Abstract
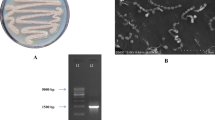
Streptomyces sp. VITHM1 isolated from marine sediment sample collected at Alappuzha Beach, Kerala, India, was screened for antibacterial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial pathogens. The isolate was identified based on phylogeny and molecular taxonomic characterization. Bioactivity-guided extraction and purification of ethyl acetate extract of the isolate lead to identification of crystalline compound 2-hydroxy benzoic acid (HBA). HBA in methanol formed a needle-shaped crystal at room temperature after 36 h. Crystals formed were observed under scanning electron microscope for surface morphology, and the crystal structure was identified by using single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. The crystal was belonged to orthorhombic system, space group pbca with \(a = 11.631(16)\) A, \(b=7.1541\)(8) A, \(c= 16.028(2)\) A, \(V= 1334.2(3)\) Å\(^{3}\). The molecular weight was calculated as 138.12 Daltons with a molecular formula C\(_{7}\) H\(_{6 }\)O\(_{3}\). The crystalline compound dissolved in ethyl acetate showed antibacterial activity against tested Gram-positive bacterial pathogens with the MIC value ranged from 12.5 to 25.0 \(\upmu \)g/mL and 12.5 to 75.0 \(\upmu \)g/mL against Gram-negative bacterial pathogens. HBA also exhibited concentration-dependent cytotoxicity on Vero cell line. This is the first report on extraction and identification of crystalline HBA from marine Streptomyces sp. VITHM1, and it can be explored further to be used as an effective antibacterial agent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
John, W.B.; Brent, R.C.; Robert, A.K.; Murray, H.G.M.; Michele, R.P.: Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 32, 116–123 (2015)
Gordon, M.C.; David, J.N.: Natural products: a continuing source of novel drug leads. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1830, 3670–3695 (2013)
Hrudayanath, T.; Bikash, C.B.; Rashmi, R.M.; Sushil, K.D.: Biodiversity and biotechnological potential of microorganisms from mangrove ecosystems: a review. Ann. Microbiol. 63, 1–19 (2013)
Zhi, Q.X.; Jian, F.W.; Yu, Y.H.; Yong, W.: Recent advances in the discovery and development of marine microbial natural products. Mar. Drugs 11, 700–717 (2013)
Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munso, M.H.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R.: Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 28, 196–268 (2011)
Renu, S.; Monisha, K.; Rup, L.: Bioactive compounds from marine actinomycetes. Indian J. Microbiol. 48, 410–431 (2008)
Jannu, V.G.; Ethiraj, S.; Krishnan, K.: Extraction of quinone derivative from Streptomyces sp. VITVSK1 isolated from Cheyyur saltpan, Tamil Nadu, India. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 56, 361–367 (2013)
Esther, S.; Krishnan, K.: Isolation and identification of anti-ESBL (Extended Spectrum \(\beta \)-Lactamase) compound from marine Streptomyces sp. VITSJK8. J. Adv. Sci. Res. 5, 13–18 (2014)
Gaille, C.; Kast, P.; Haas, D.: Salicylate biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 21768–21775 (2002)
Solimabi, W.; Deepak, N.N.; Prabha, D.: Fermentation products of solvent tolerant marine bacterium Moraxella spp. MB1 and its biotechnological applications in salicylic acid bioconversion. PLoS ONE 8, e83647 (2013)
Devika, R.; Justin, K.: Quantitative analysis of bioactive compounds from T agetes erecta linn. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 8, 185–187 (2015)
Hussein, N.M.; Hussein, M.I.; Gadelhak, S.H.; Hammad, M.A.; Shaalan, H.S.: Efficacy of exogenous elicitors against Tuta absoluta on tomato. Nat. Sci. 12, 120–128 (2014)
Leila, Y.; Roya, F.T.; Fardin, G.: Effectiveness of CaCl\(_{2}\), peppermint oil and salicylic acid treatments on shelf life extension of fresh mint during cold storage. J. Food Process. Preserv. 39, 2639–2646 (2015)
Chandrashekhar, J.P.; Chandrakant, A.N.: The azo derivatives of salicylic acid. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 51, 248–256 (2015)
Adele, S.; Beatrice, T.; Ileana, D.P.; Laura, L.P.: An innovative approach to the topical treatment of acne. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 8, 179–185 (2015)
