Abstract
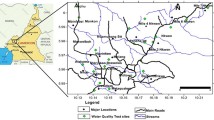
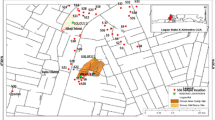
This paper discusses the groundwater quality and its suitability for various uses such as drinking, livestock and agriculture in Barka area of Northern Oman. The groundwater quality is predicted to be affected by the dumping site of this area which receives every kind of wastes. Therefore, groundwater quality assessment was done by using an integrated approach that evaluates inorganic, organic and microbiological parameters. Groundwater samples were taken from supply wells, usually equipped with permanently installed pumps and few dug wells. The results showed large variations in total dissolved solids, Cl, Na, Mg and SO4 that suggest the influences of distinguished contamination sources and processes on water chemistry. It has been considered that wastewater (domestic and industrial) disposal could be a principal threat in Barka dumping site. This observation is supported by the concentrations of metals (Ni, Cr, Ba and Pb), biochemical oxygen demand, chemical oxygen demand (COD) and total coliform count that characterize the groundwater as not appropriate for normal use. However, it has been found that the majority of the water samples are appropriate for agricultural and livestock use consistent with Food and Agricultural Organization guidelines.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papadopoulou M., Karatzas G., Bougioukou G.: Numerical modelling of the environmental impact of landfill leachate leakage on groundwater quality—a field application. Greece Environ. Model. Assess. 12(1), 43–54 (2007)
Hughes, K.; Christy, A.; Heimlich, J.: Landfill Types and Liner Systems. Ohio State University Extension Fact Sheet CDFS-138-05. http://ohioline.osu.edu (2008)
Bou-Zeid E., El-Fadel M.: Parametric sensitivity analysis of leachate transport simulations at landfills. Sci. Direct Waste Manag. 24, 681–689 (2004)
Zupanc, V.; Justin, M.Z.: Changes in soil characteristics during landfill leachate irrigation of Populus deltoides, Waste Management. 30(11), 2130–2136 (2010)
Raco B., Dotsika E., Battaglini R., Bulleri E., Doveri M., Papakostantinou K.: A quick and reliable method to detect and quantify contamination from MSW landfills: a case study. J. Water Air Soil Pollut. 224(3), 1–18 (2013)
Leeuwen F.X.R.V.: Safe drinking water: the toxicologist’s approach. J. Food Chem. Toxicol. 38, 51–58 (2000)
Guy, F.: Irrigation Water Quality Standards and Salinity Management Strategies. Texas Agricultural Extension Service, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, USA, pp. 1–18 (1997)
Lakey, R.; Easton, P.; Al-Hinai, H.: Eastern Batinah resource assessment numerical modeling report, Ministry of Water Resources, Muscat, Oman (1995)
Weyhenmeyer, C.E.; Burns, S.J.; Waber, N.; Macumber, P.G.; Matter, A.: Isotope study of moisture sources, recharge areas, and groundwater flow paths within the eastern Batinah coastal plain, Sultanate of Oman. Water Resour. Res. 38(10), 1184. doi:10.1029/2000WR000149 (2002)
Morakinyo, J.A.; Mackay, R.: Geostatistical modelling of ground conditions to support the assessment of site contamination. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 20(1–2), 106–118 (2006)
Cinnirella S., Buttafuoco G., Pirrone N.: Stochastic analysis to assess the spatial distribution of groundwater nitrate concentrations in the Po catchment (Italy), J. Environ. Pollut. 133(3), 569–580 (2005)
Komnitsas, K.; Modis, K.: Geostatistical risk estimation at waste disposal sites in the presence of hot spots. J. Hazard. Mater. 164(2–3), 1185–1190 (2009)
APHA. American Public Health Association: Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Pollution Control Federation, 19th edition, Washington, D.C (1995)
Metcalf E.: Wastewater Engineering, Treatment, and reuse. McGraw Hill Book Co. New York, USA (2003)
Reinhart, T.; Reuland, E.: Reflexivity. Linguistic Inq. 24(4), 657–720 (1993)
Jensen D.L., Ledin A., Christensen T.H.: Speciation of heavy metals in landfill leachate polluted groundwater. J. Water Res. 33, 2642–2650 (1999)
Christensen T. H., Kjeldsen P., Bjerg P.L., Jensen D.L., Christensen J.B., Baun A., Albrechtsen H.J., Heron G.: Biogeochemistry of landfill leachate plumes—Review. Appl. Geochem. 16, 659–718 (2001)
Chofqi A., Younsi A., Lhadi E.K., Mania J., Mudry J., Veron A.: Environmental impact of an urban landfill on a coastal aquifer (El Jadida, Morocco). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 39, 509–516 (2004)
