Abstract
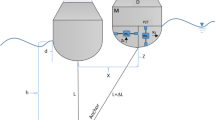
This study introduces a novel wave energy harvester (WEH) with frequency conversion capability to convert the ocean wave energy to usable electricity based on the piezoelectric effect. The presented WEH is with characteristics of space saving and minimized component quantities and is made of a cylindrical case reciprocally moving with respect to the fixed core shaft attached to identical magnetic bars. The cylindrical case contains four magnetic bar-mass-spring-lever-piezoelectric systems arranged symmetrically each other to the fixed shaft. By this smart design, the WEH is capable of converting the low frequency of ocean waves to a higher excitation frequency of motions on the piezoelectric transducer to harness higher electric power and reduce electrical leakage. A mathematical model of the WEH considering the wave–structure interaction is developed to evaluate the effectiveness of the converter. The simulation results reveal that the occurrence of resonance can lead to an outstanding power output via adjusting the distance between two adjacent magnetic bars. The power output is realized up to 750 W with the converter height and diameter, ocean wave height, and wave period being 1 m, 1 m, 1.5 m and 8 s, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khaligh, A.; Onar, O.C.: Energy Harvesting: Solar, Wind, and Ocean Energy Conversion Systems (Energy, Power Electronics, and Machines), p. 1. Hardcover, Boca Raton (2009)
Falnes, J.: A review of wave-energy extraction. Mar. Struct. 20, 185–201 (2007)
Zhang, Y.L.; Lin, Z.: Advances in technology of ocean wave energy converters using piezoelectric materials. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 5, 324–331 (2011)
Anton, S.R.; Sodano, H.A.: A review of power harvesting using piezoelectric materials 2003–2006. Smart. Mater. Struct. 16, 21–27 (2007)
http://acore.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/01. Accessed 9 Apr 2018
Sravanthi, C; James, M.C.: A Survey of Energy Harvesting Sources for Embedded Systems. IEEE (2008)
Williams, C.B.; Yates, R.B.: Analysis of a micro-electric generator for microsystems. Sens. Actuators A 52, 8–11 (1996)
Priya, S.: Advances in energy harvesting using low profile piezoelectric transducers. J. Electroceram. 19, 165–182 (2007)
http://www.piezo.com/tech3faq.html. Accessed 9 May 2018
Gu, L.; Livermore, C.: Passive self-tuning energy harvester for extracting energy from rotational motion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 04–09 (2016)
Viet, N.V.; Wu, N.; Wang, Q.A.: review on energy harvesting from ocean waves by piezoelectric technology. J. Mod. Mech. Mater. 4, 161–171 (2017)
Murray, R.; Rastegar, J.: Novel two-stage piezoelectric-based ocean wave energy harvesters for moored or unmoored buoys. Act. Passive Smart Struct. Integr. Syst. SPIE 7288, 1117–1129 (2009)
Miller, L.M; Wright, P.K; Ho, C.C; Evans, J.W; Shafer, P.C; Ramesh, R.: Integration of a low frequency, tunable MEMS piezoelectric energy harvester and a thick film micro capacitor as a power supply system for wireless sensor nodes in IEEE, ECCE, 27–34 (2009)
Zhou, S.; Cao, J.; Erturk, A.; Lin, J.: Enhanced broadband piezoelectric energy harvesting using rotatable magnets. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 01–05 (2013)
Erturk, A.; Hoffmann, J.; Inman, D.J.: A piezomagnetoelastic structure for broadband vibration energy harvesting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 02–06 (2009)
Zhou, S.; Cao, J.; Inman, D.J.; Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Lin, J.: Impact-induced high-energy orbits of nonlinear energy harvesters. Appl. Phys. Lett. 106, 01–06 (2015)
