Abstract
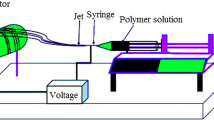
Limitless implementations of nanofibrous membrane show the importance of understanding the nanomechanical responses for water purification and piezoelectric nanogenerator applications. Here, the polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) electrospun nanofibrous films doped by 0.01, 0.05 and 0.1 wt% of ZnO nanoparticles were prepared in the method of electrospinning. Characterizations of PVDF nanocomposite fibrous films were inspected using field emission scanning electron microscope, thermogravimetric analysis, water contact angle, uniaxial tensile test and nanoindentation technique. The influence of minimal concentration of piezoelectric nanoparticles on the morphological, water contact angle, dynamic water contact angle, piezoelectric, thermal and mechanical stabilities of nanocomposite fibrous films was examined. The nanoscale mechanical properties of the PVDF/ZnO nanofibrous films were performed by nanoindentation technique at different spots of nanofibrous mat to examine the elastic–plastic behavior of membranes. The eventual ZnO nanoparticle-modified nanofibrous membranes have been shown nano-level fibers, considerable hydrophilicity and preferable thermal, mechanical and piezoelectric properties. The doping of polymer by 0.1 wt% of ZnO nanoparticles exposed significant enhancement of thermal, mechanical and nanomechanical responses of the melting temperature 2% (170–\(173\,^{\circ }\hbox {C}\)), tensile strength 20% (2.418 MPa), elastic modulus 18% (2.418 GPa) and hardness 60% (235 MPa) and piezoelectric coefficient 13.42 pC/N of the nanofibrous films. These understandings of nanoscale properties are highly promising in the development of sensor and actuators, biomedical, energy harvesting and water filtration devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, W.; Cheng, X.; Fu, X.; Stefanini, C.; Dario, P.: Preliminary study on development of PVDF nanofiber based energy harvesting device for an artery microrobot. Microelectron. Eng. 88, 2251–2254 (2011)
Park, J.M.; Gu, G.Y.; Wang, Z.J.; Kwon, D.J.; Shin, P.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Lawrence DeVries, K.: Mechanical and electrical properties of electrospun CNT/PVDF nanofiber for micro-actuator applications. Adv. Compos. Mater. 25, 305–316 (2016)
Suja, P.S.; Reshmi, C.R.; Sagitha, P.; Sujith, A.: Electrospun nanofibrous membranes for water purification. Polym. Rev. 57, 467–504 (2017)
Wang, H.; Ma, Y.; Cheng, B.; Kang, W.; Li, X.; Shi, L.; Cai, Z.; Zhuang, X.: Solution blown biofunctionalized poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofibers for application in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 258, 24–33 (2017)
Goh, Y.F.; Shakir, I.; Hussain, R.: Electrospun fibers for tissue engineering, drug delivery, and wound dressing. J. Mater. Sci. 48, 3027–3054 (2013)
Zhao, B.; Hamidinejad, M.; Zhao, C.; Li, R.; Wang, S.; Kazemi, Y.; Park, C.B.: A versatile foaming platform to fabricate polymer/carbon composites with high dielectric permittivity and ultra-low dielectric loss. J. Mater. Chem. A. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TA05556D
Zhao, B.; Zhao, C.; Wang, C.; Park, C.B.: Poly(vinylidene fluoride) foams: a promising low-K dielectric and heat-insulating material. J. Mater. Chem. C 6, 3065–3073 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8tc00547h
Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; Zhao, C.; Li, R.; Hamidinejad, S.M.; Kazemi, Y.; Park, C.B.: Synergism between carbon materials and Ni chains in flexible poly(vinylidene fluoride) composite films with high heat dissipation to improve electromagnetic shielding properties. Carbon N. Y. 127, 469–478 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.11.032
Zhao, B.; Park, C.B.: Tunable electromagnetic shielding properties of conductive poly(vinylidene fluoride)/Ni chain composite films with negative permittivity. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 6954–6961 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tc01865g
Zhao, B.; Zhao, C.; Li, R.; Hamidinejad, S.M.; Park, C.B.: Flexible, ultrathin, and high-efficiency electromagnetic shielding properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/carbon composite films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 20873–20884 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b04935
