Abstract
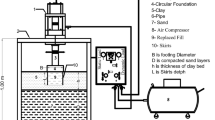
The present study investigated the behavior of model footings bounded by a wall of different depths and located at different distances from the footing resting on sandy soil. Different parameters are considered, such as relative density of sand, distance from the wall to the edge of footing (d), width of footing (B) and depth of wall (h). Test results show that the presence of the wall affects remarkably the bearing capacity, leading to improvement in the bearing capacity with different percentages according to the distance of the wall from the edge of footing and depth of wall due to the increase in the soil confinement underneath the footing. In loose sand, the largest improvement in bearing capacity for rectangular footings bounded by walls reaches about 34 %, at h/B = 0.5 and d/B = 2. In medium sand, the largest improvement in bearing capacity for these footings bounded by walls reaches about 33 %, at h/B = 0.5 and d/B = 2, while in dense sand, the largest improvement in bearing capacity for rectangular footings bounded by walls reaches about 52 %, at h/B = 0 and d/B = 2. The presence of the wall mitigates the vertical settlement, and reduction in the vertical settlement ranges from 3 to 24 % in all tests depending on the wall depth and its distance from the footing. In loose and medium sand, the maximum effect of the wall on the value of bearing capacity is when the distance between the wall and the footing edge h/B is 0.5, while in dense sand, the maximum effect of the wall on the bearing capacity is when the wall is in contact with the footing edge h/B is zero.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saleh N.M., Alsaied A.E., Elleboudy A.M.: Performance of skirted strip footing subjected to eccentric inclined load. EJGE 13, 1–33 (2008)
Giri, P.: Performance of skirted foundation in sand subjected to vibrations. In: Proceedings of 13th ICSMFE, New Delhi, India, pp. 787–790 (1994)
Byrne B., Houlsby G., Martin C., Fish P.: Suction Caisson foundation for offshore wind turbines. Wind Eng. 26(3), 145–155 (2002)
Micic, S.; Shang, J.Q.; Lo, K.Y.: Bearing capacity enhancement of skirted foundation element by electrokinetics. In: Proceedings of the Twelfth International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference Kitakyushu, Japan, May 26–31, 2002, pp. 685–692 (2002)
Yun, G.J.; Bransby, M.F.: Centrifuge modeling of the horizontal capacity of skirted foundations on drained loose sand. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Foundations, Dundee, Scotland, pp. 1–10 (2003)
Gourvenec S., Jensen K.: Effect of embedment and spacing of cojoined skirted foundation systems on undrained limit states under general loading. Int. J. Geomech. ASCE 9(6), 267–279 (2009)
Azzam W.R., Farouk A.: Experimental and numerical studies of sand slopes loaded with skirted strip footing. EJGE 15, 795–812 (2010)
Bienen B., Gaudin C., Cassidy M.J., Rausch L., Purwana O.N., Krisdani H.: Numerical modelling of a hybrid skirted foundation under combined loading. Comput. Geotech. 45, 127–139 (2012)
ASTM D422-2001.: Standard test method for particle size-analysis of soils. American Society for Testing and Materials
ASTM D854-2005.: Standard test method for specific gravity of soil solids by water pycnometer. American Society for Testing and Materials
ASTM D4253-2000.: Standard test method for maximum index density and unit weight of soils using a vibratory table. American Society for Testing and Materials
ASTM D4254-2000.: Standard test method for minimum index density and unit weight of soils and calculation of relative density. American Society for Testing and Materials
BowelsJ.E.: Engineering Properties of Soils and Their Measurement, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill International Book Company, Tokyo (1978)
ASTM D3080-1998.: Standard test method for direct shear test of soils under consolidated drained conditions. American Society for Testing and Materials
Das, B.M.: Shallow foundations: bearing capacity and settlement, 2nd edn. CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an informa business (2009)
El Sawwaf M., Nazer A.: Behavior of circular footings resting on confined granular soil. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. ASCE 131(3), 359–366 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fattah, M.Y., Shlash, K.T. & Mohammed, H.A. Bearing Capacity of Rectangular Footing on Sandy Soil Bounded by a Wall. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 7621–7633 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1353-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1353-7