Abstract
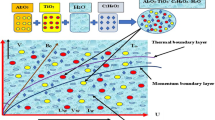
In this paper, we have studied the problem of two-dimensional transient convective flow and heat transfer in nanofluids in a quarter-circular-shaped enclosure using newly proposed nonhomogeneous dynamic mathematical model. The round wall of the enclosure is maintained at constant low temperature and the variable thermal condition on the bottom heated wall is considered, whereas the vertical wall is regarded as adiabatic. The enclosure is permeated by an inclined uniform magnetic field. The Galerkin weighted residual finite element method has been employed to solve the governing nondimensional partial differential equations. The result shows that 1- to 10-nm-sized nanoparticles are uniform and stable in the solution. The external magnetic field and its direction control the flow pattern of nanofluid significantly. The average Nusselt number increases significantly, as nanoparticle volume fraction, magnetic field inclination angle and Rayleigh number increase. Average Nusselt number of cobalt–kerosene nanofluid is much higher than other 17 types of nanofluids which are studied in the present analysis. The flow behaviors and the heat transfer rates of 18 types of nanofluids have been presented for the scientific and engineering community to become familiar with such nanofluids and apply them in practical applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B :
-
Applied magnetic field (Nm\(^{-1}\) A\(^{-1}\))
- C :
-
Concentration of nanofluid \((\hbox {mol}\,\hbox {m}^{-3})\)
- \(C_\mathrm{C}\) :
-
Reference concentration \(\hbox {(mol m}^{3})\)
- \(c_\mathrm{p}\) :
-
Specific heat \(\hbox {(J}\,\hbox {kg}^{-1} \hbox {K}^{-1})\)
- \(D_\mathrm{B}\) :
-
Brownian diffusion coefficient \( \hbox {(m}^{2}\,\hbox {s}^{-1})\)
- \(d_\mathrm{p}\) :
-
Diameter of nanoparticle \((\hbox {nm)}\)
- \(D_\mathrm{T}\) :
-
Thermal diffusion coefficient \(\hbox {(m}^{2}\,\hbox {s}^{-1})\)
- g :
-
Acceleration due to gravity \((\hbox {m}\,\hbox {s}^{-2})\)
- h :
-
Heat transfer coefficient of nanofluid \(\hbox {(W}\,\hbox {m}^{-2}\,\hbox {K}^{-1})\)
- \(k_\mathrm{B}\) :
-
Boltzmann constant \(\hbox {(J}\,\hbox {K}^{-1})\)
- L :
-
Length of the bottom wall \(\hbox {(m)}\)
- Le :
-
Lewis number
- m :
-
Mass \(\hbox {(kg)}\)
- n :
-
Empirical nanoparticle shape factor
- \(N_\mathrm{TBTC} \) :
-
Dynamic diffusion parameter
- \(N_\mathrm{TBT}\) :
-
Dynamic thermo-diffusion parameter
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- p :
-
Dimensional modified pressure \(\hbox {(Pa)}\)
- P :
-
Dimensionless modified pressure
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- \(Ra_\mathrm{T} \) :
-
Thermal Rayleigh number
- \(Ra_\mathrm{C}\) :
-
Solutal Rayleigh number
- Sc :
-
Schmidt number
- Ha :
-
Hartmann number
- Sr :
-
Shear rate \(\hbox {(s}^{-1})\)
- t :
-
Dimensional time \(\hbox {(s)}\)
- T :
-
Nanofluid temperature \(\hbox {(K)}\)
- \(T_\mathrm{C} \) :
-
Reference temperature \(\hbox {(K)}\)
- U, V :
-
Dimensionless nanofluid velocity
- (u, v):
-
Dimensional nanofluid velocity \(\hbox {(m}\,\hbox {s}^{-1})\)
- \(V_\mathrm{T}\) :
-
Thermophoretic velocity \(\hbox {(m}\,\hbox {s}^{-1})\)
- X, Y :
-
Dimensionless coordinates
- \(\alpha \) :
-
Thermal diffusivity \(\hbox {(m}^2\,\hbox {s}^{-1})\)
- \(\beta \) :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient \(\hbox {(K}^{-1}) \quad \)
- \(\Omega \) :
-
Angle between hot and cold walls (radian)
- \(\beta ^{*}\) :
-
Mass expansion coefficient \(\hbox {(mol)}^{-1}\)
- \(\gamma \) :
-
Magnetic field inclination angle
- \(\phi \) :
-
Nanoparticles volume fraction
- \(\Phi \) :
-
Dimensionless concentration
- \(\Psi \) :
-
Sphericity of the nanoparticle
- \(\psi \) :
-
Stream function
- \(\mu \) :
-
Viscosity \(\hbox {(kg}\,\hbox {m}^{-1}\,\hbox {s}^{-1})\)
- \(\nu \) :
-
Kinematic viscosity \(\hbox {(m}^2\,\hbox {s}^{-1})\)
- \(\kappa \) :
-
