Abstract
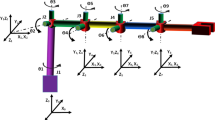
A method based on a modified electromagnetism-like with two-direction local search algorithm (MEMTDLS) and genetic algorithm (GA) is proposed to determine the optimal time of task scheduling for dual-robot manipulators. A GA is utilized to calculate the near-optimal task scheduling for both robots, and the MEMTDLS is recommended as a suitable alternative in obtaining multiple solutions at each task point for both manipulators with minimal error. During the course of the tour, the robots move from point to point with a short cycle time, while ensuring that no collision occurs between the two manipulators themselves or between the dual manipulators and the static obstacles in the workspace. The movement and the configurations of the manipulators at the task points were illustrated using a simulator that was developed via Visual Basic .Net. The method is verified using two simulators that are used as examples for two identical four-link planar robots that work in the environment, with square-shaped obstacles cluttered at different locations.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang C., Chung M.J., Lee B.H.: Collision avoidance of two general robot manipulators by minimum delay time. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 24, 517–522 (1994)
Karlik B., Aydin S.: An improved approach to the solution of inverse kinematics problems for robot manipulators. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 13, 159–164 (2000)
Köker R., öz C., Çakar T., Ekiz H.: A study of neural network based inverse kinematics solution for a three-joint robot. Robot. Auton. Syst. 49, 227–234 (2004)
Kalra P., Mahapatra P.B., Aggarwal D.K.: An evolutionary approach for solving the multimodal inverse kinematics problem of industrial robots. Mech. Mach. Theory 41, 1213–1229 (2006)
Feng Y., Nan W.Y., Ning W.S.: Inverse kinematic solution for robot manipulator based on electromagnetism-like and modified DFP algorithms. Acta Autom. Sinica. 37(1), 74–82 (2011)
Edan Y., Flash T., Peiper U.M., Shmulevich I., Sarig Y.: Near-minimum-time task planning for fruit-picking robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 7(1), 48–56 (1991)
Petiot J.-F., Chedmail P., Hascoët J.-Y.: Contribution to the scheduling of trajectories in robotics. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 14, 237–251 (1998)
Azariadis P.N., Aspragathos N.A.: Obstacle representation by Bump-surfaces for optimal motion-planning. Robot. Auton. Syst. 51, 129–150 (2005)
Nearchou A.C., Aspragathos N.A.: A genetic path planning algorithm for redundant articulated robots. Robotica 15, 213–224 (1997)
Rana, A.S.; Zalzala, A.M.S.: Collision-free motion planning of multiarm robots using evolutionary algorithms. In: Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers. Part I: Journal of Systems and Control Engineering, pp. 373–384 (1997)
Zacharia P.Th., Aspragathos N.A.: Optimal robot task scheduling based on genetic algorithms. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 21, 67–79 (2005)
Xidias E.K., Zacharia P.Th., Aspragathos N.A.: Time-optimal task scheduling for articulated manipulators in environments cluttered with obstacles. Robotica 28, 427–440 (2010)
Jiang K., Seneviratne L.D., Earles S.W.E.: Assembly scheduling for an integrated two-robot workcell. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 13(2), 131–143 (1997)
Samanlioglu F., Ferrell W.G., Kurz M.E.: A memetic random-key genetic algorithm for a symmetric multi-objective traveling salesman problem. Comput. Ind. Eng. 55, 439–449 (2008)
Xidias E.K., Zacharia P.Th., Aspragathos N.A.: Time-optimal task scheduling for two robotic manipulators operating in a three-dimensional environment. Proc. IMechE Part I J. Syst. Control Eng. 224, 845–855 (2010)
Yahya S., Moghavvemi M., Mohamed H.A.F.: Geometrical approach of planar hyper-redundant manipulators: inverse kinematics, path planning and workspace. Simulat. Model. Pract. Theory 19, 406–422 (2011)
Yao Z., Gupta K.: Path planning with general end-effector constraints. Robot. Auton. Syst. 55, 316–327 (2007)
Abed I.A., Koh S.P., Sahari K.S.M., Tiong S.K., Yap D.F.W.: Comparison between genetic algorithm and electro- magnetism-like algorithm for solving inverse kinematics. World Appl. Sci. J. 20(7), 946–954 (2012)
Selig J.M.: Introductory Robotics. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ (1992)
Ata A.A., Myo T.R.: Optimal point-to-point trajectory tracking of redundant manipulators using generalized pattern search. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2(3), 239–244 (2005)
Lai K.-C., Kang S.-C.: Collision detection strategies for virtual construction simulation. Autom. Construct. 18, 724–736 (2009)
Khalili M., Moghaddam R.T.: A multi-objective electromagnetism algorithm for a bi-objective flowshop scheduling problem. J. Manuf. Syst. 31, 232–239 (2012)
Yurtkuran A., Emel E.: A new hybrid electromagnetism-like algorithm for capacited vechicle routing problems. Exp. Syst. Appl. 37, 3427–3433 (2010)
Jhang J.-Y., Lee K.-C.: Array pattern optimization using electromagnetism-like algorithm. Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEÜ). 63, 491–496 (2009)
Lee C.-H., Chang F.-K., Lee Y.-C.: An improved electromagnetism-like algorithm for recurrent neural fuzzy controller design. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 12, 280–290 (2010)
Birbil Ş. İ., Fang S.-C.: An electromagnetism-like mechanism for global optimization. J. Global Optimiz. 25, 263–282 (2003)
Chang P.-C., Chen S.-H., Fan C.-Y.: A hybrid electromagnetism-like algorithm for single machine scheduling problem. Exp. Syst. Appl. 36, 1259–1267 (2009)
Debels D., Reyck B.D., Leus R., Vanhoucke M.: A hybrid scatter search/electromagnetism meta-heuristic for project scheduling. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 169, 638–653 (2006)
Guan X., Dai X., Qiu B., Li J.: A revised electromagnetism-like mechanism for layout design of reconfigurable manufacturing system. Comput. Ind. Eng. 63, 98–108 (2012)
Lin J.-L., Wu C.-H., Chung H.-Y.: Performance comparison of electromagnetism-like algorithms for global optimization. Appl. Math. 3, 1265–1275 (2012)
Sivanandam S.N., Deepa S.N.: Introduction to Genetic Algorithms. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Ganesan H., Mohankumar G.: Optimization of machining techniques in CNC turing centre using genetic algorithm. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 38, 1529–1538 (2013)
Lee M.: Evolution of behaviors in autonomous robot using artificial neural network and genetic algorithm. Inf. Sci. 155, 43–60 (2003)
Carter A.E., Ragsdale C.T.: A new approach to solving the multiple traveling salesperson problem using genetic algorithms. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 175, 246–257 (2006)
Chen S.-M., Chien C.-Y.: Solving the traveling salesman problem based on the genetic simulated annealing ant colony system with particle swarm optimization techniques. Exp. Syst. Appl. 38, 14439–14450 (2011)
Louis S.J., Li C.: Case injected genetic algorithms for traveling salesman problems. Inf. Sci. 122, 201–225 (2000)
Asadzadeh L., Zamanifar K.: An agent-based parallel approach for the job shop scheduling problem with genetic algorithms. Math. Comput. Model. 52, 1957–1965 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abed, I.A., Koh, S.P., Sahari, K.S.M. et al. Optimization of the Time of Task Scheduling for Dual Manipulators using a Modified Electromagnetism-Like Algorithm and Genetic Algorithm. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 6269–6285 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1250-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1250-0