Abstract
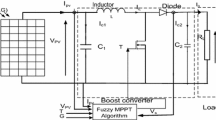
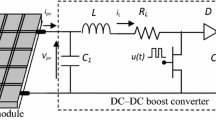
This paper proposes a new Takagi–Sugeno (T–S) fuzzy model-based maximum power tracking controller to draw the maximum power from a solar photovoltaic (PV) system. A DC–DC boost converter is used to control the output power from the PV panel. Based on the T–S fuzzy model, the fuzzy maximum power point tracking controller is designed by constructing fuzzy gain state feedback controller and an optimal reference model for the optimal PV output voltage, which corresponds actually to maximum power point (MPP). A comparative study with the two base-line controllers of perturb and observe, and the incremental conductance shows that the proposed controller offers fast dynamic response, much less oscillation around MPP, and superior performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cossutta, P.; Aguirre, M.P.; Cao, A.; Raffo, S.; Valla, M.I.: Single-stage fuel cell to grid interface with multilevel current-source inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 62(8), 5256–5264 (2015)
Singh, S.; Subhash, C.K.: Optimal sizing of grid integrated hybrid PV-biomass energy system using artificial bee colony algorithm. IET Renew. Power Gen. 10(5), 642–650 (2016)
Meghni, B.; Dib, D.; Azar, A.T.; Saadoun, A.: Effective supervisory controller to extend optimal energy management in hybrid wind turbine under energy and reliability constraints. Int. J. Dynam. Control 1–15 (2017). doi: 10.1007/s40435-016-0296-0
Rahim, A.H.M.A.; Khan, M.H.: A swarm-based adaptive neural network SMES control for a permanent magnet wind generator. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(11), 7957–7965 (2014)
Vincheh, M.R.; Kargar, A.; Markadeh, G.A.: A hybrid control method for maximum power point tracking (MPPT) in Photovoltaic systems. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(6), 4715–4725 (2014)
Azri, M.; Rahim, N.A.; Elias, M.F.M.: Transformerless DC/AC converter for grid-connected PV power generation system. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(11), 7945–7956 (2014)
Tipler, P.A.; Mosca, G.: Physics for Scientist and Engineers, 6th edn. W.H. Freeman, New York (2008)
Oladimeji, I.; Nor, Z. Y.; Nordin, S.: Matlab/Simulink model of solar PV array with perturb and observe MPPT for maximising PV array efficiency. In: Conference on Energy Conversion (CENCON). pp. 254–258 (2015)
Abdelsalam, A.K.; Massoud, A.M.; Ahmed, S.; Enjeti, P.N.: High performance adaptive perturb and observe MPPT technique for photovoltaic-based microgrids. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 26(4), 1010–1021 (2011)
Manoj, P.; Amruta, D.: Design and simulation of Perturb and Observe Maximum Power Point Tracking using MATLAB/Simulink. In: International Conference on Industrial Instrumentation and Control (ICIC). pp. 1345–1349 (2015)
Safari, A.; Mekhilef, S.: Simulation and hardware implementation of incremental conductance MPPT with direct control method using Cuk converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 58(4), 1154–1161 (2011)
Worku, M. Y.; Abido, M. A.: Real-time implementation of grid-connected PV system with decoupled P–Q controllers. In: Conference on Control and Automation (MED). pp. 841–846 (2014)
Kjaer, S.B.: Evaluation of the hill climbing and the incremental conductance maximum power point trackers for photovoltaic power systems. IEEE Trans. Energy Conver. 27(4), 922–929 (2012)
Mohammad, I.B.; Pouya, T.; Yousef, M.N.; Ali, K.K.; Paimaneh, S.: Modeling and simulation of hill climbing MPPT algorithm for photovoltaic application. In: Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion (SPEEDAM), Conference on. pp. 1041–1044 (2016)
Adel, A.E.; Hamdi, A.; Montaser, A.S.: Implementation of a modified perturb and observe maximum power point tracking algorithm for photovoltaic system using an embedded microcontroller. IET Renew. Power Gen. 10(4), 551–560 (2016)
Sera, D.; Mathe, L.; Kerekes, T.; Spataru, S.V.; Teodorescu, R.: On the perturb-and-observe and incremental conductance MPPT methods for PV systems. IEEE J. Photovolt. 3(3), 1070–1078 (2013)
Masoum, M.A.S.; Dehbonei, H.; Fuchs, E.F.: Theoretical and experimental analysis of photovoltaic systems with voltage and current-based maximum power-point tracking. IEEE Trans. Energy Conver. 17(4), 514–522 (2002)
Mellit, A.; Kalogirou, Sa: Artificial intelligence techniques for photovoltaic applications: a review. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 34(5), 574632 (2008)
Belkaid, A.; Colak, I; Kayisli, K.: Implementation of a modified P&O-MPPT algorithm adapted for varying solar radiation conditions. Electr. Eng. pp. 1–8 (2016)
Ishaque, K.; Salam, Z.; Amjad, M.; Mekhilef, S.: An improved particle swarm optimization (PSO) based MPPT for PV with reduced steady-state oscillation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 27(8), 3627–3638 (2012)
Zainuri, M.A.A.M.; Radzi, M.A.M.; Che Soh, A.; Abd Rahim, N.: Development of adaptive perturb and observe-fuzzy control maximum power point tracking for photovoltaic boost DC–DC converter. IET Renew. Power Gen. 8(2), 183–194 (2014)
