Abstract
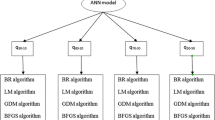
It is well known that the construction on soft clayey soil is always a great challenge to the geotechnical engineers. The soft clay poses high compressibility and low bearing capacity. It is a common practice to improve the properties of the soft clay prior to any construction on it. In this respect, ground improvement by stone columns is a usual choice of the geotechnical engineers. The stone columns increase the bearing capacity and reduce the settlement of the soft clay. Many theories are developed to determine the bearing capacity of the soft soil reinforced with stone columns. However, most of the theories are site-specific and do not show a very good match with the field observations. In this study, a large numbers of data were collected from previously reported studies from various parts of the globe and an empirical formula based on support vector regression (SVR) technique for the determination of the ultimate bearing capacity of the stone columns is achieved. Two different techniques, namely tenfold cross-validation (\({q}_{\mathrm{TFCV}}\)) and non-cross-validation (\({q}_{\mathrm{NCV}}\)), are presented for the construction of the SVR model. It is observed that the SVR method gives a better prediction than artificial neural network method. Laboratory experiments were conducted to validate the SVR-ERBF empirical approach. The formula is also validated with two field observations by two other investigators.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gucuyen, E.; Erdem, R.T.; Gokku, U.: Irregular wave effects on dynamic behavior of piles. Arab J. Sci. Eng. 38, 1047–1057 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-012-0428-6
Borthakur, N.; Dey, A.K.: Experimental investigation on load carrying capacity of micropiles in soft clay. Arab J. Sci. Eng. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2894-3
Ambily., A.P.; Gandhi, S.R.: Experimental and theoretical evaluation of stone column in soft clay (2004) ICGGE.
Ambily, A.P.; Gandhi, S.R.: Behavior of stone columns based on experimental and fem analysis. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. ASCE 133, 405–415 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2007)133:4(405)
Afshar, J.N.; Ghazavi, M.: Experimental studies on bearing capacity of geosynthetic reinforced stone columns. Arab J. Sci. Eng. 39, 1559–1571 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0709-8
Castro, J.: An analytical solution for the settlement of stone columns beneath rigid footings. Acta Geotech. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-014-0358-4
Mohanty, P.; Samanta, M.: Experimental and numerical studies on response of the stone column in layered soil. Int. J. Geosynth. Ground Eng. 1, 27 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40891-015-0029-z
Goh, A.T.C.; Kulhawy, F.H.; Chua, C.G.: Bayesian neural network analysis of undrained side resistance of drilled shafts. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. ASCE 131(1), 84–93 (2005)
Lee, J.S.; Pande, G.N.: Analysis of stone-column reinforced Foundations. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 22, 1001–1020 (1998)
Shahu, J.T.; Reddy, Y.R.: Clayey soil reinforced with stone column group: model tests and analyses. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng., ASCE 137(12) (2011). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000552
Niroumand, H.; Kassim, K.A.; Yah, C.S.: Soil improvement by reinforced stone columns based on experimental work. EJGE 16 (2011)
Nassaji, F.; Asakereh, A.: Effect of granular bed on behaviour of stone column improved ground. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Investig. 2(23) (2013)
Afshar J.N.; Ghazavi, M.: A simple analytical method for calculation of bearing capacity of stone column. Int. J. Civil Eng. 12(1) (2014)
Etezad, M.; Hanna, A.M.; Ayadat, T.: Bearing capacity of a group of stone columns in soft soil. Int. J. Geomech. ASCE, (2015)
Rentschler, T.; Schmidt, K.; Kuhn, P.; Scholten, T.: Three-dimensional mapping of soil organic carbon (SOC) based on multi-scale digital terrain analysis and data mining in Jiangxi Province, PR China. (202), Wageningen, 26 June–1 (2017)
Cheng, M.Y.; Wu, Y.W.: Dynamic prediction of project success using evolutionary support vector machine inference model. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction, vol. 203, p. 2005 (2008)
Olyaie, E.; Heydari, M.; Banejad, H.; Chau, K.W.: A laboratory investigation on the potential of computational intelligence approaches to estimate the discharge coefficient of piano key weir.
