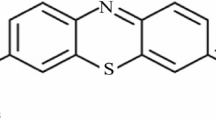
Abstract
Cottonseed cake as a domestic feed and a by-product of textile industry was utilized as a novel adsorbent for the decolorization of Yellow F3R (YF3R), Di Maria Brilliant Blue R (DBBR) and Reactive Brilliant Red M-3BE (Red F3B) aqueous solutions based on a rapid and efficient process of ultrasound-assisted adsorption. This study aimed to model the effects of the five factors on decolorization efficiency by response surface methodology: temperature, initial pH, reaction time, concentrations of initial dyestuff and adsorbent. A Box–Behnken design with five factors at three levels was used to set the experimental schedule. The maximum decolorization efficiency was obtained consistently at the lowest initial pH (2), the highest reaction time (30 min) and adsorbent concentration (1.5 g/L). Analysis of variance and the best-fit multiple nonlinear regression models were cross-validated (R 2 pred) accounting for 90.03–93.94 % of variation in decolorization efficiency. The decolorization of YF3R, DBBR and Red F3B on cottonseed cake fitted well pseudo-second-order kinetic mechanism and Langmuir isotherm and it was found to be of endothermic and spontaneous nature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sayan E., Edecan M.E.: An optimization study using response surface methods on the decolorization of reactive blue 19 from aqueous solution by ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem 15, 530–538 (2008)
Tanyildizi M.S.: Modeling of adsorption isotherms and kinetics of reactive dye from aqueous solution by peanut hull. Chem. Eng. J. 168, 1234–1240 (2011)
Sayan E.: Optimization and modelling of decolorization and COD reduction of reactive dye solutions by ultrasound-assisted adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 119, 175–181 (2006)
Dincer A.R., Gunes Y., Karakaya N., Gunes E.: Coal-based bottom ash (CBBA) waste material as adsorbent for removal of textile dyestuffs from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 141, 529–535 (2007)
Yang S.S., Guo W.Q., Zhou X.J., Meng Z.H., Liu B., Ren N.Q.: Optimization of operating parameters for sludge process reduction under alternating aerobic/oxygen-limited conditions by response surface methodology. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 9843–9851 (2011)
Song S., Fan J., He Z., Zhan L., Liu Z., Chen J., Xu X.: Electrochemical degradation of azo dye C.I. Reactive Red 195 by anionic oxidation on Ti/SnO2−Sb/PbO2 electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 55, 3606–3613 (2010)
Sahinkaya S.: COD and color removal from synthetic textile wastewater by ultrasound assisted electro-Fenton oxidation process. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 19, 601–605 (2013)
Onat A.T., Gumusdere T.H., Guvenc A., Donmez G., Mehmetoglu U.: Decolorization of textile azo dyes by ultrasonication and microbial removal. Desalination 255, 154–158 (2010)
Hamdaoui O., Chiha M., Naffrechoux E.: Ultrasound-assisted removal of malachite green from aqueous solution by dead pine needles. Ultrason. Sonochem. 15, 799–807 (2008)
Gulnaz O., Kaya A., Dincer S.: The reuse of dried activated sludge for adsorption of reactive dye. J. Hazard. Mater B134, 190–196 (2006)
Ozer A., Akkaya E.: Methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solution by dehydrated peanut hull. J. Hazard. Mater. 144, 171–179 (2007)
Zhou X.J., Guo W.Q., Yang S.S., Ren N.Q.: A rapid and low energy consumption method to decolorize the high concentration triphenylmethane dye wastewater: operational parameters optimization for the ultrasonic-assisted ozone oxidation process. Bioresour. Technol. 105, 40–47 (2012)
Zhou X.J., Guo W.Q., Yang S.S., Zheng H.S., Ren N.Q.: Ultrasonic-assisted ozone oxidation process of triphenylmethane dye degradation: evidence for the promotion effects of ultrasonic on malachite green decolorization and degradation mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 128, 827–830 (2013)
Robinson T., McMullan G., Marchant R., Nigam P.: Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour. Technol. 77, 247–255 (2001)
Voncina B.D., Majcen-Le-Marechal A.: Reactive dye decolorization using combined ultrasound/H 2 O 2. Dyes Pigm. 59, 173–179 (2004)
Demirbas E., Kobya M., Sulak M.T.: Adsorption kinetics of a basic dye from aqueous solutions onto apricot stone activated carbon. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 5368–5673 (2008)
Li Y., Hsieh W.P., Mahmudov R., Wei X., Huang C.P.: Combined ultrasound and Fenton (US-Fenton) process for the treatment of ammunition wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 244–245, 403–411 (2013)
