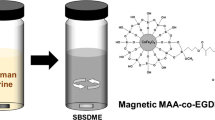
Abstract
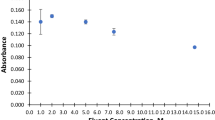
The present paper describes a highly selective method for simultaneous determination of amphetamines in urine samples by stir bar sorptive extraction method using carbon-coated magnetic nanoparticles as novel coating for stir bar. Under optimized extraction conditions, a good linearity was observed in the concentration range of 20–2000 ng/mL for amphetamine, 20–2500 ng/mL for methamphetamine, and 30–1500 ng/mL for pseudoephedrine. The positive urine samples were examined by the developed proposed method with satisfactory recovery. Results showed that the developed stir bar sorptive extraction method could be applied in different forensic and clinical laboratories.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rouhani, S.; Haghgoo, S.: A novel fluorescence nanosensor based on 1, 8-naphthalimide-thiophene doped silica nanoparticles, and its application to the determination of methamphetamine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 209, 957–965 (2015)
Lan, L.; Hu, B.; Yu, C.: pH-resistant titania hybrid organic-inorganic coating for stir bar sorptive extraction of drugs of abuse in urine samples followed by high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet visible detection. J. Chromatogr. A 1217, 7003–7009 (2010)
Rezazadeh, M.; Yamini, Y.; Seidi, S.: Application of a new nanocarbonaceous sorbent in electromembrane surrounded solid phase microextraction for analysis of amphetamine and methamphetamine in human urine and whole blood. J. Chromatogr. A 1396, 1–6 (2015)
Cao, F.; Xu, J.; Yan, S.; Yuan, X.; Yang, F.; Hou, L.; Zhao, L.; Zeng, L.; Liu, W.; Zhu, L.: A surface plasmon resonance-based inhibition immunoassay for forensic determination of methamphetamine in human serum. Forensic Chem. 8, 21–27 (2018)
Ji Kwon, N.; Han, E.: A commentary on the effects of methamphetamine and the status of methamphetamine abuse among youths in South Korea, Japan, and China. Forensic Sci. Int. 286, 81–85 (2018)
Taghvimi, A.; Hamishehkar, H.; Ebrahimi, M.: Magnetic nano graphene oxide as solid phase extraction adsorbent coupled with liquid chromatography to determine pseudoephedrine in urine samples. J. Chromatogr. B 1009, 66–72 (2016)
Fisichella, M.; Odoardi, S.; Strano-Rossi, S.: High-throughput dispersive liquid/liquid microextraction (DLLME) method for the rapid determination of drugs of abuse, benzodiazepines and other psychotropic medications in blood samples by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and application to forensic cases. Microchem. J. 123, 33–41 (2015)
Lee, H.-H.; Lee, J.-F.; Lin, S.-Y.; Chen, B.-H.: Simultaneous identification of abused drugs, benzodiazepines, and new psychoactive substances in urine by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 32, 118–127 (2016)
Cruz-Vera, M.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M.: Sorptive microextraction for liquid-chromatographic determination of drugs in urine. TRAC Trends Anal. Chem. 28, 1164–1173 (2009)
He, Y.; Kang, Y.-J.: Single drop liquid-liquid-liquid microextraction of methamphetamine and amphetamine in urine. J. Chromatogr. A 1133, 35–40 (2006)
Sánchez-González, J.; Odoardi, S.; Bermejo, A.M.; Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Romolo, F.S.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A.; Strano-Rossi, S.: Development of a micro-solid-phase extraction molecularly imprinted polymer technique for synthetic cannabinoids assessment in urine followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1550, 8–20 (2018)
Xiao, Z.; He, M.; Chen, B.; Hu, B.: Polydimethylsiloxane/metal-organic frameworks coated stir bar sorptive extraction coupled to gas chromatography-flame photometric detection for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides in environmental water samples. Talanta 156, 126–133 (2016)
Lei, Y.; He, M.; Chen, B.; Hu, B.: Polyaniline/cyclodextrin composite coated stir bar sorptive extraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detection for the analysis of trace polychlorinated biphenyls in environmental waters. Talanta 150, 310–318 (2016)
