Abstract
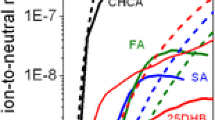
In a previous study (J. Mass Spectrom. 48, 299–305, 2013), we observed that the abundance of each ion in a matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) spectrum looked thermally determined. To find out the explanation for the phenomenon, we estimated the ionization efficiency and the reaction quotient (QA) for the autoprotolysis of matrix, M + M → [M + H]+ + [M − H]−, from the temperature-controlled laser desorption ionization spectra of α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (CHCA) and 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHB). We also evaluated the equilibrium constants (KA) for the autoprotolysis at various temperatures by quantum chemical calculation. Primary ion formation via various thermal models followed by autoprotolysis-recombination was compatible with the observations. The upper limit of the effective temperature of the plume where autoprotolysis-recombination occurs was estimated by equating QA with the calculated equilibrium constant.

ᅟ




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Hillenkamp, F., Peter-Katalinić, J.: MALDI MS. A Practical Guide to Instrumentation, Methods, and Applications. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim (2007)
Tanaka, K., Waki, H., Ido, Y., Akita, S., Yoshida, Y., Yoshida, T.: Protein and Polymer analyses up to m/z 100,000 by laser ionization time-of-flight mass spectroemtry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2, 151–153 (1988)
Karas, M., Hillenkamp, F.: Laser desorption ionization of proteins with molecular masses exceeding 10,000 Daltons. Anal. Chem. 60, 2299–2301 (1988)
Trimpin, S., Wang, B., Inutan, E.D., Li, J., Lietz, C.B., Harron, A., Pagnotti, V.S., Sardelis, D., McEwen, C.N.: A mechanism for ionization of nonvolatile compounds in mass spectrometry: considerations from maldi and inlet ionization. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 23, 1644–1660 (2012)
Duncan, M.W., Roder, H., Hunsucker, S.W.: Quantitative matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Briefings Funct. Genom. Proteom. 7, 355–370 (2008)
Bae, Y.J., Park, K.M., Kim, M.S.: Reproducibility of temperature-selected mass spectra in matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization of peptides. Anal. Chem. 84, 7107–7111 (2012)
Ahn, S.H., Park, K.M., Bae, Y.J., Kim, M.S.: Quantitative reproducibility of mass spectra in matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization and unraveling of the mechanism for gas-phase peptide ion formation. J. Mass Spectrom. 48, 299–305 (2013)
Brown, R.S., Carr, B.L., Lennon, J.J.: Factors that influence the observed fast fragmentation of peptides in matrix-assisted laser desorption. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 7, 225–232 (1996)
Yoon, S.H., Moon, J.H., Kim, M.S.: A Comparative study of in- and post-source decays of peptide and preformed ions in matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry: effective temperature and matrix effect. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 21, 1876–1883 (2010)
Ahn, S.H., Park, K.M., Bae, Y.J., Kim, M.S.: Efficient methods to generate reproducible mass spectra in matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization of peptides. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 24, 868–876 (2013)
Kinsel, G.R., Yao, D., Yassin, F.H., Marynick, D.S.: Equilibrium conditions in laser-desorbed plumes: thermodynamic properties of α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid and protonation of amino acids. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 12, 359–367 (2006)
Asakawa, D., Takayama, M.: Cα–C bond cleavage of the peptide backbone in MALDI in-source decay using salicylic acid derivative matrices. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 22, 1224–1233 (2011)
Molin, L., Seraglia, R., Czarnocki, Z., Maurin, J.K., Pluciński, F.A., Traldi, P.: On the primary ionization mechanism(s) in matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2012, Article ID 161865 (2012)
