Abstract
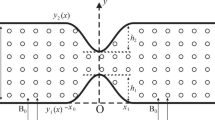
Flow of a Casson fluid through a two-dimensional porous channel containing a local constriction is numerically investigated assuming that the resistance offered by the porous medium obeys the Darcy's law. Treating the constriction as another porous medium which obeys the Darcy-Forcheimer model, the equations governing fluid flow in the main channel and the constriction itself are numerically solved using the finite-volume method (FVM) based on the pseudo-transient SIMPLE algorithm. It is shown that an increase in the porosity of the channel decreases the shear stress exerted on the constriction. On the other hand, an increase in the fluid's yield stress is predicted to increase the maximum shear stress experienced by the constriction near its crest. The porosity of the constriction itself is predicted to have a negligible effect on the plaque's shear stress. But, the momentum of the weak flow passing through the constriction is argued to lower the bulk fluid from separating downstream of the constriction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Roubaie, S., E.D. Jahnsen, M. Mohammed, C. Henderson-Toth, and E.A.V. Jones, 2011, Rheology of embryonic avian blood, Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circul. Physiol. 301, H2473–H2481.
Alimohamadi, H. and K. Sadeghy, 2015, On the use of magnetic fields for controlling the temperature of hot spots of porous plaques in stenosis arteries, Nihon Reoroji Gakkaishi 43, 135–144.
Alimohamadi, H., 2014, Simulating Blood Flow in Stenoed Artery under the Influence of External Magnetic Field, MSc Thesis, University of Tehran.
Anderson, H.I., R. Halden, and T. Glomsaker, 2000, Effects of surface irregularities on flow resistance in differently shaped arterial stenoses, J. Biomech. 33, 1257–1262.
Bear, J., 1972, Dynamics of Fluids in Porous Media, American Elsevier, New York.
Bryan, J., 2014, The rise and fall of the clot buster, Pharm. J., 293, 20065679.
Buchanan, J.R., C. Kleinstreuer, and J.K. Comer, 2000, Rheological effects on pulsatile hemodynamics in a stenosed tube, Comput. Fluids 29, 695–724.
Chakravarty, S., 1987, Effects of stenosis on the flow-behavior of blood in an artery, Int. J. Eng. Sci. 25, 1003–1016.
Charm, S. and G. Kurland, 1965, Viscometry of human blood for shear rates of 0-100,000 sec−1, Nature 206, 617–618.
Charm, S. and G. S. Kurland, 1962, Tube flow behavior and shear stress-shear rate characteristics of canine blood, Am. J. Physiol. 203, 417–421.
Charm, S.E., W. McComis, and G. Kurland, 1964, Rheology and structure of blood suspensions, J. Appl. Physiol. 19, 127–133.
Cho, Y.I. and K.R. Kensey, 1991, Effects of the non-Newtonian viscosity of blood on flows in a diseased arterial vessel. Part 1: Steady flow, Biorheology 28, 241–262.
Dash, R.K., K.N. Mehta, and G. Jayaraman, 1996, Casson fluid flow in a pipe filled with a homogeneous porous medium, Int. J. Eng. Sci. 34, 1145–1156.
Deshpande, M.D., D.P. Giddens, and R.F. Mabon, 1976, Steady laminar flow through modeled vascular stenoses, J. Biomech. 9, 165–174.
El-Shahed, M., 2003, Pulsatile flow of blood through a stenosed porous medium under periodic body acceleration, Appl. Math. Comput. 138, 479–488.
Giddens, D.P., C.K. Zarins, and S. Glagov, 1993, The role of fluid mechanics in the localization and detection of atherosclerosis, J. Biomech. Eng.-Trans. ASME 115, 588–594.
Hebbel, R.P., A. Leung, and N. Mohandas, 1990, Oxidationinduced changes in microrheologic properties of the red blood cell membrane, Blood 76, 1015–1020.