Andrew, P.D.; Keelan, C.L.: Antibacterial activity of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids against Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus aureus. Mar. Drugs 11, 4544–4557 (2013)
El-Gendy, M.M.A.; Hawas, U.W.; Jaspars, L.: Novel bioactive metabolites from a marine derived bacterium Nocardia sp. ALAA 2000. J. Antibiot. 61, 379–386 (2008)
Xu, L.Y.; Quan, X.S.; Sheng, W.C.; Zhou, G.X.; Lin, B.R.; Jiang, R.W.; Yao, X.S.: Antimycins A19 and A20, two new antimycins produced by marine actinomycete Streptomyces antibioticus H74–18. J. Antibiot. 64, 661–665 (2011)
Abdelfattah, M.S.: Isolation and crystal structure of a new anthraquinone derivative from actinomycete. Chem. Nat. Compd. 50, 613–616 (2014)
Guo, Y.-Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, Z.-X.; Mao, X.-M.; Tang, Y.; Chen, X.; Jiang, X.-H.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y.-Q.: Identification and biosynthetic characterization of natural aromatic azoxy products from Streptomyces chattanoogensis L10. Org. Letts. 17, 6114–6117 (2015)
Kavitha, A.; Prabhakar, P.; Vijayalakshmi, M.; Venkateswarlu, Y.: Purification and biological evaluation of the metabolites produced by Streptomyces sp. TK-VL_333. Res. Microbiol. 161, 335–345 (2010)
Taddei, A.; Rodriguez, M.J.; Vilchez, E.M.; Castelli, C.: Isolation and identification of Streptomyces spp. from Venezuelan soils: morphological and biochemical studies. Microbiol Res 161, 222–231 (2006)
Marmur, J.; Doty, P.: Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J. Mol. Biol. 5, 109–118 (1962)
Stach, J.E.M.; Maldonado, L.A.; Ward, A.C.; Goodfellow, M.: New primers for the class Actinobacteria: application to marine and terrestrial environments. Environ. Microbiol. 5, 828–841 (2003)
Saitou, N.; Nei, M.: The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24, 189–204 (1987)
Kumar, S.; Kannabiran, K.: Cytotoxicity and antioxidant activity of 5-(2,4-dimethylbenzyl)pyrrolidin-2-one extracted from marine Streptomyces VITSVK5 spp., Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 19, 81–86 (2012)
Ostash, B.; Makitrinskyy, R.; Walker, S.; Fedorenko, V.: Identification and characterization of Streptomyces ghanaensis ATCC14672 integration sites for three actinophage-based plasmids. Plasmid 61, 171–175 (2009)
Rainsford, K.D.: Aspirin and Related Drugs, p. 235. Taylor & Francis, London (2004)
Huang, P.; Xie, F.; Ren, B.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Abdel-Mageed, W.M.; Liu, M.; Han, J.; Oyeleye, A.; Shen, J.; Song, F.; Dai, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.: Anti-MRSA and anti-TB metabolites from marine-derived Verrucosispora sp. MS100047. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 100, 7437–7447 (2016)
Leon, I.K.; Yeaman, M.R.; Nast, C.C.; Kupferwasser, D.; Xiong, Y.; Palma, M.; Cheung, A.L.; Bayer, A.S.: Salicylic acid attenuates virulence in endovascular infections by targeting global regulatory pathways in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Invest. 112, 222–233 (2003)
Djanan, V.; Hatice, M.K.: Inhibitory effects of salicylic acid on A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cell viability. Turk. J. Biol. 39, 1–5 (2015)
Vald’es, A.; Mellinas, A.C.; Ramos, M.; Burgos, N.; Jim’enez, A.; Garrig’os, M.C.: Use of herbs, spices and their bioactive compounds in active food packaging. RSC. Adv. 5, 40324–40335 (2015)
Ismail, I.A.; Abdel-Rahaman, R.S.; Abdel-Raheem, M.A.: Influence of some essential oils, chemical compounds and their mixtures against Ceroplastes rusci L. and Asterolcanium pustolans Cock on fig trees. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 8, 187–195 (2015)
Solecka, J.; Zajko, J.; Postek, M.; Rajnisz, A.: Biologically active secondary metabolites from actinomycetes. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 7, 373–390 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnan, K., Mani, A. Structural Elucidation and Identification of 2-Hydroxy Benzoic Acid: An Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Compound from Streptomyces sp. VITHM1 Isolated from Marine Sediment Sample of Alappuzha Beach, Kerala, India. Arab J Sci Eng 43, 3339–3348 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2953-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2953-9