Abstract
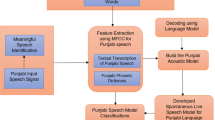
This paper presents the development of Holy Quran recitation recognizer. The decoder of recognizer performs sub-word level recognition at phoneme. The paper demonstrates high recognition accuracies achieved by applying incremental refinements to the HMM models of the phonemes during the training stage. The Maximum- likelihood (ML) criterion is first applied for HMMs parameter estimation, which produces average recognition accuracies of up to 83 %. This is followed by discriminative technique of minimum phone error (MPE), which is applied to minimize recognition error at phoneme level. Investigation shows that MPE based acoustic models improve generalization. The results show 3–4 % improvement in recognition accuracies, which are promising when compared with the case of ML approach applied alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang X., Acero A., Hon H.-W.: Spoken Language Processing, vol. 18. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (2001)
Lee K.-F., Hon H.-W.: Speaker-independent phone recognition using hidden Markov models. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 37, 1641–1648 (1989)
AbuZeina D., Al-Khatib W., Elshafei M., Al-Muhtaseb H.: Cross-word Arabic pronunciation variation modeling for speech recognition. Int. J. Speech Technol. 14, 227–236 (2011)
He X., Deng L.: Discriminative learning for speech recognition: theory and practice. Synth. Lect. Speech Audio Process. 4, 1–112 (2008)
Selouani S.A., Boudraa M.: Algerian Arabic speech database (ALGASD): corpus design and automatic speech recognition application. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 35, 158 (2010)
Kirchhoff, K.; Bilmes, J.; Das, S.; Duta, N.; Egan, M.; Ji, G.; He, F.; Henderson, J.; Liu, D.; Noamany, M.: Novel approaches to Arabic speech recognition: report from the 2002 Johns-Hopkins Summer Workshop. In: 2003 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 2003. Proceedings (ICASSP’03), vol. 1, pp. I-344–I-347 (2003)
Tabbal, H.; El Falou, W.; Monla, B.: Analysis and Implementation of a “Quranic” verses Delimitation System in Audio Files Using Speech Recognition Techniques. In: Information and Communication Technologies, 2006. ICTTA’06. 2nd, pp. 2979–2984 (2006)
Abdou, S.M.; Hamid, S.E.; Rashwan, M.; Samir, A.; Abdel-Hamid, O.; Shahin, M.; Nazih, W.: Computer Aided Pronunciation Learning System Using Speech Recognition Techniques. In: INTERSPEECH (2006)
Elhadj, Y.O.M.; Alghamdi, M.; Alkanhal, M.: Phoneme-based recognizer to assist reading the Holy Quran. In: Thampi, S.M., et al. (eds.) Recent Advances in Intelligent Informatics. Springer, Switzerland, pp. 141–152 (2014). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-01778-5_15
Sara S.I.: Ibn Sina: A Treatise on Arabic Phonetics. LINCOM publishers, Munich (2009)
Alghamdi M.M., Ajami Alotaibi Y.: HMM automatic speech recognition system of Arabic alphadigits. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 35, 137 (2010)
Alotaibi Y.A., Muhammad G.: Study on pharyngeal and uvular consonants in foreign accented Arabic for ASR. Comput. Speech Lang. 24, 219–231 (2010)
Newman D.: The phonetic status of Arabic within the world’s languages: the uniqueness of the lughat al-daad. Antwerp Pap. Linguist. 100, 65–75 (2002)
Alkhouli, M.: “Alaswaat Alaghawaiyah,” Daar Alfalah, Jordan (1990)
El-Imam Y.A.: An unrestricted vocabulary Arabic speech synthesis system. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 37, 1829–1845 (1989)
Ahmed, M.E.: Toward an Arabic text-to-speech system. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 16, 565–583 (1991)
Hamid, S.: Computer aided pronunciation learning system using statistical based automatic speech recognition. Ph.D, Electronics and Communication Engineering, Cairo University (2005)
al-Hashmi, S.A.: The Phonology of Nasal n in the language of Holy Quran. Thesis of Masters of Art, Department of Linguistics, University of Victoria (2004)
Harrag A., Mohamadi T.: QSDAS: new quranic speech database for arabic speaker recognition. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 35, 7 (2010)
Jelinek F.: Statistical Methods for Speech Recognition. MIT Press, Cambridge (1997)
Rabiner L.R., Schafer R.W.: Digital Processing of Speech Signals, vol. 100. Prentice-hall, Englewood Cliffs (1978)
Gold B., Morgan N., Ellis D.: Speech and Audio Signal Processing: Processing and Perception of Speech and Music. Wiley, Hoboken (2011)
Davis S., Mermelstein P.: Of parametric representations for monosyllabic word recognition in continuously spoken sentences. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 28, 357–366 (1980)
Alsulaiman, M.; Muhammad, G.; Ali, Z.: Comparison of voice features for Arabic speech recognition. In: 2011 Sixth International Conference on Digital Information Management (ICDIM), pp. 90–95 (2011)
Ahmed N., Natarajan T., Rao K.R.: Discrete cosine transform. Comput. IEEE Trans. 100, 90–93 (1974)
Furui S.: Speaker-independent isolated word recognition using dynamic features of speech spectrum. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 34, 52–59 (1986)
Fujimura O.: Syllable as a unit of speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 23, 82–87 (1975)
Schwartz, R.; Chow, Y.; Kimball, O.; Roucos, S.; Krasner, M.; Makhoul, J.: Context-dependent modeling for acoustic–phonetic recognition of continuous speech. In: Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, IEEE International Conference on ICASSP’85, pp. 1205–1208 (1985)
Rabiner L., Juang B.H., Levinson S., Sondhi M.: Recognition of isolated digits using hidden Markov models with continuous mixture densities. AT&T Tech. J. 64, 1211–1234 (1985)
Rabiner L.: A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proc. IEEE 77, 257–286 (1989)
Rabiner L., Juang B.-H.: An introduction to hidden Markov models. IEEE ASSP Mag. 3, 4–16 (1986)
Baum, L.E.; Petrie, T.; Soules, G.; Weiss, N.: A maximization technique occurring in the statistical analysis of probabilistic functions of Markov chains. Ann. Math. Stat. 41(1), 164–171 (1970)
Rabiner LR, Juang B.-H.: Fundamentals of speech recognition, vol. 14. PTR Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1993)
Chow, Y.-L.; Schwartz, R.: “The n-best algorithm: An efficient procedure for finding top n sentence hypotheses.” In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Speech and Natural Language, pp. 199–202 (1989)
Young, S.J.; Russell, N.; Thornton, J.: Token passing: a simple conceptual model for connected speech recognition systems: Citeseer (1989)
Nadas A.: A decision theoretic formulation of a training problem in speech recognition and a comparison of training by unconditional versus conditional maximum likelihood. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 31, 814–817 (1983)
Bahl, L.B.; de Souza, P.; Mercer, R.P: Maximum mutual information estimation of hidden Markov model parameters for speech recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, ICASSP ’86, vol. 11, pp. 49–52 (1986)
Juang B.-H., Katagiri S.: Discriminative learning for minimum error classification [rpattern recognition]. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 40, 3043–3054 (1992)
Robinson A.J.: An application of recurrent nets to phone probability estimation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 5, 298–305 (1994)
Povey, D.; Woodland, P.C.: Minimum phone error and I-smoothing for improved discriminative training. In: 2002 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. I-105–I-108 (2002)
Bahl, L.; Brown, P.; de Souza, P.V.; Mercer, R.: Maximum mutual information estimation of hidden Markov model parameters for speech recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, ICASSP’86, pp. 49–52 (1986)
Woodland P.C., Povey D.: Large scale discriminative training of hidden Markov models for speech recognition. Comput. Speech Lang. 16, 25–47 (2002)
Steve, Y.; Gunnar, E.; MARK, A.; Thomas, H.; Dan, K.; Xunying, A.L.; Gareth, M.; Julian, O.; Dave, O.; Dan, P.: The HTK book (for HTK Version 3.4) (2009)
Povey D.: Discriminative Training for Large Vocabulary Speech Recognition. University of Cambridge, Cambridge (2003)
Nahamoo, D.: An inequality for rational functions with applications to some statistical estimation problems (1991)
The Holy Quran
Elhadj, Y.O.M.; Alghamdi, M.; Alkanhal, M.: Approach for Recognizing Allophonic Sounds of the Classical Arabic Based on Quran Recitations. In: Theory and Practice of Natural Computing. Springer, pp. 57–67 (2013)
Xiao X., Li J., Chng E.S., Li H., Lee C.-H.: A study on the generalization capability of acoustic models for robust speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 18, 1158–1169 (2010)
Li J., Yuan M., Lee C.-H.: Approximate test risk bound minimization through soft margin estimation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 15, 2393–2404 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baig, M.M.A., Qazi, S.A. & Kadri, M.B. Discriminative Training for Phonetic Recognition of the Holy Quran. Arab J Sci Eng 40, 2629–2640 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1693-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1693-y