Ma, H.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B.: Thin-film nanofibrous composite membranes containing cellulose or chitin barrier layers fabricated by ionic liquids. Polymer (Guildf) 52, 2594–2599 (2011)
Chinnappan, A.; Kim, H.: Nanocatalyst: electrospun nanofibers of PVDF—dicationic tetrachloronickelate(II) anion and their effect on hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 37, 18851–18859 (2012)
Huang, L.; Manickam, S.S.; McCutcheon, J.R.: Increasing strength of electrospun nanofiber membranes for water filtration using solvent vapor. J. Membr. Sci. 436, 213–220 (2013)
Hou, H.; Gc, J.J.; Zeng, J.; Li, Q.; Reneker, D.H.; Greiner, A.; Cheng, S.Z.D.: Electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibcrs containing a high concentration of well-aligned multiwall carbon nanotubes. Chem. Mater. 17, 967–973 (2005)
Zhao, Z.; Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, J.: Preparation and properties of electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 97, 466–474 (2005)
Liang, S.; Xiao, K.; Mo, Y.; Huang, X.: A novel ZnO nanoparticle blended polyvinylidene fluoride membrane for anti-irreversible fouling. J. Memb. Sci. 394–395, 184–192 (2012)
Jia, H.; Wu, Z.; Liu, N.: Effect of nano-ZnO with different particle size on the performance of PVDF composite membrane. Plast. Rubber Compos. 46, 1–7 (2017)
Shanthi, S.I.; Poovaragan, S.; Arularasu, M.V.; Nithya, S.; Sundaram, R.; Magdalane, C.M.; Kaviyarasu, K.; Maaza, M.: Optical, magnetic and photocatalytic activity studies of Li, Mg and Sr doped and undoped zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 18, 5441–5447 (2018)
Liu, M.; Sun, J.; Sun, Y.; Bock, C.; Chen, Q.: Thickness-dependent mechanical properties of polydimethylsiloxane membranes. J. Micromech. Microeng. 19, 035028 (2009)
Lai, C.Y.; Groth, A.; Gray, S.; Duke, M.: Enhanced abrasion resistant PVDF/nanoclay hollow fibre composite membranes for water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 449, 146–157 (2013)
Zhao, C.; Wu, H.; Li, X.; Pan, F.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Cao, X.; Wang, B.: High performance composite membranes with a polycarbophil calcium transition layer for pervaporation dehydration of ethanol. J. Membr. Sci. 429, 409–417 (2013)
Nili, H.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Bhaskaran, M.; Sriram, S.: In situ nanoindentation: probing nanoscale multifunctionality. Prog. Mater. Sci. 58, 1–29 (2013)
Meza, L.R.; Das, S.; Greer, J.R.: Strong, lightweight, and recoverable three-dimensional ceramic nanolattices. Science 345, 1322–1326 (2014)
Chalker, P.R.; Bull, S.J.; Rickerby, D.S.: A review of the methods for the evaluation of coating-substrate adhesion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 140, 583–592 (1991)
Fu, W.E.; Chang, Y.Q.; Chang, C.W.; Yao, C.K.; Der, L.J.: Mechanical properties of ultra-thin HfO2films studied by nano scratches tests. Thin Solid Films 529, 402–406 (2013)
Hodzic, A.; Stachurski, Z.H.; Kim, J.K.: Nano-indentation of polymer—glass interfaces. Part I. Experimental and mechanical analysis. Polymer (Guildf) 41, 6895–6905 (2000)
Tan, E.P.S.; Lim, C.T.: Physical properties of a single polymeric nanofiber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 1603–1605 (2004)
Liu, Z.H.; Pan, C.T.; Lin, L.W.; Lai, H.W.: Piezoelectric properties of PVDF/MWCNT nanofiber using near-field electrospinning. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 193, 13–24 (2013)
Baniasadi, M.; Xu, Z.; Moreno, S.; Daryadel, S.; Cai, J.; Naraghi, M.; Minary-Jolandan, M.: Effect of thermomechanical post-processing on chain orientation and crystallinity of electrospun P(VDF-TrFE) nanofibers. Polymer (UK) 118, 223–235 (2017)
Baniasadi, M.; Xu, Z.; Hong, S.; Naraghi, M.; Minary-Jolandan, M.: Thermo-electromechanical behavior of piezoelectric nanofibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 2540–2551 (2016)
Naraghi, M.; Chasiotis, I.; Kahn, H.; Wen, Y.; Dzenis, Y.: Novel method for mechanical characterization of polymeric nanofibers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 78, 085108 (2007)
Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M.; Introduction, I.: An improved technique for determining hardness and elasticmodulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564–1583 (1992)
Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M.: Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J. Mater. Res. 19, 3–20 (2004)
