Abstract
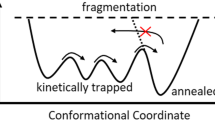
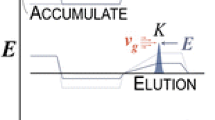
During their travel inside a traveling wave ion mobility cell (TW IMS), ions are susceptible to heating because of the presence of high intensity electric fields. Here, we report effective temperatures T eff,vib obtained at the injection and inside the mobility cell of a SYNAPT G2 HDMS spectrometer for different probe ions: benzylpyridinium ions and leucine enkephalin. Using standard parameter sets, we obtained a temperature of ~800 K at injection and 728 ± 2 K into the IMS cell for p-methoxybenzylpyridinium. We found that T eff,vib inside the cell was dependent on the separation parameters and on the nature of the analyte. While the mean energy of the Boltzmann distributions increases with ion size, the corresponding temperature decreases because of increasing numbers of vibrational normal modes. We also investigated conformational rearrangements of 7+ ions of cytochrome c and reveal isomerization of the most compact structure, therefore highlighting the effects of weak heating on the gas-phase structure of biologically relevant ions.

ᅟ






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shvartsburg, A.A.: Differential Ion Mobility Spectrometry: Nonlinear Ion Transport and Fundamentals of FAIMS, pp. 1–54. CRC Press Inc, Florida (2008)
Mason, E.A., McDaniel, E.W.: Transport Properties of Ions in Gases, pp. 1–29. Wiley, New York (1988)
Song, J., Grun, C.H., Heeren, R.M., Janssen, H.G., van den Brink, O.F.: High-resolution ion mobility spectrometry-mass spectrometry on poly(methyl methacrylate). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 49(52), 10168–10171 (2010)
Hilton, G.R., Jackson, A.T., Thalassinos, K., Scrivens, J.H.: Structural analysis of synthetic polymer mixtures using ion mobility and tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 80(9720–9725), 639 (2008)
Ruotolo, B.T., Benesch, J.L., Sandercock, A.M., Hyung, S.J., Robinson, C.V.: Ion mobility-mass spectrometry analysis of large protein complexes. Nat. Protoc. 3(7), 1139–1152 (2008)
Henderson, S.C., Valentine, S.J., Counterman, A.E., Clemmer, D.E.: ESI/Ion trap/ion mobility/time-of-flight mass spectrometry for rapid and sensitive analysis of biomolecular mixtures. Anal. Chem. 71(2), 291–301 (1999)
Karpas, Z., Eiceman, G.A., Krylov, E.V., Krylova, N.: Models on ion heating and mobility in linear field drift tubes and in differential mobility spectrometers. Int. J. Ion Mobil. Spectrom. 7(1), 42–52 (2004)
Giles, K., Pringle, S.D., Worthington, K.R., Little, D., Wildgoose, J.L., Bateman, R.H.: Applications of a traveling wave-based radio-frequency-only stacked ring ion guide. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 18(20), 2401–2414 (2004)
Shvartsburg, A.A., Smith, R.D.: Fundamentals of traveling wave ion mobility spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 80(24), 9689–9699 (2008)
Guevremont, R.: High-field asymmetric waveform ion mobility spectrometry: a new tool for mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1058(1/2), 3–19 (2004)
May, J.C., McLean, J.A.: The influence of drift gas composition on the separation mechanism in traveling wave ion mobility spectrometry: insight from electrodynamic simulations. Int. J. Ion Mobil. Spectrom. 16(2), 85–94 (2013). 659
Bush, M.F., Campuzano, I.D.G., Robinson, C.V.: Ion mobility mass spectrometry of peptide ions: effects of drift gas and calibration strategies. Anal. Chem. 84(16), 7124–7130 (2012)
McLuckey, S.A.: Principles of collisional activation in analytical mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 3, 599–614 (1992)
Merenbloom, S.I., Flick, T.G., Williams, E.R.: How hot are your ions in TWAVE ion mobility spectrometry? J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 23(3), 553–562 (2012)
Michaelevski, I., Kirshenbaum, N., Sharon, M.: T-wave ion mobility mass spectrometry: basic experimental procedures for protein complex analysis. Anal. Chem. 82(22), 9484–9491 (2010)
Morsa, D., Gabelica, V., De Pauw, E.: Effective temperature of ions in traveling wave ion mobility spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 83(14), 5775–5782 (2011)
Collette, C., De Pauw, E.: Calibration of the internal energy distribution of ions produced by electrospray. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 12, 165–170 (1998)
Collette, C., Drahos, L., De Pauw, E., Vekey, K.: Comparison of the internal energy distributions of ions produced by different electrospray sources. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 12, 1673–1678 (1998)
Gabelica, V., De Pauw, E.: Internal energy and fragmentation of ions produced in electrospray sources. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 24(4), 566–587 (2005)
Schnier, P.D., Price, W.D., Strittmatter, E.F., Williams, E.R.: Dissociation energetics and mechanisms of leucine enkephalin (M+H)+ and (2M+X)+Ions (X=H, Li, Na, K, and Rb) measured by blackbody infrared radiative dissociation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 8, 771–780 (1997)
Valentine, S.J., Counterman, A.E., Clemmer, D.E.: Conformer-dependent proton-transfer reactions of ubiquitin ions. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 8, 954–961 (1997)
Counterman, A.E., Valentine, S.J., Srebalus, C.A., Henderson, S.C., Hoaglund, C.S., Clemmer, D.E.: High-order structure and dissociation of gaseous peptide aggregates that are hidden in mass spectra. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 9, 743–759 (1998)
Clemmer Cross Section Database, h.w.i.e.c. Available at: http://www.indiana.edu/~clemmer. Accessed July 2013.
