Abstract
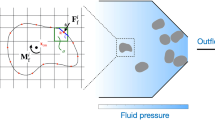
In the present article we present computational investigations of fluid–solid interaction flow. Such fluid–solid interaction flow was created in three different cavity shapes on the floor of a horizontal channel. The flow and solid particle dynamics were explored using cubic interpolated pseudo-particle method and Lagrangian scheme of Newton’s law, respectively, for two objectives. The first is to demonstrate the validity of the proposed Eulerian–Lagrangian in predicting the main characteristics of fluid–solid interaction flow. The second objective is to shed light on the dynamics of the solid particle that are present in the three types of cavities, which has not been fully covered in the literature. The results show that the particles’ trajectories are critically dependent on the magnitude of Reynolds numbers and the vortex behavior in the cavity. We also found that the highest rate of removal occurs in the early penetration of flow into the cavity, especially for the triangular cavity. Good comparisons with the previous studies demonstrate the multidisciplinary applications of this scheme.
Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hayashi, H.; Kubo, S.: Computer simulation study on filtration of soot particles in diesel particulate filter. Comp. Math. App. 55(7), 1450–1460 (2008)
Rockwell, D.; Lin, J.C.; Oshkai, P.; Reiss, M.; Pollack, M.: Shallow cavity flow tone experiments: onset of locked-on states. J. Fluids. Struct. 17(3), 381–414 (2003)
Xu, B.H.; Yu, A.B.: Numerical simulation of the gas-solid flow in a fluidized bed by combining discrete particle method with computational fluid dynamics. Chem. Eng. Sci. 52(16), 2785–2809 (1997)
Mesalhy, O.M.; Abdel Aziz, S.S.; El- Sayed, M.M.: Flow heat transfer over shallow cavities. Int. J. Thermal Sci. 49(3), 514–521 (2010)
Zdanski, P.S.B.; Ortega, M.A.; Nide, G.C.R., Fico, J.: On the flow over cavities of large aspect ratio: a physical analysis. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 33(4), 458–466 (2006)
Kang, W.; Sung, H.J.: Large-scale structures of turbulent flows over an open cavity. J. Fluids Struct. 25(8), 1318–1333 (2009)
Ozalp, C.; Pinarbasi, A.; Sahin, B.: Experimental measurement of flow past cavities of different shapes. Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci. 34(5), 505–515 (2010)
Li, S.L.; Yi, C.C.; Chao, A.L.: Multi relaxation time lattice Boltzmann simulations of deep lid driven cavity flows at different aspect ratios. Comput. Fluids 45(1), 233–240 (2011)
Arlindo, D.M.; Francisco, A.A.P.; Aristeu, S.N.: Large-eddy simulation of turbulent flow over a two dimensional cavity with temperature fluctuations. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 42(1), 49–59 (1999)
Stiriba, Y.: Analysis of the flow and heat transfer characteristics for assisting incompressible laminar flow past an open cavity. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 35(8), 901–907 (2008)
Yapici, K.; Karasozen, B.; Uludag, Y.: Finite volume simulation of viscoelastic laminar flow in a lid- driven cavity. J. Non Newton. Fluids Mech. 164(1), 51–65 (2009)
Yang, Y.; Rockwell, D.; Cody, K.L.F.; Pollack, M.: Generation of tones due to flow past a deep cavity: Effect of streamwise length. J. Fluids Struct. 25(2), 364–388 (2009)
Ekmekci, A.; Rockwell, D.: Oscillation of shallow flow past a cavity: Resonant coupling with a gravity wave. J. Fluids Struct. 23(6), 809–838 (2007)
Zaki, M.M.; Nirdosh, I.; Sedahmed, G.H.: Mass transfer inside conical cavities under transverse laminar flow. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 44(12), 1306–1311 (2005)
Fang, L.C.; Nicolaou, D.; Cleaver, J.W.: Transient removal of a contaminated fluid from a cavity. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 20(6), 605–613 (1999)
Patil, D.V.; Lakshmisha, K.N.; Rogg, B.: Lattice Boltzmann simulation of lid-driven flow in deep cavities. Comput. Fluids 35(10), 1116–1125 (2006)
Stiriba, Y.; Grau F.X.; Ferre J.A.; Vernet, A.: A numerical study of three-dimensional laminar mixed convection past an open cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 53(21), 4797–4808 (2010)
Tsorng, S.J.; Capart, H.; Lai, J.S.; Young, D.L.: Three-dimensional tracking of the long time trajectories of suspended particles in a lid-driven cavity flow. Exp. Fluids 40(2), 314–328 (2006)
Adrian, R.J.: Particle-imaging techniques for experimental fluid mechanics. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 23(1), 261–304 (1991)
Han, M.; Kim, C.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.: Particle migration in tube flow of suspensions. J. Rheo. 43(5), 1157–1174 (1999)
Matas, J.P.; Morris, J.F.; Guazzelli, E.: Inertial migration of rigid spherical particles in Poiseuille flow. J. Fluid Mech. 515(1), 171–195 (2004)
Ushijima, S.; Tanaka, N.: Three-dimensional particle tracking velocimetry with laser-light sheet scannings. Fluid Eng. 118(2), 352–357 (1996)
Ide, K.; Ghil, M.: Extended Kalman filtering for vortex system. Dyn. Atm. Oceans 27(1), 301–332 (1997)
Hu, C.C.: Analysis of motility for aquatic sperm in videomicroscopy, PhD. Thesis, National Taiwan University, Taiwan (2003)
Liao, J.I.: Trajectory and velocity determination by smoother, PhD Thesis, National Taiwan University, Taiwan (2002)
Kosinki, P.; Kosinska, A.; Hoffmann, A.F.: Simulation of solid particles behavior in a driven cavity flow. Pow. Tech. 191(3), 327–339 (2009)
Ilea, C.G.; Kosinski, P.; Hoffmann, A.C.: Three-dimensional of a dust lifting process with varying parameters. J. Multiph. Flow 34(9), 869–878 (2008)
Kosinski, P.; Hoffmann, A.C.: An extension of the hard-sphere particle-particle collision model to study agglomeration. Chem. Eng. Sci. 65(10), 3231-3239 (2010)
Takewaki, H.; Nishigushi, A.; Yabe, T.: Cubic interpolated pseudo particle method for solving hyperbolic type equations. J. Comput. Phys. 61(2), 261–268 (1985)
Nor Azwadi, C.S.; Mohd Rosdzimin, A.R.; Al-Mola, M.H.: Contrained interpolated profile for solving BGK Boltzmann equation. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 35(4), 559-569 (2009)
Yabe, T.; Aoki, T.: A universal solver for hyperbolic equations by cubic-polynomial interpolation I. One-dimensional solver. Comput. Phys. Commun. 66(2), 219–232 (1991)
Nor Azwadi, C.S.; Mohd Rosdzimin, A.R.: Cubic interpolated pseudo particle (CIP)—thermal BGK lattice Boltzmann numerical scheme for solving incompressible thermal fluid flow problem. Malay. J. Math. Sci. 3(2), 183–202 (2009)
Chilukuri, R.; Middleman, S.: Circulation, diffusion and reaction within a liquid trapped in a cavity. Chem. Eng. 22(3), 127–138 (1983)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Che Sidik, N.A., Salehi, M. Eulerian–Lagrangian Numerical Scheme for Contaminant Removal from Different Cavity Shapes. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 3181–3189 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0886-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0886-5