Hang, Y.; Liu, G.; Huang, K.; Jin, W.: Mechanical properties and interfacial adhesion of composite membranes probed by in-situ nano-indentation/scratch technique. J. Membr. Sci. 494, 205–215 (2015)
Jin, T.; Niu, X.; Xiao, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Yuan, G.; Shu, X.: Effects of experimental variables on PMMA nano-indentation measurements. Polym. Test. 41, 1–6 (2015)
Mani, M.R.; Gebrekrstos, A.; Madras, G.; Pötschke, P.; Bose, S.: PVDF-MWNT interactions control process induced \(\upbeta \)-lamellar morphology and orientation in the nanocomposites. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20, 24821–24831 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CP03739F
Martins, P.; Lopes, A.C.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.: Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): determination, processing and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 39, 683–706 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2013.07.006
Kim, Y.S.; Xie, Y.; Wen, X.; Wanga, S.; Kim, S.J.; Song, H.K.; Wanga, Z.L.: Highly porouspiezoelectricPVDF membraneaseffectivelithiumion transferchannelsforenhanced self-charging powercell. Nano Energy 14, 77–86 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2015.01.006
Noei, H.; Qiu, H.; Wang, Y.; Löffler, E.; Wöll, C.; Muhler, M.: The identification of hydroxyl groups on ZnO nanoparticles by infrared spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 10, 7092–7097 (2008)
Celebioglu, A.; Yildiz, Z.I.; Uyar, T.: Electrospun crosslinked poly-cyclodextrin nanofibers: highly efficient molecular filtration thru host-guest inclusion complexation. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–11 (2017)
Huang, L.; Arena, J.T.; McCutcheon, J.R.: Surface modified PVDF nanofiber supported thin film composite membranes for forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 499, 352–360 (2016)
Bae, J.; Baek, I.; Choi, H.: Efficacy of piezoelectric electrospun nanofiber membrane for water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 307, 670–678 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.125
Chipara, M.; Lozano, K.; Hernandez, A.; Chipara, M.: TGA analysis of polypropylene-carbon nanofibers composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 93, 871–876 (2008)
Shin, I.H.; Hong, S.; Lim, S.J.; Son, Y.S.; Kim, T.H.: Surface modification of PVDF membrane by radiation-induced graft polymerization for novel membrane bioreactor. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 46, 103–110 (2017)
Wu, M.; Huang, H.X.; Tong, J.: Enhancing \(\upbeta \)-phase content and tensile properties in poly(vinylidene fluoride) by adding halloysite nanotubes and injecting water during extrusion. Mater. Des. 108, 761–768 (2016)
Asai, H.; Kikuchi, M.; Shimada, N.; Nakane, K.: Effect of melt and solution electrospinning on the formation and structure of poly(vinylidene fluoride) fibres. RSC Adv. 7, 17593–17598 (2017)
Kancheva, M.; Toncheva, A.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.: Enhancing the mechanical properties of electrospun polyester mats by heat treatment. Express Polym. Lett. 9, 49–65 (2015)
Yu, H.; Huang, T.; Lu, M.; Mao, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.: Enhanced power output of an electrospun PVDF/MWCNTs-based nanogenerator by tuning its conductivity. Nanotechnology 24, 405401 (2013)
Hong, J.; He, Y.: Effects of nano sized zinc oxide on the performance of PVDF microfiltration membranes. Desalination 302, 71–79 (2012)
McKee, C.T.; Last, J.A.; Russell, P.; Murphy, C.J.: Indentation versus tensile measurements of Young’s modulus for soft biological tissues. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 17, 155–164 (2011)
Callister, W.; Rethwisch, D.: Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction. Wiley, New York (2007)
Singh, H.H.; Khare, N.: Flexible ZnO-PVDF/PTFE based piezo-tribo hybrid nanogenerator. Nano Energy 51, 216–222 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.06.055
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Satthiyaraju, M., Ramesh, T. Nanomechanical, Mechanical Responses and Characterization of Piezoelectric Nanoparticle-Modified Electrospun PVDF Nanofibrous Films. Arab J Sci Eng 44, 5697–5709 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-03694-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-03694-6