Abstract
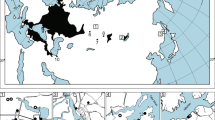
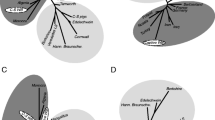
In total, 721 specimens from eight populations of the raccoon dog Nyctereutes procyonoides across native and colonized areas have been studied. The most polymorphic populations inhabit the European part of Russia and a part of the native area. The raccoon dog from Eastern Poland and the Primorie Far East is characterized by low intrapopulational variability. Quantitative genetic variations in the studied populations indicate a relatively higher level in the population from the Primorie Far East compared to the Southern Vologda and Eastern Poland. The pattern of morphological variability in the raccoon dog is shaped by such factors as the latest phylogenetic history of the species and the structure of the morphotype frequency in the time of the divergence of the populations on both micro-and macro-geographic levels. The influence of geographic and climatic factors forms a well-pronounced trend towards diversification in tooth morphology, which is most probably the consequence of adaptations to changes in the food niche.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansorge H, Ranyuk M, Kauhala K, Kowalczyk R, Stier N (2009) Raccoon dog, Nyctereutes procyonoides, populations in the area of origin and in colonized regions—the epigenetic variability of an immigrant. Ann Zool Fenn 46:51–62
Bacigalupe LD (2009) Biological invasions and phenotypic evolution: a quantitative genetic perspective. Biol Invasions 11:2243–2250
Bauchau V (1988) Non-metrical variation in wild mammals: a bibliography. Mammal Revue 18:195–200
Berry RJ (1986) Genetics of insular populations of mammals, with particular reference to differentiation and founder effects in British small mammals. Biol J Linn Soc 28:205–230
Berry AC, Berry RJ (1967) Epigenetic variation in the human cranium. J Anat 101:361–379
Borisov VI, Baranov AS, Valetsky AV, Zakharov VM (1997) Developmental stability of the mink Mustela vison under the impact of PCB. [In: Developmental homeostasis in natural populations of mammals: phenetic approach. V. M. Zakharov and A. V. Yablokov, eds]. Acta Theriologica, Suppl. 4: 17–26.
Danilov PI (2009) New mammal species in the European north of Russia. Karelskii Nauchnyi Tsentr Russ Akad Nauk, Petrozavodsk [in Russian with English resume]
Dayan T, Wool D, Simberloff D (2002) Variation and covariation of skulls and teeth: modern carnivores and interpretation of fossil mammals. Paleobiology 28:508–526
Dgebuadze YY (2014) Invasions of alien species in Holarctic: some results and prospects of studies. Russian Journal of Biological Invasions 5:61–64
Drygala F, Stier N, Zoller H, Mix HM, Bögelsack K, Roth M (2008a) Spatial organization and intra-specific relationship of the raccoon dog Nyctereutes procyonoides in Central Europe. Wildl Biol 14:457–466
Drygala F, Stier N, Zoller H, Bögelsack K, Mix HM, Roth M (2008b) Habitat use of the raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in North-Eastern Germany. Mamm Biol 73:371–378
Haba C, Oshida T, Sasaki M, Endo H, Ichikawa H, Masuda Y (2008) Morphological variation of the Japanese raccoon dog: implications for geographical isolation and environmental adaptation. J Zool 274:239–247
Jędrzejewska B, Jędrzejewski W (1998) Predation in vertebrate communities: the Białowieża primeval Forest as a case study. Ecological studies 13e5. Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York
Kauhala K, Kowalczyk R (2011) Invasion of the raccoon dog Nyctereutes procyonoides in Europe: history of colonization features behind its success and threats to native fauna. Current Zoology 57:584–598
Kauhala K, Viranta S, Kishimoto M, Helle E, Obara I (1998) Skull and tooth morphology of Finnish and Japanese raccoon dogs. Ann Zool Fenn 35:1–16
Kilvitis H, Alvarez M, Foust CM, Robertson M, Schrey AW, Richards CL (2014) Ecological epigenetics. In: Landry C, Aubin-Horth N (eds) Ecological and evolutionary genomics. Springer, Dordrecht, pp. 191–210
Korablev PN, Alekseeva TA (1997) Grey wolf Canis lupus in population phonetic. Nauka, Moscow [In Russian]
Korablev NP, Korablev PN (2013) Patterns of morphological variability in reintroduced populations with two beaver subspecies Castor fiber orientoeuropaeus and Castor fiber belorussicus (Castoridae, Rodentia) as an example. Biol Bull Rev 3:84–97