Huang, H. and B.R. Seymour, 1995, A finite difference method for flow in a constricted channel, Comput. Fluids 24, 153–160.
Hunt, R., 1990, Numerical solution of the laminar flow in a constricted channel at moderately high Reynolds number using Newton iteration, Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 11, 247–259.
Karageorghis, A. and T.N. Phillips, 1991, Conforming Chebyshev spectral collocation methods for the solution of laminar flow in a constricted channel, IMA J. Numer. Anal. 11, 33–54.
Khakpour, M. and K. Vafai, 2008, Critical assessment of arterial transport models, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 51, 807–822.
Ku, D.N., 1970, Blood flow in arteries, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 29, 399–434.
Layek, G.C. and C. Midya, 2007, Effect of constriction height on flow separation in a two-dimensional channel, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 12, 745–759.
Lee, J.S. and Y.C. Fung, 1970, Flow in locally-constricted tubes at low Reynolds numbers, J. Appl. Mech.-Trans. ASME 37, 9–16.
Lee, T.S., 1994, Steady laminar fluid flow through a variable constrictions in vascular tube, J. Fluids Eng.-Trans. ASME 116, 66–71.
Macosko, C.W., 1994, Rheology: Principles, Measurements and Applications, 1st Ed., VCH, New York.
Mandal, P.K., 2005, An unsteady analysis of non-Newtonian blood flow through tapered arteries with a stenosis, Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 40, 151–164.
Merril, E.W., 1969, Rheology of blood, Physiol. Rev. 49, 863–888.
Mustapha, N., P.K. Mandal, P.R. Johnston, and N. Amin, 2010, A numerical simulation of unsteady blood flow through multiirregular arterial stenoses, Appl. Math. Model. 34, 1559–1573.
Neren, R.M., 1992, Vascular fluid mechanics, the arterial wall and atherosclerosis, J. Biomech. Eng.-Trans. ASME 114, 274–282.
Panagiotis, N. and D. Drikakis, 2003, Effects of blood models on flows through a stenosis, Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 43, 597–635.
Papanastasiou, T.C., 1987, Flows of materials with yield, J. Rheol. 31, 385–404.
Ramesh, K. and M. Devakar, 2015, Some analytical solutions for flows of Casson fluid with slip boundary conditions, Ain Shams Eng. J. 6, 967–975.
Simmonds, M.J., H.J. Meiselman, and O.K. Baskurt, 2013, Blood rheology and aging, J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 10, 291–301.
Solzbach, U., H. Wollschläger, A. Zeiher, and H. Just, 1987, Effect of stenotic geometry on flow behavior across stenotic models, Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 25, 543–550.
Stroud, J.S., S.A. Berger, and D. Saloner, 2000, Influence of stenosis morphology on flow through severely stenotic vessels: Implications for plaque rupture, J. Biomech. 33, 443–455.
Venkatesan, J., D.S. Sankar, K. Hemalatha, and Y. Yatim, 2013, Mathematical analysis of Casson fluid model for blood rheology in stenosed narrow arteries, J. Appl. Math. 2013, 583809.
Walburn, F.J. and D.J. Schneck, 1976, A constitutive equation for whole human blood, Biorheology 13, 201–210.
Wei, H.H., S.L. Waters, S.Q. Liu, and J.B. Grotberg, 2003, Flow in a wavy-walled channel lined with a poroelastic layer, J. Fluid Mech. 492, 23–45.
Whale, M.D., A.J. Grodzinsky, and M. Johnson, 1996, The effect of aging and pressure on the specific hydraulic conductivity of the aortic wall, Biorheology 33, 17–44.
Young, D.F., 1979, Fluid mechanics of arterial stenoses, J. Biomech. Eng.-Trans. ASME 101, 157–175.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amlimohamadi, H., Akram, M. & Sadeghy, K. Flow of a Casson fluid through a locally-constricted porous channel: a numerical study. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 28, 129–137 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-016-0012-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-016-0012-9