Xie, X.D.; Wang, Q.; Wu, N.: A ring piezoelectric energy harvester excited by magnetic forces. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 77, 71–78 (2014)
Viet, N.V.; Al-Qutayri, M.; Liew, K.M.; Wang, Q.: An octo-generator for energy harvesting based on the piezoelectric effect. Appl. Ocean Res. 64, 128–134 (2017)
Viet, N.V.; Wang, Q.; Carpinteri, A.: Development of an ocean wave energy harvester with a built-in frequency conversion function. Int. J. Energy. Res. 42, 684–695 (2017)
Wu, N; Wang, Q; Xie, X.: Ocean wave energy harvesting with a piezoelectric coupled buoy. US Patent 9,726,143, 08/August (2017)
McCormick, M.: Ocean Engineering Mechanics With Applications. Cambridge University Press, New York (2009)
McCormick, M.: Ocean Wave Energy Conversion. Dover Publications, Mineola, NY (2007)
Rafael, E.V.; Carl, D.C.; Julio, C.C.: Analysis of a planar tensegrity mechanism for ocean wave energy harvesting. J. Mech. Robot. 6, 31015–31021 (2014)
Kristiansen, E; Egeland, O.: Frequency dependent added mass in models for controller design for wave motion ship damping. MCMC’03, Girona, Spain 17–19 (2003)
Taghipour, R.; Perez, T.; Moan, T.: Hybrid frequency-time domain models for dynamic response analysis of marine structures. Ocean Eng. 35(7), 685–705 (2008)
Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I.A.: Handbook of Mathematical Functions, Dover Publications. New York. Originally published by the U. S. Printing Office, Washington, DC (1965)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drag_coefficient. Accessed 9 Apr 2018
Spooner, E.; Grimwade, J.: \(\text{Snapper}^{{\rm TM}}\): an efficient and compact direct electric power take-off device for wave energy converters. In: Proceedings of the World Maritime Technology Conference, 6–10 March, London, UK (2006)
John, S.W.M; Adams, D.: Gyroscopic roll stabilizer for boats. US10454905, 04/June (2003)
http://www.piezo.com/tech3faq.html. Accessed 5 Mar 2018
www.kjmagnetics.com/calculator.asp. Accessed 16 Mar 2018
http://www.intemag.com/magnetic_properties.html#neodymium_props. Accessed 9 May 2018
Al-Ashtari, W.; Hunstig, M.; Hemsel, T.; Sextro, W.: Frequency tuning of piezoelectric energy harvesters by magnetic force. Smart Mater. Struct. 21, 19–24 (2012)
Viet, N.V.; Xie, X.D.; Liew, K.M.; Banthia, N.; Wang, Q.: Energy harvesting from ocean waves by a floating energy harvester. Energy 112, 1219–1226 (2016)
Blevins, R.D.: Formulas for Natural Frequency and Mode Shape. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York (1979)
Woodhouse, J.: Linear damping models for structural vibration. J. Sound. Vib. 215(3), 547–69 (1998)
Mitcheson, P.D.; Yeatman, E.M.; Rao, G.K.; Holmes, A.S.; Green, T.C.: Energy harvesting from human and machine motion for wireless electronic devices. IEEE 96, 1455–1458 (2008)
Xie, X.D.; Wang, Q.: Energy harvesting from a vehicle suspension system. Energy 86, 385–92 (2015)
Ravi, T.T.; Krishna, C.T.: Computation of natural frequencies of multi degree of freedom system. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 10, 2278–2281 (2012)
Wu, N.; Wang, Q.; Xie, X.D.: Wind energy harvesting with a piezoelectric harvester. Smart Mater. Struct. 22, 23–28 (2013)
Tao, J.X.; Viet, N.V.; Carpinteri, A.; Wang, Q.: Energy harvesting from wind by a piezoelectric harvester. Eng. Struct. 133, 74–80 (2017)
http://www.oceanpowertechnologies.com/pb3/. Accessed 19 Apr 2018
Acknowledgements
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viet, N.V., Carpinteri, A. & Wang, Q. A Novel Heaving Ocean Wave Energy Harvester with a Frequency Tuning Capability. Arab J Sci Eng 44, 5711–5722 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-03707-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-03707-4