Thermal conductivity \(\hbox {(W}\,\hbox {m}^{-1}\,\hbox {K}^{-1})\)
- \(\sigma \) :
-
Electric conductivity \((\hbox {S}\,\hbox {m}^{-1})\)
- \(\Delta C\) :
-
Film concentration drop \(\hbox {(mol}\,\hbox {m}^{-3})\)
- \(\Delta T\) :
-
Film temperature drop \(\hbox {(K)}\)
- \(\theta \) :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- \(\theta _\mathrm{C} \) :
-
Dimensionless temperature at cold wall
- \(\theta _\mathrm{h} \) :
-
Dimensionless temperature at hot wall
- \(\rho \) :
-
Density \(\hbox {(kg}\,\hbox {m}^{-3})\)
-
 :
: -
Correction factor
- \(\xi \) :
-
Dimensionless time
- bf:
-
Base fluid
- p:
-
Nanoparticles
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- ave:
-
Average
References
Omri, A.; Orfi, J.; Nasallah, S.B.: Natural convection effects in solar stills. Desalination 183, 173–178 (2005)
Tzeng, S.C.; Liou, J.H.; Jou, R.Y.: Numerical simulation-aided parametric analysis of natural convection in a roof of triangular enclosures. Heat Transf. Eng. 26, 69–79 (2005)
Choi, S.U.S.: Nanofluids: from vision to reality through research. J. Heat Transf. 131, 1–9 (2009)
Rahman, M.M.; Al-Rashdi, M.H.; Pop, I.: Convective boundary layer flow and heat transfer in a nanofluid in the presence of second order slip, constant heat flux and zero nanoparticles flux. Nucl. Eng. Des. 297, 95–103 (2016)
Eastman, J.A.; Choi, S.U.S.; Li, S.; Yu, W.; Thompson, L.J.: Anomalously increased effective thermal conductivities of ethylene glycol based nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78(6), 718–720 (2001)
Das, S.K.; Putra, N.; Thiesen, P.; Roetzel, W.: Temperature dependence of thermal conductivity enhancement for nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 125(4), 567–574 (2003)
Xuan, Y.; Li, Q.: Investigation on convective heat transfer and flow features of nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 125(1), 151–155 (2003)
Wen, D.; Ding, Y.: Experimental investigation into convective heat transfer of nanofluids at the entrance region under laminar flow conditions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 47(24), 5181–5188 (2004)
Uddin, M.J.; Al Kalbani, K.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Alam, M.S.; Al-Salti, N.; Eltayeb, I.A.: Fundamentals of nanofluids: evolution, applications and new theory. Int. J. Biomath. Syst. Biol. 2(1), 1–32 (2016)
Xuan, Y.; Roetzel, W.: Conceptions for heat transfer correlation of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 43(19), 3701–3707 (2000)
Buongiorno, J.: Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 128(3), 240–250 (2006)
Rahman, M.M.; Rosca, A.V.; Pop, I.: Boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a permeable exponentially shrinking surface with convective boundary condition using Buongiorno’s model. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 25(2), 299–319 (2015)
Sheremet, M.A.; Pop, I.: Mixed convection in a lid- driven square cavity filled by a nanofluid: Buongiorno’s mathematical model. Appl. Math. Comput. 266, 792–808 (2015)
Rahman, M.M.; Grosan, T.; Pop, I.: Oblique stagnation-point flow of a nanofluid past a shrinking sheet. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 26(1), 189–213 (2016)
Rahman, M.M.; Alam, M.S.; Al-Salti, N.; Eltayeb, I.A.: Hydromagnetic natural convective heat transfer flow in an isosceles triangular cavity filled with nanofluid using two-component nonhomogeneous model. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 107, 272–288 (2016)
Ouyahia, S.; Benkahla, Y.K.; Labsi, N.: Numerical study of the hydrodynamic and thermal proprieties of titanium dioxide nanofluids trapped in a triangular geometry. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 41, 1995–2009 (2016)
Khanafer, K.; Vafai, K.; Lightstone, M.: Buoyancy driven heat transfer enhancement in a two-dimensional enclosure utilizing nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 46(19), 3639–3653 (2003)
