Abstract
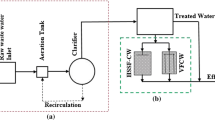
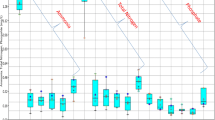
Four small-scale cylindrical, vertical upward flow constructed wetland units were installed and evaluated to determine the effectiveness of these units to treat highway runoff. The highway runoff was collected during various rainfall events in the year 2009 from Lukou Viaduct section of Nanjing airport express highway. The natural zeolite and gravel were used as filter substrates and all four units were planted with common reed (Phragmites spp.). These four units were subjected to similar hydraulic retention time (6 h HRT) with different hydraulic loads. Water samples were collected from the influent and effluent of vertical flow constructed wetlands, and were analyzed for determination of total suspended solids, COD, ammoniacal nitrogen, total nitrogen and total phosphorus. The results show that vertical flow constructed wetlands with zeolite–gravel substrate combination achieved the best performance between all systems with mean removal efficiency of 57 % TSS, 45 % COD and 78 % ammoniacal nitrogen. The average ammoniacal nitrogen decreased by approximately 65 % in all wetland units, suggesting that this design had the highest nitrification rate. The study also revealed that the use of substrate materials with specific characteristics, such as zeolite and gravel, can enhance the removal of nutrients. However, the overall performance of vertical upward flow constructed wetlands was not effective.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kayhanian M., Suverkropp C., Ruby A., Tsay K.: Characterization and prediction of highway runoff constituent event mean concentration. J. Environ. Manag. 85(2), 279 (2007)
Mungasavalli D.P., Viraraghavan T.: Constructed wetlands for stormwater management: a review. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 15(11), 1363–1372 (2006)
Terzakis S., Fountoulakis M.S., Georgaki I., Albantakis D., Sabathianakis I., Karathanasis A.D.: Constructed wetlands treating highway runoff in the central Mediterranean region. Chemosphere 72(2), 141–149 (2008)
Kalainesan S., Neufeld R.D., Quimpo R., Yodnane P.: Sedimentation basin performance at highway construction sites. J. Environ. Manag. 90(2), 838–849 (2009)
Tsihrintzis V.A., Hamid R.: Modeling and management of urban stormwater runoff quality: a review. Water Resour. Manag. 11(2), 137–164 (1997)
Gikas G.D., Tsihrintzis V.A.: On-site treatment of domestic wastewater using a small-scale horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland. Water Sci. Technol. 62(3), 603–614 (2010)
Vymazal J.: The use constructed wetlands with horizontal sub-surface flow for various types of wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 35, 1–17 (2009)
Shutes, R.B.E.: Artificial wetlands and water quality improvement. Environ. Int. 26(5–6), 441–447 (2001)
Vyamazal J.: Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: five decades of experience. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45(1), 61–69 (2011)
Zhang D., Gersberg R.M., Keat T.S.: Constructed wetlands in China. Ecol. Eng. 35(10), 1367–1378 (2009)
Vymazal, J.: Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 380(1–3), 48–65 (2007)
Akratos C.S., Tsihrintzis V.A.: Effect of temperature, HRT, vegetation and porous media on removal efficiency of pilot-scale horizontal sub-surface flow constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 29(2), 173–191 (2007)
Siriwardene N.R., Deletic A., Fletcher T.D.: Clogging of stormwater gravel infiltration systems and filters: insights from a laboratory study. Water Res. 41(7), 1433–1440 (2007)
Kadlec, R.H; Knight, R.L.: Treatment wetlands, 893. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1996)
Korkusuz E., Bekliogle M., Demirer G.: Treatment efficiencies of the vertical flow pilot-scale constructed wetlands for domestic wastewater treatment. Turkish J. Eng. Environ. Sci. 28(5), 333–344 (2004)
Dong C.S., Ju S.C., Hong J.L., Jong S.H.: Phosphorus retention capacity of filter media for estimating the longevity of constructed wetland. Water Res. 39, 2445–2457 (2005)
