Abstract
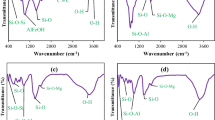
A new composite clay, aluminum pillared palygorskite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (Al–P-nZVI), was prepared by reducing ferric ion (FeCl3.6H2O) to Fe0 with sodium borohydride (NaBH4) on aluminum pillared palygorskite, in order to improve metal ions adsorption capacities of palygorskite and reduce nanoscale zero-valent iron reunion. The composite clay was characterized by FTIR, TEM and XRD spectra. Batch isothermal equilibrium adsorption experiments were conducted to evaluate the clay adsorbent for the removal of Cu(II) and Ni(II) from water. The effects of pH, shaking time on adsorption capacity were also investigated. The pseudo-second-order model was relatively suitable for describing the reaction process. The equilibrium adsorption data were fitted to Langmuir adsorption models. The maximum adsorption capacities of aluminum pillared palygorskite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron sorbent as obtained from Langmuir adsorption isotherm were found to be 787 and 704 mg g−1 for Cu(II) and Ni(II), respectively. A comparison of the results of the present investigation with those reported in the literature showed that Al–P-nZVI exhibits greater adsorption capacity for Cu(II)and Ni(II). These results demonstrated that Al–P-nZVI could potentially be used as an effective material for environmental remediation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulkareem S. A, Muzenda E, Afolabi A. S, Kabuba J.: Treatment of clinoptilolite as an adsorbent for the removal of copper ion from synthetic wastewater solution. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 38, 2263–2272 (2013)
Bailey E.S, Olin T.J, Bricka R.M, Adrian D.D.: A review of potentially low-cost sorbents for heavy metals, Water Res.. 33, 2469 (1999)
Spiro, G.T.; Stigliani, W.M.: Chemistry of the Environment, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey (1996)
Li X.Q, Elliott D.W, Zhang W.X.: Zero-valent iron nanoparticles for abatement of environmental pollutants: materials and engineering aspects. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mat. Sci. 31, 111–122 (2006)
Sun Y.P, Li X.Q, Cao J, Zhang W.X, Wang H.P.: Characterization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 120, 47–56 (2006)
Cumbal L, Greenleaf J, Leun D, Sen Gupta A.K.: Polymer supported inorganic nanoparticles: characterization and environmental applications. React. Funct. Polym. 54, 167–180 (2003)
Nurmi J.T, Tratnyek P.G, Sarathy V, Baer D.R, Amonette J.E, Pecher K, Wang C, Linehan J.C, Matson D.W, Penn R.L, Driessen M.D.: Characterization and properties of metallic ion nanoparticles: spectroscopy, electrochemistry, and kinetics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 1221–1230 (2005)
Wei, Y.T.; Wu, S.C.; Yang, S.W.; Che, C.H.; Lien, H.L.; Huang, D.H.: Biodegradable surfactant stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron for in situ treatment of vinyl chloride and 1,2-dichloroethane. J. Hazard. Mater. 211–212, 373–380 (2012)
He F, Zhao D.Y.: Preparation and characterization of a new class of starch-stabilized bimetallic nanoparticles for degradation of chlorinated hydrocarbons in water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 3314–3320 (2005)
Shi Z, Nurmi J.T, Tratnyek P.G.: Effects of nano zero-valent iron on oxidation–reduction potential. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45, 586–1592 (2011)
Fu F.G, Han W.J, Huang C.J, Tang B, Hu M.: Removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater by supported nanoscale zero-valent iron on granular activated carbon. Desalination Water Treat. 51, 2680–2686 (2013)
Zhang Y, Li Y, Li J, Hu L, Zheng X.: Enhanced removal of nitrate by a novel composite: nanoscale zero valent iron supported on pillared clay. Chem. Eng. J. 171, 526–531 (2011)
Lv X.S, Xu J, Jiang G.M, Xu X.H.: Removal of chromium(VI) from wastewater by nanoscale zero-valent iron particles supported on multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chemosphere 85, 1204–1209 (2011)
Liu, T.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhao, L.; Yang, X.: Enhanced chitosan/Fe0-nanoparticles beads for hexavalent chromium removal from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 189–190, 196–202 (2012)
Calabro, P.S.; Moraci, N.; Suraci, P.: Estimate of the optimum weight ratio in zero-valent/pumice granular mixtures used in permeable reactive barriers for the remediation of nickel contaminated groundwater, J. Hazard. Mater. 207–208, 111–116 (2012)