Korablev NP, Szuma E (2014) Variability of native and invasive raccoon dog Nyctereutes procyonoides populations: looking at translocations from a morphological point of view. Acta Theriol 59:61–79
Korablev PN, Alekseeva TA, Korablev NP (1997) European beaver (Castor fiber), population phenetics. catalogue of the main nonmetric variations of craniological characters of mammals. Nauka, Moscow In Russian
Korablev PN, Korablev MP, Korablev NP (2011a) The state of predatory mammal populations in the impact zone of the Kalinin nuclear power plant as inferred from their phene pool. Russ J Ecol 42:288–295
Korablev NP, Korablev MP, Korablev PN (2011b) Introduction of alien species and microevolution: the European beaver, raccoon dog and American mink. Biol Bull 38:146–155
Korablev NP, Korablev MP, Rozhnov VV, Korablev PN (2011c) Polymorphism of the mitochondrial DNA control region in the population of raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides gray, 1834) introduced into the upper Volga Basin. Russ J Genet 47:1378–1385
Korablev NP, Korablev MP, Korablev PN (2012) Craniometrical variability of raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides Grey., Carnivora, Canidae) of the Tver region: from introducents to modern populations. MOIP Otdel Biologicheskij 117:16–25 [In Russian with English summary]
Korablev MP, Korablev PN, Korablev NP, Tumanov IL (2014) Polymorphism of the endangered European mink (Mustela lutreola, Carnivora, Mustelidae) population in the central Forest reserve and neighboring areas. Biol Bull 41:620–628
Korablev NP, Saveljev AP, Puzachenko YG (2015) Polymorphism factors in autochthonous and reintroduced populations of Eurasian beavers (Castor fiber, Castoridae, Rodentia. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal 94:241–258 [In Russian with English summary]
Korablev NP, Korablev MP, Korablev PN, Tumanov IL (2016a) Epigenetic variation in the American mink, Neovison vison, from Eastern Europe: a search for polymorphism factors. Russ J Ecol 47(3):289–295
Korablev MP, Korablev NP, Korablev PN, Tumanov IL (2016b) Intrapopulation polymorphism of the pine Marten (Martes martes, Carnivora, Mustelidae) from Tver region. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal 95(1):80–93 In Russian with English summary
Kowalczyk R, Jędrzejewska B, Zalewski A, Jędrzejewski W (2008) Facilitative interactions between the Eurasian badger (Meles meles), the red fox (Vulpes vulpes), and the invasive raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in Bialowieza primeval Forest, Poland. Can J Zool 86:1389–1396
Makarov VV, Sukharev OI, Gulyukin AM, Sokolov MN, Litvinov OB (2009) Rabies of raccoon dog: statistical analysis of morbidity. Veterinariya 6:20–25 In Russian with English summary
Markova E, Malygin V, Montuir S, Nadachowski A, Jean-Pierre Quéré JP, Ochman K (2010) Dental variation in sibling species Microtus arvalis and M. rossiaemeridionalis (Arvicolinae, Rodentia): between-species comparisons and geography of morphotype dental patterns. J Mamm Evol 17:121–139
Mazak JH (2010) Craniometric variation in the tiger (Panthera tigris): implications for patterns of diversity, taxonomy and conservation. Mamm Biol 75:45–68
Meiri S, Dayan T, Simberloff D (2004) Carnivores, biases and Bergmann’s rule. Biol J Linn Soc 81:579–588
Monakhov VG (2001) Phenetic analysis of aboriginal and introduced populations of sable (Martes zibellina) in Russia. Genetics 37:1281–1289 In Russian with English summary
Nowak E (1993) Nyctereutes procyonoides Gray, 1834. Marderhund. In: Niethammer, Krapp F (eds) Handbuch der Säugetiere Europas, Bd. 5/2. Aula-Verlag, Wiesbaden, pp. 213–248
Orlov VN, Okulova NM (2001) Implication of the Hardy-Weinberg equation for analyzing the geographical variability of the yellow-necked mouse Apodemus flavicollis (Muridae, Rodentia. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal 80:607–617
Pankakoski E (1985) Epigenetic asymmetry as an ecological indicator in muskrats. J Mammal 66(1):52–57
Pavlov MP, Korsakov IB, Lavrov NP (1974) Acclimatization of commercial game mammals and birds. Volgo-Vyatskoe Izdatelstvo, Kirov. [In Russeian].