Mohammed R.R.: Removal of heavy metals from waste water using black tea waste. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 37(6), 1505–1520 (2012)
Prochaska C.A., Zouboulis A.I.: Removal of phosphates by pilot vertical-flow constructed wetlands using a mixture of sand and dolomite as substrate. Ecol. Eng. 26, 293–303 (2006)
Vohla C., Kõiv M., Bavor H.J., Chazarenc F., Mander Ü.: Filter materials for phosphorus removal from wastewater in treatment wetlands? A review. Ecol. Eng. 37, 70–89 (2011)
Stefanakis, A.I.; Tsihrintzis, V.A.: Effect of loading, resting period, temperature, porous media, vegetation and aeration on performance of pilot-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands. Chem. Eng. J. 181–182, 416–430 (2012)
Stefanakis, A.I.; Akratos, C.S.; Gikas, G.D.; Tsihrintzis, V.A.: Effluent quality improvement of two pilot-scale, horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands using natural zeolite (clinoptilolite). Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 124(1–3), 131–143 (2009)
Bruch I., Fritsche J., Bänninger D., Alewell U., Sendelov M., Hürlimann H., Hasselbach R., Alewell C.: Improving the treatment efficiency of constructed wetlands with zeolite-containing filter sands. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 937–941 (2011)
Pansini M.: Natural zeolite as cation exchangers for environmental protection. Mineral Depos. 31, 563–575 (1996)
Tuszynska A., Obarska-Pempkowiak H.: Dependence between quality and removal effectiveness of organic matter in hybrid constructed wetlands. Bioresour. Technol. 99(14), 6010–6016 (2008)
Milan Z., Sanchez E., Weiland P., Borja R., Martin A., Langovan K.: Influence of different natural zeolite concentrations on the anaerobic digestion of piggery waste. Bioresour. Technol. 80(1), 37–43 (2001)
Clark D.L., Asplund R.: Composite sampling of highway runoff. J. Environ. Eng. 107(EE5), 1067–1081 (1981)
American Wastewater Association/APHA: Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Washington DC, USA (1998)
Barrett, M.E; Manila, J.F; Charbrnrau, R.J.: Characterization of Highway Runoff in the Austin, Texas Area. Technical Report, Center for Research in Water Resources, Austin (1995)
Qin, Z; Qian, G; Tang, R; He, J.: Research Progress of Pavement Runoff. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering, pp. 3433–3437 (2011)
Shuib N., Baskaran K., Jegatheesan V.: Evaluating the performance of horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands using natural zeolite (escott). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Develop. 2(4), 311–315 (2011)
Stefanakis A.I., Tsihrintzis V.A.: Use of zeolite and bauxite as filter media treating the effluent of vertical flow constructed wetlands. Microporous and Mesoporous Mater. 155, 106–116 (2012)
Vymazal, J.; Brix, H.; Cooper, P.F.; Green, M.B.; Haberl, R.: Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment in Europe. Backheys Publishers, Leiden (1998)
Gikas G.D., Tsihrintzis V.A., Akratos C.S.: Performance and modeling of a vertical flow constructed wetland-maturation pond system. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 46(7), 692–708 (2011)
Westholm, J.L.: Substrates for phosphorus removal? Potential benefits for on-site wastewater treatment? Water Res. 40, 23–36 (2006)
Gao Y., Ye J., Li H.: Phosphorus removal performance of vertical flow constructed wetland with zeolite as substrate material. Ind. Water Wastewater 38(2), 20–22 (2007)
Drizo A., Frost A.C., Grace J., Smith A.K.: Physico-chemical screening of phosphate-removing substrates for use in constructed wetland systems. Water Res. 33(17), 3595–3602 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R.P., Fu, D., Fu, D. et al. Pollutant Removal Efficiency of Vertical Sub-surface Upward Flow Constructed Wetlands for Highway Runoff Treatment. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 3571–3578 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1029-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1029-3