Kim H, Hong H.J, Lee Y.J, Shin H.J, Yang J.W.: Degradation of trichloroethylene by zero-valent iron immobilized in cationic exchange membrane. Desalination 223, 212–220 (2008)
Kim S.A, Kannan S. K, Lee K.J, Park Y.J, Shea P. J, Lee W.H, Kim H.M, Oh B.T.: Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by a zeolite-nanoscale zero-valent iron composite. Chem. Eng. J. 217, 54–60 (2013)
Zhang X, Lin S, Chen Z.L, Mallavarapu M, Ravendra N.D.: Kaolinite-supported nanoscale zero-valent ion for removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solution: reactivity, characterization and mechanism. Water Res. 45, 3481–3488 (2011)
Zhang X, Lin S, Lu X.Q, Chen Z.L.: Removal of Pb(II) from water using natural kaolin loaded with synthesized nanoscale zero-valent ion. Chem. Eng. J. 163, 243–248 (2010)
Helmy A.K, Bussetti S.G, Ferreiro E.A.: The surface energy of palygorskite. Powder Technol. 171, 126–131 (2007)
Ponder S.M, Darab J.G, Mallouk T.E.: Remediation of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) aqueous solutions using nanoscale zero valent iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 34, 2564–2569 (2000)
Zhang L.X, Jin Q.Z, Shan L, Liu Y.F, Wang X.G, Huang J.H.: H3PW12O40 immobilized on silylated palygorskite and catalytic activity in esterification reactions. Appl. Clay. Sci. 47, 229–234 (2010)
Frost R. L, Xi Y.F, He H.P.: Synthesis, characterization of palygorskite supported zero-valent iron and its application for methylene blue adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 341, 153–161 (2010)
Ruiz-Hitaky E, Galvan J. C, Merino J, Casal B, Aranda P, Jimenenz-Morales A.: Proton conductivity in Al-montmorillonite pillared clays. Solid State Ionics 85, 313–317 (1996)
Pires J, Francisco J, Carvalho A, Brotasde Carvalho M, Silva A.R, Freire C.: Development of novel pillared clays for the encapsulation of inorganic complexes. Langmuir 20, 2861–2866 (2004)
Barrera-Vargas M, Valencia-Rios J, Vicente M. A, Korili S. A, Gil A.: Effect of the platinum content on the microstructure and micropore size distribution of Pt/Alumina-pillared clays. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 23461–23465 (2005)
Uzum C, Shahwan T, Eroglu A.E, Hallam K.R, Scott T.B, Lieberwirth I.: Synthesis and characterization of kaolinite-supported zero-valent iron nanoparticles and their application for the removal of aqueous Cu2+ and Co2+ ions. Appl. Clay. Sci. 43, 172–181 (2009)
Canafoglia M.E, Lick I.D, Ponzi E.N, Botto I.L.: Natural materials modified with transition metals of the cobalt group: feasibility in catalysis. J. Argent. Chem. Soc. 97, 58–68 (2009)
Lee S, Lee K, Rhee S, Park J.: Development of a new zero-valent iron zeolite material to reduce nitrate without ammonium release. J. Environ. Eng. 133, 6–12 (2007)
Drbohlavova J, Hrdy R, Adam V, Kizek R, Schneeweiss O, Hubalek J.: Preparation and properties of various magnetic nanoparticles. Sensors 9, 2352–2362 (2009)
Selwyn, L.: Overview of archaeological ion: the corrosion problem, key factors affecting treatment, and gaps in current knowledge. In: J. Ashton, Hallam (eds) Metal 2004: Proceedings of Interim Meeting of the ICOM-CC Metal WG, National Museum of Australia, Canberra, pp. 294–306 (2004)
Boudrahem, F.; Aissani-Benissad, F.; A. Soualah A.: Kinetic and Equilibrium study of the sorption of lead(II) ions from aqueous phase by activated carbon. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 38, 1939–1949 (2013)
Albadarin A.B, Mangwandi C, Al-Muhtaseb A. H, Walker G.M, Allen S.J, Ahmad M.N.M.: Kinetic thermodynamics of chromium ions adsorption onto low-cost dolomite adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 179, 193–202 (2012)
Nityanandi D, Subbhuraam C.V.: Kinetics and thermodynamic of adsorption of chromium(VI) from aqueous solution using puresorbe. J. Hazard. Mater. 170, 876–882 (2009)
Eren E, Afsin B.: Investigation of a basic dye adsorption from the aqueous solution onto raw and pre-treated bentonite surface. Dyes Pigm. 76, 220–225 (2008)
Liu Z.G, Zhang F.S.: Removal of lead from water using biochars prepared from hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 167, 933–939 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, Y., He, Yy., Liu, T. et al. Aluminum Pillared Palygorskite-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron for Removal of Cu(II), Ni(II) From Aqueous Solution. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 6727–6736 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1229-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1229-x