Pitra C, Schwarz S, Fickel J (2010) Going west—invasion genetics of the alien raccoon dog Nyctereutes procyonoides in Europe. Eur J Wildl Res 56:117–129
Renaud S, Rodrigues HG, Ledevin R, Pisanu B, Chapuis JL, Hardoin EA (2015) Fast evolutionary response of house mice to anthropogenic disturbance on a sub-Antarctic island. Biol J Linn Soc 114:513–526
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Saveljev AP (1996) Künstliche Aussiedlung von Tieren—ein Atavismus oder eine Notwendigkeit in der Mensch-Natur-Beziehung. Beiträge zur Jagd- und Wildforschung 21:255–259
Selander RK, Johnston RF (1967) Evolution in the house sparrow. I. Intrapopulation variation in North America. Condor 69:217–258
Sjöberg G (1996) Genetic characteristics of introduced birds and mammals. Wildl Biol 2:159–164
Sorokin MG (1956) Biological and morphological changes of Raccoon dog, acclimatized in Kalinin oblast. Uch Zapiski Kalininskogo Gos Ped Inst 20:183–214 [in Russian]
Suchentrunk F, Alkon PU, Willing R, Yom-Tov Y (2000) Epigenetic dental variability of Israeli hares (Lepus sp.): ecogenetic or phylogenetic causation? J Zool 252:503–515
Sutor A, Kauhala K, Ansorge H (2010) Diet of the raccoon dog Nyctereutes procyonoides—a canid with an opportunistic foraging strategy. Acta Theriol 55:165–176
Szuma E (1994) Quasi-continuous variation of the first premolars in the polish population of the badger Meles meles. Acta Theriol 39:201–208
Szuma E (2002) Microevolutionary trends in the dentition of the red fox (Vulpes vulpes. J Zool Syst Evol Res 40:1–10
Szuma E (2003) Microevolutionary trends in the dentition of the red fox (Vulpes vulpes. J Zool Syst Evol Res 41:47–56
Szuma E (2004) Evolutionary implications of morphological variation in the lower carnassial of red fox Vulpes vulpes. Acta Theriol 49:433–447
Szuma E (2008) Evolutionary and climatic factors affecting tooth size in the red fox Vulpes vulpes in the Holarctic. Acta Theriol 53(4):289–332
Szuma E (2011) Ecological and evolutionary determinants of dental polymorphism in the arctic fox Vulpes (Alopex) lagopus. Ann Zool Fenn 48:191–213
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Ulevicius A, Sidorovich V, Lauzhel G (2001) Specificity of non-metric parameters of American mink (Mustela vison) populations in relation to habitat differences in Belarus. Mamm Biol 66:35–47
Virgos E, Kowalczyk R, Trua A, Marinis A, Mangas JG, Barea-Azcon JV, Geffen E (2011) Body size clines in the European badger and the abundant centre hypothesis. J Biogeogr 38:1546–1556
Wolsan M (1989) Dental polymorphism in the genus Martes (Carnivora: Mustelidae) and its evolutionary significance. Acta Theriol 34:545–593
Yablokov AV (1987) Population biology. Vysshaja Schkola, Moscow [In Russian]
Yudin VG (1977) Raccoon dog in Primor’ye and Priamur’ye. Nauka, Moscow [in Russian]
Zhivotovskii LA (1979) Index of the similarity of populations in polymorphic characters. Zhurnal Obshchei Biologii 40:587–602 In Russian with English summary
Zhivotovskii LA (1982) The index of population variability in polymorphic features, in population Phenetics. Nauka, Moscow [In Russian]
Zubov AA, Khaldeeva NI (1989) Odontology in modern anthropology. Nauka, Moscow [In Russian]
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the BIOCONSUS 7th EU Framework Programme and RFBR grant 14-04-97510. We also thank two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments regarding the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Magdalena Niedziałkowska
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 39 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korablev, N.P., Szuma, E., Korablev, P.N. et al. Dental polymorphism of the raccoon dog in indigenous and invasive populations: internal and external causation. Mamm Res 62, 163–177 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13364-016-0293-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13364-016-0293-x