Yau, P.Y., Chan, T.W.D., Cullis, P.G., Colburn, A.W., Derrick, P.J.: Threshold fluences for production of positive and negative ions in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization using liquid and solid matrices. Chem. Phys. Lett. 202, 93–100 (1993)
Dashtiev, M., Wäfler, E., Röhling, U., Gorshkov, M., Hillenkamp, F., Zenobi, R.: Positive and negative analyte ion yield in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 268, 122–130 (2007)
Bae, Y.J., Yoon, S.H., Moon, J.H., Kim, M.S.: Optimization of reflectron for kinetic and mechanistic studies with multiplexed multiple tandem (MSn) time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 31, 92–99 (2010)
Spengler, B.: Post-source decay analysis in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry of biomolecules. J. Mass Spectrom. 32, 1019–1036 (1997)
Bae, Y.J., Shin, Y.S., Moon, J.H., Kim, M.S.: Degree of ionization in MALDI of peptides: thermal explanation for the gas-phase ion formation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 23, 1326–1335 (2012)
Frisch, M.J., Trucks, G.W., Schlegel, H.B., Scuseria, G.E., Robb, M.A., Cheeseman, J.R., Scalmani, G., Barone, V., Mennucci, B., Petersson, G.A., Nakatsuji, H., Caricato, M., Li, X., Hratchian, H.P., Izmaylov, A.F., Bloino, J., Zheng, G., Sonnenberg, J.L., Hada, M., Ehara, M., Toyota, K., Fukuda, R., Hasegawa, J., Ishida, M., Nakajima, T., Honda, Y., Kitao, O., Nakai, H., Vreven, T., Montgomery, J.A. Jr., Peralta, J.E., Ogliaro, F., Bearpark, M., Heyd, J.J., Brothers, E., Kudin, K.N., Staroverov, V.N., Kobayashi, R., Normand, J., Raghavachari, K., Rendell, A., Burant, J.C., Iyengar, S.S., Tomasi, J., Cossi, M., Rega, N., Millam, J.M., Klene, M., Knox, J.E., Cross, J. B., Bakken, V., Adamo, C., Jaramillo, J., Gomperts, R., Stratmann, R.E., Yazyev, O., Austin, A.J., Cammi, R., Pomelli, C., Ochterski, J.W., Martin, R.L., Morokuma, K., Zakrzewski, V.G., Voth, G.A., Salvador, P., Dannenberg, J.J., Dapprich, S., Daniels, A.D., Farkas, Ö., Foresman, J.B., Ortiz, J.V., Cioslowski, J., Fox, D.J.: Gaussian 09, revision A. 02, Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford CT (2009)
Feldhaus, D., Menzel, C., Berkenkamp, S., Hillenkamp, F., Dreisewerd, K.: Influence of the laser fluence in infrared matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization with a 2.94 μm Er:YAG laser and a flat-top beam profile. J. Mass Spectrom. 35, 1320–1328 (2000)
Nishikaze, T., Takayama, M.: Disappearance of interfering alkali-metal adducted peaks from matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectra of peptides with serine addition to α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid matrix. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 21, 3345–3351 (2007)
Liao, P.-C., Allison, J.: Ionization processes in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry: matrix-dependent formation of [M + H]+ versus [M + Na]+ ions of small peptides and some mechanistic comments. J. Mass Spectrom. 30, 408–423 (1995)
Park, K.M., Bae, Y.J., Ahn, S.H., Kim, M.S.: A simple method for quantification of peptides and proteins by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 84, 10332–10337 (2012)
Moon, J.H., Shin, Y.S., Bae, Y.J., Kim, M.S.: Ion yields for some salts in MALDI: mechanism for the gas-phase ion formation from preformed ions. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 22, 162–170 (2012)
Zhigilei, L.V., Leveugle, E., Garrison, B.J., Yingling, Y.G., Zeifman, M.I.: Computer simulations of laser ablation of molecular substrates. Chem. Rev. 103, 321–347 (2003)
Quist, A.P., Huth-Fehre, T., Sundqvist, B.U.R.: Total yield measurements in matrix-assisted laser desorption using a quartz crystal microbalance. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 8, 149–154 (1994)
Puretzky, A.A., Geohegan, D.B.: Gas-phase diagnostics and LIF-imaging of 3-hydroxypicolinic acid MALDI-matrix plumes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 286, 425–432 (1998)
Yassin, F.H., Marynick, D.S.: Computational estimates of the gas-phase acidities of dihydroxybenzoic acid radical cations and their corresponding neutral species. J. Mol. Struct. Theochem. 629, 223–235 (2003)
Yassin, F.H., Marynick, D.S.: Computational estimates of the gas-phase basicities, proton affinities and ionization potentials of the six isomers of dihydroxybenzoic acid. Mol. Phys. 103, 183–189 (2005)