Mikac N., Cosovic B., Ahel M., Andreis S., Toncic Z.: Assessment of groundwater contamination in the vicinity of a municipal solid waste landfill (Zagreb, Croatia). Water Sci. Technol. 37(8), 37–44 (1998)
Kjeldsen P.: Groundwater pollution source characterization of an old landfill. J. Hydrol. 142, 349–371 (1993)
Kjeldsen P., Grundtvig A., Winther P., Andersen J.S.: Characterization of an old municipal landfill (Grindsted, Denmark) as a groundwater pollution source: landfill history and leachate composition. Waste Manag. Res. 16, 14–22 (1998)
Sadiq M., Alam I.: Metal concentrations in a shallow groundwater aquifer underneath petrochemical complex. J. Water Res. 31, 3089–3097 (1998)
Malard F., Datry T., Gibert J.: Subsurface sediment contamination during borehole drilling with an air-actuated down-hole hammer. J. Contam. Hydrol. 79, 156–164 (2005)
Whisman, M.L.; Goetzinger, J.W.; Cotton, F.O.: Waste lubricating oil research. In: An Investigation of Services Re-refining Methods. Bureau of Mine, Bartlesville, Energy Research Center (1974)
Basberg L., Banks D., Saether O.M.: Redox processes in groundwater impacted by landfill leachate. J. Aquat. Geochem. 4, 253–272 (1998)
Baumann T., Fruhstorfer P., Klein T., Niessner R.: Colloid and heavy metal transport at landfill sites in direct contact with groundwater. J. Water Res. 40, 2776–2786 (2006)
Panno, S.V.; Weibel, C.P.; Krapac, I.G.; Storment, E.C.: Bacterial contamination of ground water from private septic systems in Illinois’ sinkhole plain: Regulatory considerations, pp. 443–447. In: Beck B.F.; Stephenson J.B. (eds.) The engineering geology and hydrogeology of karst terranes. Proceedings of Sixth Multidisciplinary Conference. Sinkholes and Engineering and Environment Impacts of Karst, Springfield, MO, pp. 6–9 (1997)
Goss M.J., Barry D.A.J., Rudolph D.L.: Contamination in Ontario Farmstead domestic wells and its association with agriculture: 1. Results from drinking water wells. J. Contam. Hydrol. 32, 267–293 (1998)
Allen M.J., Morrison S.M.: Bacterial movement through fractured bedrock. J. Groundw. 11(2), 6–10 (1973)
Malard F.J., Reygrobellet L., Soulie M.: Transport and retention of fecal bacteria at sewage-polluted fractured rock sites. J. Environ. Qual. 23, 1352–1363 (1994)
Story S.P., Amy P.S., Bishop C.W., Colwell F.S.: Bacterial transport in volcanic tuff cores under saturated flow conditions. Geomicrobiol. J. 13, 249–264 (1995)
Gerba C.P., Wallis C., Melnick J.L.: Fate of wastewater bacteria and viruses in soil. J. Irrigat. Drain. Div. 101(3), 157–174 (1975)
Harvey R.W., George L.H., Smith R.L., LeBlanc D.R.: Transport of microspheres and indigenous bacteria through a sandy aquifer: results of natural and forced-gradient tracer experiments. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 23(1), 51–56 (1989)
Gerba, C.P.; Bitton, G.: Microbial pollutants: their survival and transport pattern to groundwater. In: Bitton, G.; Gerba, C.P. (eds.), Groundwater Pollution Microbiology. Wiley, Toronto, pp. 65–88 (1984)
ODWS.: Omani drinking water standard, O.S. 8/1998, Directorate General for specifications and measurements, Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Sultanate of Oman (1998)
EPA.: National primary drinking water standards. EPA816-F-03-016 (2003)
Ayers R.S., Westcot D.W.: Water quality for agriculture. FAO irrigation and drainage. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, Italy. 1(1), 1–95 (1994)
FAO. Aquaculture Production 1986–1992. FAO Fisheries Circular 815 (Rev. 6). FAO, Rome (1994)
Ruiz, A.I.; Fernández, R.; Sánchez Jiménez, N.; Rodríguez Rastrero, M.; Regadío, M.; de Soto, I.S.; Cuevas, J.: Improvement of attenuation functions of a clayey sandstone for landfill leachate containment by bentonite addition. Sci. Tot. Environ. 419, 81–89 (2012)
Bartzas G., Komnitsas K., Paspaliaris I.: Laboratory evaluation of Fe0 barriers to treat acidic leachates, J. Miner. Eng. 19(5), 505–514 (2006)
Jun D., Yongsheng Z., Weihong Z., Mei H.: Laboratory study on sequenced permeable reactive barrier remediation for landfill leachate-contaminated groundwater. J. Hazard. Mater. 161(1), 224–230 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baawain, M.S., Al-Futaisi, A.M. Studying Groundwater Quality Affected by Barka Dumping Site: An Integrated Approach. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 5943–5957 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1197-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1197-1