl. Energy 132, 288–297 (2014)
Faghri, A.; Harley, C.: Transient lumped heat pipe analyses. Heat Recovery Syst. CHP 14, 351–363 (1994)
Ting, C.; Chen, C.: Analyzing the heat transfer property of heat pipe influenced by integrated cooling apparatus. Chin. J. Eng. 2014, 1–10 (2014)
Yang, X.; Yan, Y.Y.; Mullen, D.: Recent developments of lightweight, high performance heat pipes. Appl. Therm. Eng. 33–34, 1–14 (2012)
Swanepoel, G.: Thermal Management of Hybrid Electrical Vehicles. University of Stellenbosch, Stellenbosch (2001)
Wu, M.S.; Liu, K.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wan, C.C.: Heat dissipation design for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 109, 160–166 (2002)
Rao, Z.; Wang, S.; Wu, M.; Lin, Z.; Li, F.: Experimental investigation on thermal management of electric vehicle battery with heat pipe. Energy Convers. Manag. 65, 92–97 (2013)
Tran, T.-H.; Harmand, S.; Desmet, B.; Filangi, S.: Experimental investigation on the feasibility of heat pipe cooling for HEV/EV lithium-ion battery. Appl. Therm. Eng. 63, 551–558 (2014)
Zhao, R.; Gu, J.; Liu, J.: An experimental study of heat pipe thermal management system with wet cooling method for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 273, 1089–1097 (2015)
Wang, Q.; Jiang, B.; Xue, Q.F.; Sun, H.L.; Li, B.; Zou, H.M.; et al.: Experimental investigation on EV battery cooling and heating by heat pipes. Appl. Therm. Eng. 88, 54–60 (2014)
Ye, Y.; Shi, Y.; Saw, L.H.; Tay, A.A.O.: Performance assessment and optimization of a heat pipe thermal management system for fast charging lithium ion battery packs. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 92, 893–903 (2016)
Smith, J.; Singh, R.; Hinterberger, M.; Mochizuki, M.: Battery thermal management system for electric vehicle using heat pipes. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 134, 517–529 (2018)
Yamada, T.; Koshiyama, T.; Yoshikawa, M.; Yamada, T.; Ono, N.: Analysis of a lithium-ion battery cooling system for electric vehicles using a phase-change material and heat pipes. J. Therm. Sci. Technol. 12, JTST0011-JTST0011 (2017)
Hata, H.; Wada, S.; Yamada, T.; Hirata, K.; Yamada, T.; Ono, N.: Performance evaluation of a battery-cooling system using phase-change materials and heat pipes for electric vehicles under the short-circuited battery condition. J. Therm. Sci. Technol. 13, JTST0024-JTST0024 (2018)
Liu, F.-F.; Lan, F.-C.; Chen, J.-Q.; Li, Y.-G.: Experimental investigation on cooling/heating characteristics of ultra-thin micro heat pipe for electric vehicle battery thermal management. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 31, 53 (2018)
Elnaggar, M.H.A.; Abdullah, M.Z.; Munusamy, S.R.R.: Experimental and numerical studies of finned L-shape heat pipe for notebook-PC cooling. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 3, 978–988 (2013)
Sadeghinezhad, E.; Mehrali, M.; Rosen, M.A.; Akhiani, A.R.; Tahan, Latibari S.; Mehrali, M.; et al.: Experimental investigation of the effect of graphene nanofluids on heat pipe thermal performance. Appl. Therm. Eng. 100, 775–787 (2016)
Sözen, A.; Menlik, T.; Gürü, M.; Boran, K.; Kiliç, F.; Aktaş, M.; et al.: A comparative investigation on the effect of fly-ash and alumina nanofluids on the thermal performance of two-phase closed thermo-syphon heat pipes. Appl. Therm. Eng. 96, 330–337 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the supports provided by Universiti Sains Malaysia and Universiti Kuala Lumpur Malaysian Spanish Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nasir, F.M., Abdullah, M.Z. & Ismail, M.A. Experimental Investigation of Water-Cooled Heat Pipes in the Thermal Management of Lithium-Ion EV Batteries. Arab J Sci Eng 44, 7541–7552 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-03851-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-03851-5