Behnajady M.A., Modirshahla N., Shokri M., Vahid B.: Effect of operational parameters on degradation of malachite green by ultrasonic irradiation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 15, 1009–1014 (2008)
Korkut O., Sayan E., Lacin O., Bayrak B.: Investigation of adsorption and ultrasound assisted desorption of lead (II) and copper (II) on local bentonite: a modelling study. Desalination 259, 243–248 (2010)
Guo W.Q., Ding J., Cao G.L., Ren N.Q., Cui F.Y.: Treatability study of using low frequency ultrasonic pretreatment to augment continuous biohydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 36, 14180–14185 (2011)
Lacin O., Bayrak B., Korkut O., Sayan E.: Modeling of adsorption and ultrasonic desorption of cadmium (II) and zinc (II) on local bentonite. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 292, 330–335 (2005)
Hosmer D.W., Lemeshow S.: Appilied Logistic Regression, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken (2000)
Frank I.E., Friedman J.H.: A statistical view of some chemometrics regression tools. Technometrics 35, 109–135 (1993)
McCullagh P., Nelder J.A.: Generalized Linear Model. Chapman and Hall, London (1992)
Dursun A.Y., Tepe O.: Removal of Chemazol Reactive Red 195 from aqueous solution by dehydrated beet pulp carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 194, 303–311 (2011)
Zhang H., Duan L., Zhang X.: Decolorization of methyl orange by ozonation in combination with ultrasonic irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. B138, 53–59 (2006)
Chiou M.S., Li H.Y.: Equilibrium and kinetic modeling of adsorption of reactive dye on cross-linked chitosan beads. J. Hazard. Mater. 93, 233–248 (2002)
Dutta S.: Optimization of Reactive Black 5 removal by adsorption process using Box-Behnken design. Desalination Water Treat. 51, 40–42 (2013)
Jumasiah A., Chuah T.G., Gimbon J., Choong T.S.Y., Azni I.: Adsorption of basic dye onto palm kernel shell activated carbon: sorption equilibrium and kinetics studies. Desalination 186, 57–64 (2005)
Al-Ghouti M., Khraisheh M.A.M., Ahmad M.N.M., Allen S.: Thermodynamic behaviour and the effect of temperature on the removal of dyes from aqueous solution using modified diatomite: a kinetic study. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 287, 6–13 (2005)
Ozacar M., Sengil I.A.: Adsorption of reactive dyes on calcined alunite from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. B98, 211–224 (2003)
Gong R.M., Ding Y., Lie M., Yang C., Liu H.J., Sun Y.Z.: Utilization of powdered peanut hull as biosorbent for removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solution. Dyes Pigm. 64, 187–192 (2005)
Arami M., Limaee N.Y., Mahmoodi N.M., Tabrizi N.S.: Equilibrium and kinetics studies for the adsorption of direct and acid dyes from aqueous solution by sol meal hull. J. Hazard. Mater. 135, 171–179 (2006)
Hashemian S., Misrhamsi M.: Kinetic and thermodynamic of adsorption of 2-picoline by sawdust from aqueous solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem 18, 2010–2015 (2012)
Hanafiah M.A.K.M., Ngah W.S.W., Zolkafly S.H., Teong J.C., Majid Z.A.A.: Acid Blue 25 adsorption on base treated Shorea dasyphylla sawdust: Kinetic, isotherm, thermodynamic and spectroscopic analysis. J. Environ. Sci. 24(2), 261–268 (2012)
Mittal A.: Adsorption kinetics of removal of a toxic dye, Malachite Green, from wastewater by using hen feathers. J. Hazard. Mater. 133, 196–202 (2006)
Wu C.H., Yu C.H.: Effects of TiO2 dosage, pH and temperature on decolorization of C.I. Reactive Red 2 in a UV/US/TiO2 system. J. Hazard. Mater. 169, 1179–1183 (2009)
Cicek F., Ozer D., Ozer A., Ozer A.: Low cost removal of reactive dyes using wheat bran. J. Hazard. Mater. 146, 408–416 (2007)
Ozer A., Dursun G.: Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by dehydrated wheat bran carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 146, 262–269 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
The Below is the Electronic Supplementary Material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buyukada, M. Removal of Yellow F3R, Di Maria Brilliant Blue R and Reactive Brilliant Red M-3BE from Aqueous Solutions by a Rapid and Efficient Ultrasound-Assisted Process with a Novel Biosorbent of Cottonseed Cake: Statistical Modeling, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies. Arab J Sci Eng 40, 2153–2168 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1751-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1751-5