Abstract
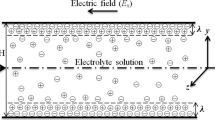
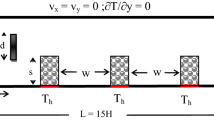
In the present work, a new Lattice Boltzmann model has been developed to study the electroosmotic flows in a 2-D flat microchannel. The governing equations are presented in the continuum model, while a set of equivalent equations in Lattice Boltzmann model is introduced and solved numerically. In particular, the Poisson and the Nernst–Planck (NP) equations are solved by two new lattice evolution methods. In the analysis of electroosmotic flows, when the convective effects are not negligible or the electric double layers have overlap, the NP equations must be employed to determine the ionic distribution throughout the microchannel. The results of this new model have been validated by available analytical and numerical results. The model has also been used to examine the electroosmotic flows in a heterogeneous flat microchannel. Furthermore, the predictions of the NP model are compared with those of the Poisson Boltzmann (PB) equation to identify the applicability of the PB equations for such flows, which can also serve as validations for the present model.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Ratio of the externally applied voltage to the elementary voltage
- B :
-
Ratio of ionic pressure to dynamic pressure
- D :
-
Diffusion coefficient
- e :
-
Elementary charge of an electron
- E :
-
Electric field intensity
- H :
-
Width of microchannel
- K :
-
Debye–Huckel parameter
- k :
-
Double layer thickness parameter, k = KH
- k B :
-
Boltzmann constant
- n + :
-
Concentration of positive ions
- n − :
-
Concentration of negative ions
- n 0 :
-
Bulk ion concentration
- P :
-
Pressure
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- Sc :
-
Schmidt number
- T :
-
Absolute temperature
- u *, v * :
-
Dimensionless velocity components
- U ref :
-
Reference velocity
- x *, y * :
-
Dimensionless Cartesian coordinates
- z :
-
Valance number of positive and negative ions
- \({\varepsilon _0}\) :
-
Permittivity of vacuum
- \({\varepsilon _r}\) :
-
Dielectric constant of the solution
- \({\phi}\) :
-
Applied electric potential
- \({\mu}\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity of working fluid
- \({\rho}\) :
-
Density of working fluid
- \({\rho_{\rm e}}\) :
-
Net electrical charge density
- \({\zeta}\) :
-
Zeta potential
- \({\psi}\) :
-
EDL potential
References
Ren L., Li D.: Electroosmotic flow in heterogeneous microchannels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 243, 255–261 (2001)
Fu L.M., Lin J.Y., Yang R.J.: Analysis of electroosmotic flow with step change in zeta potential. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 258, 266–275 (2003)
Mirbozorgi S.A., Niazmand H., Renksizbulut M.: Electro-osmotic flow in reservoir-connected flat mircrochannels with non-uniform zeta potential. J. Fluids Eng. 128, 1133–1143 (2006)
Sadeghi A., Saidi M.H.: Viscous dissipation effects on thermal transport characteristics of combined pressure and electroosmotically driven flow in microchannels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 53, 3782–3791 (2010)
Liu Q.S., Jian Y.J., Yang L.G.: Time periodic electroosmotic flow of the generalized Maxwell fluids between two micro-parallel plates. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 166, 478–486 (2011)
Hadigol M., Nosrati R., Raisee M.: Numerical analysis of mixed electroosmotic/pressure driven flow of power-law fluids in microchannels and micropumps. Colloids Surf. A 374, 142–153 (2011)
Succi S.: The Lattice Boltzmann equation for fluid dynamics and beyond. Clarendon Press, UK (2001)
Wang J., Wang M., Li Z.: Lattice Poisson–Boltzmann simulations of electro-osmotic flows in microchannels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 296, 729–736 (2006)
Wang J., Wang M., Li Z.: Lattice evolution solution for the nonlinear Poisson–Boltzmann equation in confined domains. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 13, 575–583 (2008)
Wang M., Wang J., Chen S.: Roughness and cavitations effects on electro-osmotic flows in rough microchannels using the lattice Poisson–Boltzmann methods. J. Comput. Phys. 226, 836–851 (2007)
Chai Z., Shi B.: Simulation of electro-osmotic flow in microchannel with lattice Boltzmann method. Phys. Lett. A 364, 183–188 (2007)
Chai Z., Shi B.: A novel lattice Boltzmann model for the Poisson equation. Appl. Math. Model. 32, 2050–2058 (2008)
Tang G.H., Li Z., Wang J.K., He Y.L., Tao W.Q.: Electroosmotic flow and mixing in microchannels with the lattice Boltzmann method. J. Appl. Phys. 100, 094908 (2006)
Wang M., Wang J., Chen S., Pan N.: Electrokinetic pumping effects of charged porous media in microchannels using the lattice Poisson–Boltzmann method. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 304, 246–253 (2006)
Wang M., Chen S.: Electroosmosis in homogeneously charged micro- and nanoscale random porous media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 314, 264–273 (2007)
Wang D., Summers J.L., Gaskell P.H.: Modelling of electrokinetically driven mixing flow in microchannels with patterned blocks. Comput. Math. Appl. 55, 1601–1610 (2008)
Tang G.H., Ye P.X., Tao W.Q.: Pressure-driven and electroosmotic non-Newtonian flows through microporous media via lattice Boltzmann method. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 165, 1536–1542 (2010)
Park H.M., Lee J.S., Kim T.W.: Comparison of the Nernst–Planck model and the Poisson–Boltzmann model for electroosmotic flows in microchannels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 315, 731–739 (2007)
Wang M., Kang Q.: Modeling electrokinetic flows in microchannels using coupled lattice Boltzmann methods. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 728–744 (2010)
Dupuis, A.: From a lattice Boltzmann model to a parallel and reusable implementation of a virtual river. PhD Thesis, University of Geneva, Geneva (2002)
Zou Q., He X.: On pressure and velocity boundary conditions for the lattice Boltzmann BGK model. Phys. Fluids 9, 1591–1598 (1997)
Ginzburg I.: Variably saturated flow described with the anisotropic Lattice Boltzmann methods. Comput. Fluids 35, 831–848 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadipoor, O.R., Niazmand, H. & Mirbozorgi, S.A. Numerical Simulation of Electroosmotic Flow in Flat Microchannels with Lattice Boltzmann Method. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 1291–1302 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0679-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0679-x