Shelimov, K.B., Clemmer, D.E., Hudgins, R.R., Jarrold, M.F.: Protein structure in vacuo: gas-phase conformations of BPTI and cytochrome c. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119, 2240–2248 (1997)
Frisch, M.J., Trucks, G.W., Schlegel, H.B., Scuseria, G.E., Robb, M.A., Cheeseman, J.R., Scalmani, G., Barone, V., Mennucci, B., Petersson, G.A., Nakatsuji, H., Caricato, M., Li, X., Hratchian, H.P., Izmaylov, A.F., Bloino, J., Zheng, G., Sonnenberg, J.L., Hada, M., Ehara, M., Toyota, K., Fukuda, R., Hasegawa, J., Ishida, M., Nakajima, T., Honda, Y., Kitao, O., Nakai, H., Vreven, T., Montgomery Jr., J.A., Peralta, J.E., Ogliaro, F., Bearpark, M., Heyd, J.J., Brothers, E., Kudin, K.N., Staroverov, V.N., Kobayashi, R., Normand, J., Raghavachari, K., Rendell, A., Burant, J.C., Iyengar, S.S., Tomasi, J., Cossi, M., Rega, N., Millam, J.M., Klene, M., Knox, J.E., Cross, J.B., Bakken, V., Adamo, C., Jaramillo, J., Gomperts, R., Stratmann, R.E., Yazyev, O., Austin, A.J., Cammi, R., Pomelli, C., Ochterski, J.W., Martin, R.L., Morokuma, K., Zakrzewski, V.G., Voth, G.A., Salvador, P., Dannenberg, J.J., Dapprich, S., Daniels, A.D., Farkas, Ö., Foresman, J.B., Ortiz, J.V., Cioslowski, J., Fox, D.J.: Gaussian 09, Revision A.1. Gaussian Inc, Wallingford (2009)
Andersson, M.P., Uvdal, P.: New scale factors for harmonic vibrational frequencies using the B3LYP density functional method with the triple-basis set 6–311+G(d, p). J. Phys. Chem. A 109, 2937–2941 (2005)
Shvartsburg, A.A., Mashkevich, S.V., Baker, E.S., Smith, R.D.: Optimization of algorithms for ion mobility calculations. J. Phys. Chem. A 111(10), 2002–2010 (2007)
Breuker, K.: Principles of mass spectrometry applied to biomolecules, pp. 177–212. Wiley, New-York (2006)
Chen, Y.-L., Collings, B.A., Douglas, D.J.: Collision cross sections of myoglobin and cytochrome c ions with Ne, Ar, and Kr. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 8, 681–687 (1997)
Clemmer, D.E., Hudgins, R.R., Jarrold, M.F.: Naked protein conformations: cytochrome c in the gas phase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 117(40), 10141–10142 (1995)
Mao, Y., Woenckhaus, J., Kolafa, J., Ratner, M.A., Jarrold, M.F.: Thermal unfolding of unsolvated cytochrome c: experiment and molecular dynamics simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121, 2712–2721 (1999)
Balthasart, F., Plavec, J., Gabelica, V.: Ammonium ion binding to DNA G-quadruplexes: do electrospray mass spectra faithfully reflect the solution-phase species? J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 24(1), 1–8 (2013)
López, A., Tarragó, T., Vilaseca, M., Giralt, E.: Applications and future of ion mobility mass spectrometry in structural biology. New J. Chem. 37(5), 1283–1289 (2013)
Saikusa, K., Fuchigami, S., Takahashi, K., Asano, Y., Nagadoi, A., Tachiwana, H., Kurumizaka, H., Ikeguchi, M., Nishimura, Y., Akashi, S.: Gas-phase structure of the histone multimers characterized by ion mobility mass spectrometry and molecular dynamics simulation. Anal. Chem. 85(8), 4165–4171 (2013). 737
Cramer, C.J.: Essentials of Computational Chemistry, pp. 233–271. Wiley, New-York (2004)
Hünenberger, P.H.: Thermostat algorithms for molecular dynamics simulations. Adv. Polym. Sci. 173, 105–149 (2005)
Acknowledgment
The authors thank the FRS-FNRS for financial support. Professor Bernard Leyh (University of Liege) is acknowledged for discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 303 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morsa, D., Gabelica, V. & De Pauw, E. Fragmentation and Isomerization Due to Field Heating in Traveling Wave Ion Mobility Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 25, 1384–1393 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-014-0909-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-014-0909-9