Jou, R.; Tzeng, S.: Numerical research of nature convective heat transfer enhancement filled with nanofluids in rectangular enclosures. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 33(6), 727–736 (2006)
Tiwari, R.K.; Das, M.K.: Heat transfer augmentation in a two-sided lid-driven differentially heated square cavity utilizing nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50(9–10), 2002–2018 (2007)
Rahman, M.M.; Mojumder, S.; Saha, S.; Mekhilef, S.; Saidur, R.: Effect of solid volume fraction and tilt angle in a quarter circular solar thermal collectors filled with CNT-water nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 57, 79–90 (2014)
Sheikholeslami, M.; Gorji-Bandpy, M.; Ganji, D.D.; Soleimani, S.: Effect of a magnetic field on natural convection in an inclined half-annulus enclosure filled with Cu-water nanofluid using CVFEM. Adv. Powder Technol. 24, 980–991 (2013)
Maxwell, J.A.: A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism, vol. I–II. Clarendon Press, Oxford (1873)
Hamilton, R.L.; Crosser, Ok: Thermal conductivity of heterogeneous two component systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1(3), 187–191 (1962)
Timofeeva, E.V.; Routbort, J.L.; Singh, D.: Particle shape effects on thermophysical properties of alumina nanofluids. J. Appl. Phys. 106(1), 1–10 (2009)
Xuan, Y.; Li, Q.; Hu, W.: Aggregation structure and thermal conductivity of nanofluids. AIChE J. 49(4), 1038–1043 (2003)
Shiundu, P.M.; Williams, P.S.; Giddings, J.C.: Magnitude and direction of thermal diffusion of colloidal particles measured by thermal field-flow fractionation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 266(2), 366–376 (2003)
Iacopini, S.; Rusconi, R.; Piazza, R.: The macromolecular tourist: universal temperature dependence of thermal diffusion in aqueous colloidal suspensions. Eur. Phys. J. E 19(1), 59–67 (2006)
Mutuku, W.N.: Analysis of hydromagnetic boundary layer flow and heat transfer of nanofluids. Ph.D. Thesis, Cape Cape Peninsula University of Technology, South Africa (2014)
Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Taylor, R.L.; Nithiarasu, P.: The Finite Element Method for Fluid Dynamics, 6th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2005)
Codina, R.: Comparison of some finite element methods for solving the diffusion-convection-reaction equation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 156(1–4), 185–210 (1998)
Rahman, M.M.; Alim, M.A.; Mamun, M.A.H.: Finite element analysis of mixed convection in a rectangular cavity with a heat-conducting horizontal circular cylinder. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control 14(2), 217–247 (2009)
Rahman, M.M.; Parvin, S.; Saidur, R.; Rahim, N.A.: Magnetohydrodynamic mixed convection in a horizontal channel with an open cavity. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 38, 184–193 (2011)
Uddin, M.B.: Magnetic field effect on double-diffusive mixed convection in a lid driven trapezoidal enclosure for unsteady flow. Dhaka, BUET, M. Phil. Thesis (2015)
Del Campo, E.M.; Sen, M.; Ramos, E.: Analysis of laminar natural convection in triangular enclosure. Numer. Heat Transf. 13(3), 353–372 (1988)
Ghasemi, B.; Aminossadati, S.M.; Raisi, A.: Magnetic field effect on natural convection in a nanofluid-filled square enclosure. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 50, 1748–1756 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. S. Alam: On leave from the Department of Mathematics, Jagannath University, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uddin, M.J., Alam, M.S. & Rahman, M.M. Natural Convective Heat Transfer Flow of Nanofluids Inside a Quarter-Circular Enclosure Using Nonhomogeneous Dynamic Model. Arab J Sci Eng 42, 1883–1901 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2330-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2330-0



 :
: