Abstract
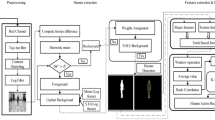
Motion representation is a challenging task in human action recognition. To represent motion, most traditional methods usually require certain intermediate processing steps such as actor segmentation, body tracking, and interest point detection, which make these methods sensitive to errors caused by these processing steps. In this paper, motivated by the successful recovery of low-rank matrix using robust principal component analysis (RPCA), we present a novel motion representation method for action recognition by extracting refined low-rank features of RPCA. Compared with the traditional methods, our method does not require the intermediate processing steps mentioned above. Unfortunately, with traditional λ, RPCA is incapable of extracting the discriminative information of motion in action videos, thus we first conduct extensive experiments to determine a feasible parameter λ suitable for action recognition. Then, we perform RPCA with this λ to obtain the low-rank images including the discriminative information of motion. To represent characteristic of the obtained low-rank images, we define two descriptors [i.e., edge distribution histogram (EDH) and accumulated edge distribution histogram (AEDH)] to refine the low-rank images. Finally, a support vector machine is trained to classify human actions represented by EDH or AEDH features. The efficacy of the proposed method is verified on three public datasets, and experimental results have shown the promising results of our method for human action recognition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hasan H.S., Kareem S.B.A.: Gesture feature extraction for static gesture recognition. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 38(12), 3349–3366 (2013)
Yousaf M.H., Habib H.A.: Virtual keyboard: real-time finger joints tracking for keystroke detection and recognition. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(2), 923–934 (2014)
Candamo J., Shreve M., Goldgof D.B.S.: Understanding transit scenes: a survey on human behavior-recognition algorithms. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 11(1), 206–224 (2010)
Weinland D., Ronfard R., Boyer E.: A survey of vision-based methods for action representation, segmentation and recognition. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 115(2), 224–241 (2011)
Guo G., Lai A.: A survey on still image based human action recognition. Pattern Recognit. 47(10), 3343–3361 (2014)
Wang, L.; Suter, D.: Recognizing human activities from silhouettes: motion subspace and factorial discriminative graphical model. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–8 (2007)
Gorelick L., Blank M., Shechtman E., Irani M., Basri R.: Actions as space–time shapes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 29(12), 2247–2253 (2007)
Wu D., Shao L.: Silhouette analysis-based action recognition via exploiting human poses. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 23(2), 236–243 (2013)
Sun, X.; Chen, M.; Hauptmann, A.: Action recognition via local descriptors and holistic features. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 58–65 (2009)
Ahad M.A.R., Tan J.K., Kim H., Ishikawa S.: Motion history image: its variants and applications. Mach. Vis. Appl. 23(2), 255–281 (2012)
Hemati R., Mirzakuchaki S.: Using local-based Harris-Phog features in a combination framework for human action recognition. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(2), 903–912 (2014)
Zia Uddin Md.: An efficient local feature-based facial expression recognition system. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(11), 7885–7893 (2014)
Zhang Z., Tao D.: Slow feature analysis for human action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(3), 436–450 (2012)
Laptev, I.; Lindeberg, T.: Space–time interest points. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 432–439 (2003)
Willems, G.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L.: An efficient dense and scale-invariant spatio-temporal interest point detector. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 650–663 (2008)
Lee, W.; Chen, H.: Histogram-based interest point detectors. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1590–1596 (2009)
Laptev I.: On space–time interest points. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 64(2–3), 107–123 (2005)
Dollar, P.; Rabaud, V.; Cottrell, G.; Belongie, S.: Behavior recognition via sparse spatio-temporal features. In: IEEE International Workshop on Visual Surveillance and Performance Evaluation of Tracking and Surveillance, pp. 65–72 (2005)
Wang, H.; Ullah, M.M.; Klaser, A.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C.: Evaluation of local spatio-temporal features for action recognition. In: British Machine Vision Conference, pp. 1–11 (2009)
Laptev, I.; Marszalek, M.; Schmid, C.; Rozenfeld, B.: Learning realistic human actions from movies. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3222–3229 (2008)
Klaser, A.; Marszalek, M.; Schmid, C.: A spatio-temporal descriptor based on 3d-gradients. In: British Machine Vision Conference, pp. 1–10 (2008)
