Abstract
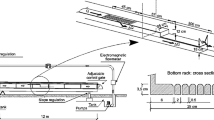
Bottom intakes are frequently used as diversion structures in mountainous regions, because of their simplicity and low costs in comparison with other methods of river diversion. In this study, Flow-3D software is utilized to simulate the flow passing through the racks. Verification tests are performed on the results of numerical method by using the experimental results of Righetti and Lanzoni (J. Hydraul. Eng. 134(1), 15–22, 2008). Also, calibration tests and mesh sensitivity are performed on the mathematical model. The diverted discharge in the numerical model is compared with the experimental data, and a good correlation (R 2 = 0.99) was obtained. Among the different existing turbulence models, the kɛ RNG model performed best. Afterward, the racks with eight different cross-sectional geometries are simulated by the numerical method. The diverted discharge, velocity and pressure distributions around the racks for each cross section are obtained and compared with each other. Results revealed that lozenge shape is the most effective geometry in flow diversion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bina K., Faghfour Maghrebi M., Abrishami J.: Experimental investigation of discharge coefficient in mesh panel bottom intakes. Water Wastewater. 23(1), 24–33 (2011)
Kuntzman J., Bouvard M.: Theoretical study of bottom type water intake grids. La Houille Blanche. 5, 559–574 (1954)
Noseda G.: Operation and design of bottom intake racks. 6th Int. Assoc. Hydraul. Res. Congr., La Haye 3(C17), 1–11 (1955)
Orth J., Chardonnet E., Meynardi G.: Study of bottom type water intake grids. La Houille Blanche. 3, 343–351 (1954)
Kamanbedast, A.; Shafaei Bajestan, M.: Characteristics of slope and expansion of bottom intakes using physical models, National Conference on irrigation and drainage networks, Ahvaz, pp. 2631–2635 (2008)
Kamanbedast A., Masjedi A., Assareh A.: Investigation of hydraulics of flow in bottom intake structures by software modeling. J. Food Agric. Environ. 10(2), 776–780 (2012)
Righetti M., Lanzoni S.: Experimental study of the flow field over bottom intake racks. J. Hydraul. Eng. 134(1), 15–22 (2008)
Khajeh M., Fatahi M.H., Shamsaei A.: Numerical simulation of flow on the bottom intake using computational fluid dynamics. J. Water Eng. 2, 49–58 (2008)
Dorbir H., Kienberger V., Krouzecky N.: The wetted rack length of the Tyrolean weir. Institute of Hydraulic Engineering, Vienna University of Technology, Vienna (2003)
Attarian A.R., Hosseini Kh., Abdi H., Hosseini M.: The effect of step height on energy dissipation in stepped spillways using numerical simulation. AJSE. 39, 2587–2594 (2014)
Chaudry M.A., Rahman M.H., Akhtar M.N., Hashmim H.M.: Modeling sediment deposition and sediment flushing through reservoir using 1-D numerical model. AJSE. 39, 647–657 (2014)
Nikpor M.K., Nazemi A.H., Hosseinzadeh A., Shoja F., Varjavand P.: Experimental and numerical simulation of water hammer. AJSE. 39, 2669–2675 (2014)
Pope S.: Turbulent Flows. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Flow Science, Flow-3D user’s manual, Version 9.2, p. 250 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseini, K., Rikhtegar, S., Karami, H. et al. Application of Numerical Modeling to Assess Geometry Effect of Racks on Performance of Bottom Intakes. Arab J Sci Eng 40, 677–684 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1542-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1542-4