Hasted, J.B.: Physics of Atomic Collisions, p. 444. American Elsevier, New York (1972)
Niu, S., Zhang, W., Chait, B.T.: Direct comparison of infrared and ultraviolet wavelength matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry of proteins. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 9, 1–7 (1998)
Chen, X., Carroll, J.A., Beavis, R.C.: Near-ultraviolet-induced matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization as a function of wavelength. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 9, 885–891 (1998)
Liao, P.-C., Allison, J.: Enhanced Detection of Peptides in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry through the use of charge-localized derivatives. J. Mass Spectrom. 30, 511–512 (1995)
Zhu, Y.F., Lee, K.L., Tang, K., Allman, S.L., Taranenko, N.I., Chen, C.H.: Revisit of MALDI for small proteins. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 9, 1315–1320 (1995)
Karas, M., Krüger, R.: Ion Formation in MALDI: the cluster ionization mechanism. Chem. Rev. 103, 427–439 (2003)
Jaskolla, T.W., Karas, M.: Compelling evidence for lucky survivor and gas phase protonation: the unified MALDI analyte protonation mechanism. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 22, 976–988 (2011)
Land, C.M., Kinsel, G.R.: The mechanism of matrix to analyte proton transfer in clusters of 2,5-dyhydroxybenzoic acid and the tripeptide VPL. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 12, 726–731 (2001)
Knochenmuss, R., Zhigilei, L.V.: Molecular dynamics model of ultraviolet matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization including ionization process. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 22947–22957 (2005)
Karas, M., Bachmann, D., Hillenkamp, F.: Influence of the wave length in high-irradiance ultraviolet laser desorption mass spectrometry of organic molecules. Anal. Chem. 57, 2935–2939 (1985)
Musapelo, T., Murray, K.K.: Particle formation in ambient MALDI plumes. Anal. Chem. 83, 6601–6608 (2011)
Asfandiarov, N.L., Pshenichnyuk, S.A., Fokin, A.I., Lukin, V.G., Fal’ko, V.S.: Electron capture negative ion mass spectra of some typical matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization matrices. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 16, 1760–1765 (2002)
Knochenmuss, R.: Ion formation mechanisms in UV-MALDI. Analyst 131, 966–986 (2006)
Vertes, A., Irinyi, G., Gijbels, R.: Hydrodynamic model of matrix-assisted laser desorption mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 65, 2389–2393 (1993)
Luo, G., Marginean, I., Vertes, A.: Internal energy of ions generated by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization. Anal. Chem. 74, 6185–6190 (2002)
Vertes, A., Luo, G., Ye, L., Chen, Y., Marginean, I.: Laser pulse length dependence of internal energy transfer in UV-MALDI-MS. Appl. Phys. A 79, 823–825 (2004)
Liang, C.W., Lee, C.H., Lin, Y., Lee, Y.T., Ni, C.K.: MALDI mechanism of dihydroxybenzoic acid isomers: desorption of neutral matrix and analyte. J. Phys. Chem. B 117, 5058–5064 (2013)
Stimson, E., Truong, O., Richter, W.J., Waterfield, W.D., Burlingame, A.L.: Enhancement of charge remote fragmentation in protonated peptides by high-energy CID MALDI-TOF-MS using “cold” matrices. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Processes 169/170, 231–240 (1997)
Trimpin, S., Inutan, E.D.: Matrix Assisted Ionization in Vacuum, a Sensitive and Widely Applicable Ionization Method for Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 24, 722–732 (2013)
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge support for this work by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MEST) (2012054350). J.H.M. thanks the KRIBB research initiative program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 1832 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bae, Y.J., Choe, J.C., Moon, J.H. et al. Why do the Abundances of Ions Generated by MALDI Look Thermally Determined?. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 24, 1807–1815 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-013-0717-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-013-0717-7