Schuldt, C.; Laptev, I.; Caputo, B.: Recognizing human actions: a local SVM approach. In: International Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp. 32–36 (2004)
Candes E., Li X., Ma Y., Wright J.: Robust principal component analysis?. J. ACM 58(3), 11–11137 (2011)
Wright, J.; Ganesh, A.; Rao, S.; Peng, Y.; Ma, Y.: Robust principal component analysis: exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices via convex optimization. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2080–2088 (2009)
Bouwmans T., Zahzah E.H.: Robust PCA via principal component pursuit: a review for a comparative evaluation in video surveillance. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 122, 22–34 (2014)
Zhang C., Liu R., Qiu T., Su Z.: Robust visual tracking via incremental low-rank features learning. Neurocomputing 131, 237–247 (2014)
Luan X., Fang B., Liu L., Yang W., Qian J.: Extracting sparse error of robust PCA for face recognition in the presence of varying illumination and occlusion. Pattern Recognit. 47(2), 495–508 (2014)
Eckart C., Young G.: The approximation of one matrix by another of lower rank. Psychometrika 1(3), 211–218 (1936)
Lin, Z.; Chen, M.; Ma, Y.: The augmented lagrange multiplier method for exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices. preprint arXiv:1009.5055
Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Yu, K.; Lv, F.; Huang, T.; Gong, Y.: Locality-constrained linear coding for image classification. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3360–3367 (2010)
Rodriguez, M.D.; Ahmed, J.; Shah, M.: Action mach: a spatio-temporal maximum average correlation height liter for action recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–8 (2008)
Kuehne, H.; Jhuang, H.; Garrote, E.; Poggio, T.; Serre T.: HMDB: a large video database for human motion recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2556–2563 (2011)
Hu M.K.: Visual pattern recognition by moment invariants. IRE Trans. Inf. Theory 8(2), 179–187 (1962)
Khotanzad A., Hong Y.H.: Invariant image recognition by Zernike moments. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 12(5), 489–497 (1990)
Bosch, A.; Zisserman, A.; Munoz, X.: Representing shape with a spatial pyramid kernel. In: Proceedings of the 6th ACM International Conference on Image and Video Retrieval. ACM, pp. 401–408 (2007)
Gernimo, D.; Lopez, A.; Ponsa, D.; Sappa, AD.: Haar wavelets and edge orientation histograms for on-board redestrian detection. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 418–425 (2007)
Kovashka, A.; Grauman, K.: Learning a hierarchy of discriminative space–time neighborhood features for human action recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2046–2053 (2010)
Wu, X.; Xu, D.; Duan, L.; Luo, J.: Action recognition using context and appearance distribution features. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 489–496 (2011)
Liu J., Yang Y., Saleemi I., Shah M.: Learning semantic features for action recognition via diusion maps. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 116(3), 361–377 (2012)
Bilinski, P.; Bremond, F.: Contextual statistics of space–time ordered features for human action recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal-Based Surveillance, pp. 228–233 (2012)
Zhao D., Shao L., Zhen X., Liu Y.: Combining appearance and structural features for human action recognition. Neurocomputing 113, 88–96 (2013)
Yuan, C.; Li, X.; Hu, W.; Ling, H.; Maybank, S.: 3D R transform on spatio-temporal interest points for action recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 724–730 (2013)
Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Wang, T.; Huang, S.: Augmenting bag-of-words: a robust contextual representation of spatio-temporal interest points for action recognition. Vis. Comput. (2014). doi:10.1007/s00371-014-1020-8
Wang, H.; Klaser, A.; Schmid, C.; Liu, C.L.: Action recognition by dense trajectories. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3169–3176 (2011)
Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Yuille, A.L.: An approach to pose-based action recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 915–922 (2013)
Kliper-Gross, O.; Gurovich, Y.; Hassner, T.; Wolf, L.: Motion interchange patterns for action recognition in unconstrained videos. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 256–269 (2012)
Jiang, Y.G.; Dai, Q.; Xue, X.; Liu, W.; Ngo, C.W.: Trajectory-based modeling of human actions with motion reference points. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 425–438 (2012)
Jain, M.; Jegou, H.; Bouthemy, P.: Better exploiting motion for better action recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2555–2562 (2013)
Wang, H.; Schmid, C.: Action recognition with improved trajectories. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3551–3558 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, S., Ye, J., Wang, T. et al. Extracting Refined Low-Rank Features of Robust PCA for Human Action Recognition. Arab J Sci Eng 40, 1427–1441 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1635-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1635-8