Benedé, J.L.; Chisvert, A.; Giokas, D.L.; Salvador, A.: Stir bar sorptive-dispersive microextraction mediated by magnetic nanoparticles-nylon 6 composite for the extraction of hydrophilic organic compounds in aqueous media. Anal. Chim. Acta 926, 63–71 (2016)
Kole, P.L.; Millership, J.; McElnay, J.C.: Determination of diclofenac from paediatric urine samples by stir bar sorptive extraction (SBSE)-HPLC-UV technique. Talanta 85, 1948–1958 (2011)
Fernandes, C.; Jiayu, P.; Sandra, P.; Lanšas, F.: Stir bar sorptive extraction-LC-MS for the analysis of fluoxetine in plasma. Chromatographia 64, 517–521 (2006)
Prieto, A.; Basauri, O.; Rodil, R.; Usobiaga, A.; Fernández, L.; Etxebarria, N.; Zuloaga, O.: Stir-bar sorptive extraction: a view on method optimisation, novel applications, limitations and potential solutions. J. Chromatogr. A 1217, 2642–2666 (2010)
Sánchez-Rojas, F.; Bosch-Ojeda, C.; Cano-Pavón, J.M.: A review of stir bar sorptive extraction. Chromatographia 69, 79–94 (2009)
Lancas, F.M.; Queiroz, M.E.C.; Grossi, P.; Olivares, I.R.: Recent developments and applications of stir bar sorptive extraction. J. Sep. Sci. 32, 813–824 (2009)
Chong, S.L.; Wang, D.; Hayes, J.D.; Wilhite, B.W.; Malik, A.: Sol- gel coating technology for the preparation of solid-phase microextraction fibers of enhanced thermal stability. Anal. Chem. 69, 3889–3898 (1997)
Gbatu, T.P.; Sutton, K.L.; Caruso, J.A.: Development of new SPME fibers by sol-gel technology for SPME-HPLC determination of organometals. Anal. Chim. Acta 402, 67–79 (1999)
Zeng, Z.; Qiu, W.; Yang, M.; Wei, X.; Huang, Z.; Li, F.: Solid-phase microextraction of monocyclic aromatic amines using novel fibers coated with crown ether. J. Chromatogr. A 934, 51–57 (2001)
Azenha, M.; Malheiro, C.; Silva, A.F.: Ultrathin phenyl-functionalized solid phase microextraction fiber coating developed by sol-gel deposition. J. Chromatogr. A 1069, 163–172 (2005)
Yu, J.; Dong, L.; Wu, C.; Wu, L.; Xing, J.: Hydroxyfullerene as a novel coating for solid-phase microextraction fiber with sol-gel technology. J. Chromatogr. A 978, 37–48 (2002)
Shi, L.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Niu, W.; Xu, G.: Application of ceramic carbon materials for solid-phase extraction of organic compounds. Anal. Chem. 78, 1345–1348 (2006)
Heidari, H.; Razmi, H.; Jouyban, A.: Preparation and characterization of ceramic/carbon coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle nanocomposite as a solid-phase microextraction adsorbent. J. Chromatogr. A 1245, 1–7 (2012)
Taghvimi, A.; Hamishehkar, H.: Carbon coated magnetic nanoparticles as a novel magnetic solid phase extraction adsorbent for simultaneous extraction of methamphetamine and ephedrine from urine samples. J. Chromatogr. B 1041, 113–119 (2017)
Chafer-Pericas, C.; Campıns-Falcó, P.; Herraez-Hernandez, R.: Application of solid-phase microextraction combined with derivatization to the determination of amphetamines by liquid chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 333, 328–335 (2004)
Chafer-Pericas, C.; Campins-Falco, P.; Herraez-Hernandez, R.: Application of solid-phase microextraction combined with derivatization to the enantiomeric determination of amphetamines. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 40, 1209–1217 (2006)
Chou, C.-C.; Lee, M.-R.: Solid phase microextraction with liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry for analysis of amphetamine and methamphetamine in serum. Anal. Chim. Acta 538, 49–56 (2005)
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly appreciate Biotechnology Research Center and Faculty of Pharmacy of Tabriz University of Medical Science for supporting this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent is applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taghvimi, A., Dastmalchi, S. & Javadzadeh, Y. Novel Ceramic Carbon-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles as Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction Coating for Simultaneous Extraction of Amphetamines from Urine Samples. Arab J Sci Eng 44, 6373–6380 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-03810-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-03810-0