Abstract
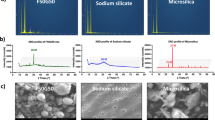
The aim of this study is to compare sinking beads (SB) with fly ash (FA) and metakaolin (MK) with regard to their ability to improve the performance of concretes. The workability, compressive strength, free shrinkage and chloride resistance of concretes with and without the above mineral admixtures are investigated. To explicate the differences of above results, the pore structure and pore solution chemistry were also studied. Besides, the Chapelle test was adopted to compare the pozzolanic activity of the mineral admixtures. The water-to-binder ratio of concretes and pastes was 0.35 by mass. The incorporation level of MK was 5 and 10 wt%, while that of FA and SB was 10, 20 and 30 wt%. A systematic improvement in flowability, compressive strength, chloride resistance, free shrinkage is observed for SB concretes compared with FA concretes due to the smaller particle size, more round particle shape and higher pozzolanic activity of SB. MK shows the overwhelming ability to improve compressive strength and chloride resistance ability of concretes compared with SB and FA for the same replacement level, but comparable compressive strength and chloride resistance for SB concretes can be obtained by increasing the content of SB. In addition, inclusion of 20 wt% SB demonstrates remarkable potential to reduce free shrinkage to 25% less than concretes with 10 wt% MK. It may be ascribed to the dense structure of SB, which brings less volume reduction or even some increase during pozzolanic reaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, A.Q.; Zhang, C.Z.; Sun, W.: Fly ash effects-III. The microaggregate effect of fly ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 34(11), 2061–2066 (2004)
Poon, C.S.; Wong, Y.L.; Lam, L.: The influence of different curing conditions onthe pore structure and related properties of fly-ash cement pastes and mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 11(7), 383–393 (1997)
Chindaprasirt, P.; Jaturapitakkul, C.; Sinsiri, T.: Effect of fly ash fineness on compressive strength and pore size of blended cement paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 27(4), 425–428 (2005)
Duan, P.; Shui, Z.; Chen, W.: Effects of metakaolin, silica fume and slag on pore structure, interfacial transition zone and compressive strength of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 44, 1–6 (2013)
Ramezanianpour, A.A.: Effect of curing on the compressive strength, resistance to chloride-ion penetration and porosity of concretes incorporating slag, fly ash or silica fume. Cem. Concr. Compos. 17(2), 125–133 (1995)
Roy, D.M.; Arjunan, P.; Silsbee, M.R.: Effect of silica fume, metakaolin, and low-calcium fly ash on chemical resistance of concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 31(12), 1809–1813 (2001)
Nehdi, M.; Mindess, S.; Aı Tcin, P.C.: Rheology of high-performance concrete: effect of ultrafine particles. Cem. Concr. Res. 28(5), 687–697 (1998)
Johari, M.A.M.; Brooks, J.J.; Kabir, S.: Influence of supplementary cementitious materials on engineering properties of high strength concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 25(5), 2639–2648 (2011)
Sabir, B.B.; Wild, S.; Bai, J.: Metakaolin and calcined clays as pozzolans for concrete: a review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 23(6), 441–454 (2001)
Duxson, P.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.: The role of inorganic polymer technology in the development of ’green concrete’. Cem. Concr. Res. 37(12), 1590–1597 (2007)
Tafraoui, A.; Escadeillas, G.; Lebaili, S.: Metakaolin in the formulation of UHPC. Constr. Build. Mater. 23(2), 669–674 (2009)
Hooton, R.D.; Stanish K.; Angel J.P.: The effect of ground, granulated blast furnace slag (slag cement) on the drying shrinkage of concrete—a critical review of the literature. In: Proceedings of the 8th ACI International Confenrence, pp. 79–94. Detroit (2009)
Ramezanianpour, A.A.; Ghiasvand, E.; Nickseresht, I.: Influence of various amounts of limestone powder on performance of Portland limestone cement concretes. Cem. Concr. Compos. 31(10), 715–720 (2009)
Ghrici, M.; Kenai, S.; Said-Mansour, M.: Mechanical properties and durability of mortar and concrete containing natural pozzolana and limestone blended cements. Cem. Concr. Compos. 29(7), 542–549 (2007)
Bonavetti, V.; Donza, H.; Rahhal, V.: Influence of initial curing on the properties of concrete containing limestone blended cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 30, 703–708 (2000)
Bian, B.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Z.: Study on the separation and comprehensive utilization of the hollow microbeads in fly ash. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 22(2), 23–30 (1993). (in Chinese)
Bian, B.; Chen, W.: Mechanisim and test of separating sinking beads from coal ash. China Min. Mag. 6(1), 64–68 (1997). (in Chinese)
Li, H.; Xu, D.; Feng, S.: Microstructure and performance of fly ash micro-beads in cementitious material system. Constr. Build. Mater. 52, 422–427 (2014)
Pontes, J.; Santos, Silva A.; Faria, P.: Evaluation of pozzolanic reactivity of artificial pozzolans. Mater. Sci. Forum 730, 433–438 (2013)
Seiffarth, T.; Hohmann, M.; Posern, K.: Effect of thermal pre-treatment conditions of common clays on the performance of clay-based geopolymeric binders. Appl. Clay Sci. 73, 35–41 (2013)
Esteves, T.C.; Rajamma, R.; Soares, D.: Use of biomass fly ash for mitigation of alkali-silica reaction of cement mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 26(1), 687–693 (2012)
Wild, S.; Khatib, J.M.; Jones, A.: Relative strength, pozzolanic activity and cement hydration in superplasticised metakaolin concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 26(10), 1537–1544 (1996)
Brooks, J.J.; Johari, M.: Effect of metakaolin on creep and shrinkage of concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 23(6), 495–502 (2001)
Li, Z.; Ding, Z.: Property improvement of Portland cement by incorporating with metakaolin and slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 33(4), 579–584 (2003)
Tregger, N.A.; Pakula, M.E.; Shah, S.P.: Influence of clays on the rheology of cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 40(3), 384–391 (2010)
Shi, C.: Effect of mixing proportions of concrete on its electrical conductivity and the rapid chloride permeability test (ASTM C1202 or ASSHTO T277) results. Cem. Concr. Res. 34(3), 537–545 (2004)
Zhao, T.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, J.: Conductivity of pore fluid and permeability of concrete measured by electricity. Concrete 2, 12–15 (2000). (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by “National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFC0305101)”, “YangFan Innovative & Entrepreneurial Research Team Project (No. 201312C12)”, “Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (WUT:2017II51GX)” and “Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (No. 2013B09060085)”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Shui, Z., Sun, T. et al. Effect of Fly Ash, Sinking Beads and Metakaolin on the Workability, Strength, Free Shrinkage and Chloride Resistance of Concretes: A Comparative Study. Arab J Sci Eng 43, 5243–5254 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3068-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3068-7