Ahmed, A.; Ali, N.H.; Tshilidzi, M.: Perturb and observe based on fuzzy logic controller maximum power point tracking (MPPT). In: 2014 International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Application (ICRERA). pp. 406–411 (2014)
Radak, B.; Chitralekha, M.; Anup, K.G.: MPPT of solar photovoltaic cell using perturb & observe and fuzzy logic controller algorithm for buck-boost DC–DC converter. In: 2015 International Conference on Energy, Power and Environment, pp. 1–5 (2015)
Liu, C.-L.; Chen, J.-H.; Liu, Y.-H.; Yang, Z.-Z.: An asymmetrical fuzzy-Logic-control-based MPPT algorithm for photovoltaic systems. Energies 7(4), 2178–2193 (2014)
Vincheh, M.R.; Kargar, A.; Markadeh, G.A.: A hybrid control method for maximum power point tracking (MPPT) in photovoltaic systems. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(6), 4715–4725 (2014)
Abu-Rub, H.; Iqbal, A.; Moin Ahmed, S.; Peng, F.Z.; Li, Y.; Baoming, G.: Quasi-Z-source inverter-based photovoltaic generation system with maximum power tracking control using ANFIS. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 4(1), 11–20 (2013)
Afghoul, H.; Krim, F.; Chikouche, D.: Increase the photovoltaic conversion efficiency using neuro-fuzzy control applied to MPPT. In: Renewable and Sustainable Energy Conference (IRSEC). pp. 348–353 (2013)
Abido, M.A.; Khalid, M.S.; Worku, M.Y.: An efficient ANFIS-based PI controller for maximum power point tracking of PV systems. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 40(9), 2641–2651 (2015)
Dragan, M.; Srete, N.: ANFIS as a method for determinating MPPT in the photovoltaic system simulated in MATLAB/Simulink. In: Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics, pp. 1082–1086 (2015)
Elkhatib, K.; Abdel, A.: Design of maximum power fuzzy controller for PV systems based on the LMI-based stability. Intelligent Systems in Technical and Medical Diagnostics, Volume 230 of the series Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing. pp. 77–88 (2012)
Abid, H.; Toumi, A.; Chaabane, M.: MPPT algorithm for photovoltaic panel based on augmented TakagiSugeno fuzzy model. Hindawi Publishing Corporation ISRN Renewable Energy, Article ID 253146 (2014)
Abid, H.; Toumi, A.; Chaabane, M.: TS fuzzy algorithm for photovoltaic panel. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 17(2), 215–223 (2015)
Zhang, S.; Wang, T.; Li C., Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.: Maximum power point tracking control of solar power generation systems based on type-2 fuzzy logic. In: International World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Guilin, pp. 12–15 (2016)
Zayani, H.; Allouche, M.; Kharrat M.; Chaabane M.: Maximum power point tracking control of solar power generation systems based on type-2 fuzzy logic. In: International Conference on Sciences and Techniques of Automatic Control and Computer Engineering, Monastir, Tunisia, December, pp. 21–23 (2016)
Tanaka, K.; Wang, H.O.: Fuzzy Control Systems Design and Analysis: A Linear Matrix Inequality Approach. Wiley, New York (2001)
Gahinet, P.; Nemirovski, A.; Laub, A.J.; Chilali, M.: LMI Control Toolbox. MathWorks, Natick (1995)
Villalva, M.G.; Gazoli, J.R.; Filho, E.R.: Comprehensive approach to modelling and simulation of photovoltaic array. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 25(5), 1198–1208 (2009)
Ballouti, A.; Djahli, F.; Bendjadou, A.: MPPT system for photovoltaic module connected to battery adapted for unstable atmospheric conditions using VHDL-AMS. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 36(3), 2021–2031 (2014)
Ohtake, H.; Tanaka, K.; Wang, H.: Fuzzy modeling via sector nonlinearity concept. Integr. Comput. Aided Eng. 10(4), 333–341 (2003)
Lian, K.Y.; Liou, J.: Output tracking control for fuzzy systems via output feedback design. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Sys. 14(5), 381–392 (2006)
Ounnas, D.; Ramdani, M.; Chenikher, S.; Bouktir, T.: Optimal reference model based fuzzy tracking control for wind energy conversion system. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 6(3), 1129–1136 (2016)
Bayod-Rjula, -A.; Cebollero-Abin, J.-A.: A novel MPPT method for PV systems with irradiance measurement. Sol. Energy 109, 95–104 (2014)
Atiqah, H.b M.N.; Ahmad, M.b O.; Hedzlin, b Z.: Modeling and simulation of grid inverter in grid-connected photovoltaic system. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 4(4), 949–957 (2014)
Ounnas, D.; Ramdani, M.; Chenikher, S.; Bouktir, T.: A combined methodology of \(H_\infty \) fuzzy tracking control and virtual reference model for a PMSM. Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. 13(3), 212–222 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ounnas, D., Ramdani, M., Chenikher, S. et al. An Efficient Maximum Power Point Tracking Controller for Photovoltaic Systems Using Takagi–Sugeno Fuzzy Models. Arab J Sci Eng 42, 4971–4982 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2532-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2532-0