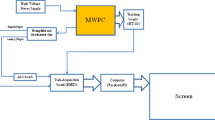
Abstract
We present a measurement of the most probable cosmic muon energy at near sea level using a two-paddle cosmic ray detector. Muon rates at two different elevations (27 and 326 m) were measured. Data were collected for 2–3 h for each data set at 1 min intervals in the afternoon of successive days. Muon counts were extracted from a Gaussian fit to the distributions of both sets. Despite the fact that only a limited amount of data were collected and measurements were performed at relatively close altitudes, we observed good agreement between the 2.28 ± 0.21 GeV energy measured in this work and the value of 2 GeV that is reported in the literature.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badhwar G.D., Stephens S.A., Golden R.L.: Analytic representation of the proton–proton and proton–nucleus cross-sections and its application to the sea-level spectrum and charge ratio of muons. Phys. Rev. D 15, 820–831 (1977)
Greider P.K.F.: Researcher’s reference manual and data book. Cosmic Rays at Earth. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2001)
Honda M., Kasahara K., Hidaka K., Midorikawa S.: Atmospheric neutrino fluxes. Phys. Lett. B 248, 193–198 (1990)
Rastin B.C.: An accurate measurement of the sea-level muon spectrum within the range 4 to 3000 GeV/c. J. Phys. G Nucl. Phys. 10, 1609–1628 (1984)
Kremer J. et al.: Measurements of ground-level muons at two geomagnetic locations. Phys. Rev. Lett 83, 4241–4244 (1999)
Collier, M.; Wolfley, L.: Assembly Manual for the Berkeley Lab Cosmic Ray Detector. LBNL-51419 (2006)
Particle Data Group: Cosmic rays. Rev. Particle Phys. (2010). http://pdg.lbl.gov/2010/reviews/rpp2010-rev-cosmic-rays.pdf
United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR): Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation, p. 36. United Nations, New York (1993)
National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements: Exposure of the Population in the United States and Canada from Natural Background Radiation. NCRP Report No. 94 (1987)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bektasoglu, M., Tonguc, B.T. Estimation of the Most Probable Muon Energy at Sea Level Using Two-Paddle Cosmic Ray Detectors. Arab J Sci Eng 37, 197–200 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-011-0164-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-011-0164-3