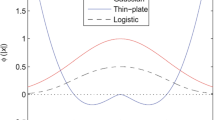
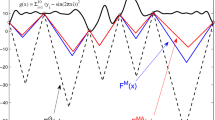
Abstract
Artificial neural networks in general and radial basis function in particular are known for high accuracies in function approximation, nonlinear system identification, and pattern classification problems; however, they pose numerous challenges with regards to the optimality of parameters involved. This paper proposes the use of a classical Nelder–Mead simplex method to optimize the parameters of activation function implicit in the design of radial basis function network. The key advantage of using Nelder–Mead simplex method lies in the fact that it provides a simple yet effective derivative-free approach for the numerical optimization of scalar variables such as spread and learning rate for Kernels of the radial basis function network. We thus present a novel hybrid algorithm in which weights of neurons are updated using gradient decent approach, while spread and learning rate is updated, viz. the Nelder–Mead simplex method. In results, the efficiency of proposed algorithm is statistically compared with the existing algorithms in different applications such as classification of digital signals in noise-limited wireless communication system, synthesis of microstrip patch antenna, and curve fitting problem. Lastly, we consider a two-variable function approximation problem to pedagogically express contrasting features of the hybrid algorithm, thereby pointing toward its potential usage in some engineering design problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khan, J.; Wei, J.S.; Ringner, M.; Saal, L.H.; Ladanyi, M.; Westermann, F.; Meltzer, P.S.: Classification and diagnostic prediction of cancers using gene expression profiling and artificial neural networks. Nat. Med. 7(6), 673–679 (2001)
Leung, H.; Lo, T.; Wang, S.: Prediction of noisy chaotic time series using an optimal radial basis function neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 12(5), 1163–1172 (2001)
Haykin, S.: Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation. Prentice Hall PTR, Upper Saddle River (1994)
Broomhead, D.S.; Lowe, D.: Multivariable functional interpolation and adaptive networks. Complex Syst. 2(3), 321–355 (1988)
Wettschereck, D.; Dietterich, T.: Improving the performance of radial basis function networks by learning center locations. In: NIPS, vol. 4, pp. 1133–1140 (1991)
Karayiannis, N.B.; Randolph-Gips, M.M.: On the construction and training of reformulated radial basis function neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 14(4), 835–846 (2003)
Park, J.; Sandberg, I.W.: Universal approximation using radial-basis-function networks. Neural Comput. 3(2), 246–257 (1991)
Yu, H.; Xie, T.; Paszczynski, S.; Wilamowski, B.M.: Advantages of radial basis function networks for dynamic system design. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 58(12), 5438–5450 (2011)
Wild, S.M.; Regis, R.G.; Shoemaker, C.A.: ORBIT: optimization by radial basis function interpolation in trust-regions. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 30(6), 3197–3219 (2008)
Nelder, J.A.; Mead, R.: A simplex method for function minimization. Comput. J. 7(4), 308 (1965)
Runarsson, T.P.; Yao, X.: Search biases in constrained evolutionary optimization. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 35, 233–243 (2005)
Fan, S.K.; Zahara, E.: A hybrid simplex search and particle swarm optimization for unconstrained optimization. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 181, 527–548 (2007)
Gao, F.; Han, L.: Implementing the Nelder–Mead simplex algorithm with adaptive parameters. Comput. Optim. Appl. 51(1), 259–277 (2012)
Rios, L.M.; Sahinidis, N.V.: Derivative-free optimization: a review of algorithms and comparison of software implementations. J. Glob. Optim. 56(3), 1247–1293 (2013)
Reiner, P.; Wilamowski, B. M.: Nelder–Mead enhanced extreme learning machine. In: 17th IEEE Intelligent Engineering Systems Conference, Costa Rica, pp. 225-230 (2013)
Reiner, P.; Wilamowski, B.M.: Efficient incremental construction of RBF networks using quasi-gradient method. Neurocomputing 150, 349–356 (2015)
Wu, X.; Wilamowski, B.M.: A greedy incremental algorithm for universal approximation with RBF networks. In: Advances in Soft Computing, Intelligent Robotics and Control, pp. 145-157. Springer, Berlin (2014)
Akhtar, M.T.; Abe, M.; Kawamata, M.: A new variable step size LMS algorithm-based method for improved online secondary path modeling in active noise control systems. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 14(2), 720–726 (2006)
Ali, S.S.A.; Moinuddin, M.; Raza, K.; Adil, S.H.: An adaptive learning rate for RBFNN using time-domain feedback analysis. Sci. World J. 2014, 850189. doi:10.1155/2014/850189 (2014)
Spendley, W.; Hext, G.R.; Himsworth, F.R.: Sequential application of simplex designs in optimisation and evolutionary operation. Technometrics 4(4), 441–461 (1962)
Baudin, M.: Nelder–Mead user’s manual. Consortium Scilab - Digiteo (2010)
Wright, M.H.: Nelder, Mead, and the other simplex method. Doc. Math. 7, 271–276 (2010)
Zahara, E.; Kao, Y.T.: Hybrid Nelder–Mead simplex search and particle swarm optimization for constrained engineering design problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 36(2), 3880–3886 (2009)
Huang, G.B.; Chen, L.: Enhanced random search based incremental extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 71(16–18), 3460–3468 (2008)
Kohonen, T.: Self-Organizing Maps, p. 30. Springer, Berlin (2001)
Kim, D.W.; Lee, K.; Lee, D.; Lee, K.H.: A kernel-based subtractive clustering method. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 26(7), 879–891 (2005)
Kolda, T.G.; Lewis, R.M.; Torczon, V.J.: Optimization by direct search: new perspectives on some classical and modern methods. SIAM Rev. 45, 385–482 (2003)
Su, W.; Xu, J.L.; Zhou, M.: Real-time modulation classification based on maximum likelihood. IEEE Commun. Lett. 12(11), 801–803 (2008)
Yang, Y.; Chang, J.N.; Liu, J.C.; Liu, C.H.: Maximum log-likelihood function-based QAM signal classification over fading channels. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 28(1), 77–94 (2004)
Yang, Y.; Soliman, S.S.: An improved moment-based algorithm for signal classification. Signal Process. 43(3), 231–244 (1995)
Wu, H.C.; Saquib, M.; Yun, Z.: Novel automatic modulation classification using cumulant features for communications via multipath channels. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 7(8), 3098–3105 (2008)
Aftab, W.; Moinuddin, M.; Shaikh, M.S.: A novel kernel for rbf based neural networks. In: Abstract and Applied Analysis (2014)
Türker, N.; Güneş, F.; Yildirim, T.: Artificial neural design of microstrip antennas. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 14(3), 445–453 (2007)
Hassan, A.K.; Affandi, A.: On Modelling and comparative study of LMS and RLS algorithms for synthesis of MSA. Modelling Simul. Eng. 2016, 9742483. doi:10.1155/2016/9742483 (2016)
Edwards, C.; Steer, M.B.: Foundations of Interconnect and Microstrip Design. Wiley. ISBN 0-471-60701-0 (2000)
Balanis, C.A.: Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design, 3rd edn. Wiley, Hoboken. ISBN 047166782X (2005)
Passino, K.M.: Biomimicry for Optimization, Control, and Automation. Springer, London (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, A.K., Moinuddin, M., Al-Saggaf, U.M. et al. On the Kernel Optimization of Radial Basis Function Using Nelder Mead Simplex. Arab J Sci Eng 43, 2805–2816 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2888-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2888-1