Li, X.; Miao, J.: Life Prediction Method of Lithium-Ion Battery Based on Grey Support Vector Machines. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, International Journal of Medical and Health Sciences, 9(5), (2015)
Liu, H.X.; Zhang, R.S.; Yao, X.J.; Liu, M.C.; Hu, Z.D.; Fan, B.T.: Prediction of the isoelectric point of an amino acid based on GA-PLS and SVMs. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 44(1), 161–167 (2004)
Kostic, S.; Vasovic, D.: Prediction model for compressive strength of basic concrete mixture using artificial neural networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 26, 1005–1024 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1763-1
Samui, P.: Support vector machine applied to settlement of shallow foundations on cohesionless soils. Comput. Geotechn. 35, 419–427 (2008)
Chik, Z.; Aljanabi, Q.A.: Intelligent prediction of settlement ratio for soft clay with stone columns using embankment improvement techniques. Neural Comput. Appl. 25, 73–82 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-013-1449-0
Chik, Z.; Aljanabi, Q.A.; Kasa, A.; Taha, M.R.: Tenfold cross validation artificial neural network modeling of the settlement behavior of a stone column under a highway embankment. Arab J. Geosci. 7, 4877–4887 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1128-6
Vapnik, V.N.; Golowich, S.E.; Smola, A.: Support Vector Method for Function Approximation, Regression Estimation, and Signal Processing, Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo (1996)
IS 15284-1: Design and construction for ground improvement-Guidelines. Part-1: Stone columns [CED 43: Soil and foundation engineering], ICS 93.020. (2003)
Gunn, S.R.: Support vector machines for classification and regression. Tech Rep. University of Southampton. (2001) http://www.isis.ecs.soton.ac.uk/isystems/kernel/ svm.zip,
Mozumder, et al.: Support vector regression approach to predict the strength of FRP confined concrete. Arab J. Sci. Eng. (2016) https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2340-y
Leung, : Empirical approach for determining ultimate FRP strain in FRP-strengthened concrete beams. J. Compos. Constr. 10(2), 125–138 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0268(2006)10:2(125)
Mozumder, R.A.; Laskar, A.I.; Hussain, M.: Empirical approach for strength prediction of geopolymer stabilized clayey soil using support vector machines. Constr. Build. Mater. 132, 412–424 (2017)
Bhosle, S.; Vaishampayan, V.V.: Ground Improvement Using Vibro Stone Columns Capacity Of Stone Column. Guntur, INDIA (2009). IGC 2009
Report no. FHWA/RD-83/026 (1983) www.dot.ca.gov/hq/esc/geotech/references/Ground.../4-Stone_Columns.pdf.
Poorooshasb, H.B.; Meyerhof, G.: Analysis of behavior of stone columns and lime columns. Comput. Geotech. 20(1), 47–70 (1997)
Andreou, P.; Papadopoulos, V.: Factors affecting the settlement estimation of stone column reinforced soils. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 32(23), 1175–1185 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-014-9788-x
Etezad, M.: Geotechnical performance of group of stone columns. Phd Thesis (2007)
Murugesan, S.; Rajagopal, K.: Performance of encased stone columns and design guidelines for construction on soft clay soils. In: Proceedings of the 4th Asian Regional Conference on Geosynthetics, June 17–20, Shanghai, China (2008)
Malarvizhi, S.N.; Ilampurthi, K.: Comparative study on the behavior of encased stone column and conventional stone column. Soils found. Jpn. Geotechn. Soc. 47(5), 873–885 (2007)
Golait, Y.S.; Satyanarayana, V.; Raju, S.S.V.: Concept of Under Reamed Cemented Stone Columns for Soft Clay Ground Improvement. Guntur, INDIA (2009). IGC 2009
Zhang, L.; Zhao, M.; Shi, C.; Zhao, H.: Settlement calculation of composite foundation reinforced with stone columns. Int. J. Geomech. 13(3), 248–256 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000212
Hassen, G.; Buhan, P.D.; Abdelkrim, M.: Finite element implementation of a homogenized constitutive law for stone column-reinforced foundation soils, with application to the design of structures. Comput. Geotech. 2010(37), 40–49 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, M., Dey, A.K. Prediction of Bearing Capacity of Stone Columns Placed in Soft Clay Using SVR Model. Arab J Sci Eng 44, 4681–4691 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3513-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3513-7