Abstract
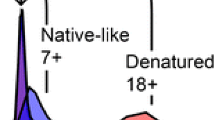
Changes in protein ion conformation as a result of nonspecific adduction of metal ions to the protein during electrospray ionization (ESI) from aqueous solutions were investigated using traveling wave ion mobility spectrometry (TWIMS). For all proteins examined, protein cations (and in most cases anions) with nonspecific metal ion adducts are more compact than the fully protonated (or deprotonated) ions with the same charge state. Compaction of protein cations upon nonspecific metal ion binding is most significant for intermediate charge state ions, and there is a greater reduction in collisional cross section with increasing number of metal ion adducts and increasing ion valency, consistent with an electrostatic interaction between the ions and the protein. Protein cations with the greatest number of adducted metal ions are no more compact than the lowest protonated ions formed from aqueous solutions. These results show that smaller collisional cross sections for metal-attached protein ions are not a good indicator of a specific metal–protein interaction in solution because nonspecific metal ion adduction also results in smaller gaseous protein cation cross sections. In contrast, the collisional cross section of α-lactalbumin, which specifically binds one Ca2+, is larger for the holo-form compared with the apo-form, in agreement with solution-phase measurements. Because compaction of protein cations occurs when metal ion adduction is nonspecific, elongation of a protein cation may be a more reliable indicator that a specific metal ion–protein interaction occurs in solution.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gray, H.B., Winkler, J.R.: Electron transfer in proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem 65, 537–561 (1996)
Browner, M.F., Smith, W.W., Castelhano, A.L.: Matrilysin-Inhibitor Complexes: common themes among metalloproteases. Biochemistry 34, 6602–6610 (1995)
Klein, D.J., Moore, P.B., Steitz, T.A.: The contribution of metal ions to the structural stability of the large ribosomal subunit. RNA 10, 1366–1379 (2004)
Waldron, K.J., Robinson, N.J.: How do bacterial cells ensure that metalloproteins get the correct metal? Nat. Rev. Microbiol 7, 25–35 (2009)
Andreini, C., Bertini, I., Rosato, A.: A hint to search for metalloproteins in gene banks. Bioinformatics 20, 1373–1380 (2004)
Antonini, E.: Interrelationship between structure and function in hemoglobin and myoglobin. Physiol. Rev 45, 123–128 (1965)
Crivici, A., Ikura, M.: Molecular and Structural basis of target recognition by calmodulin. Ann. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct 24, 85–116 (1995)
Ogawa, Y.: Calcium binding to troponin C and troponin: effects of Mg2+, ionic-strength, and pH. J. Biochem 97, 1011–1023 (1985)
Hardman, K.D., Agarwal, R.C., Freiser, M.J.: Manganese and calcium binding sites of concanavalin A. J. Mol. Biol 157, 69–86 (1982)
Hasnain, S.S., Hodgson, K.O.: Structure of metal centres in proteins at subatomic resolution. J. Synchrotron. Radiat. 6, 852–864 (1999)
Braun, W., Vašák, M., Robbins, A.H., Stout, C.D., Wagner, G., Kägi, J.H.R., Wüthrich, K.: Comparison of the NMR solution structure and the X-ray crystal-structure of rat metallothionein-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 10124–10128 (1992)
Bertini, I., Turano, P., Vila, A.J.: Nuclear magnetic resonance of paramagnetic metalloproteins. Chem. Rev 93, 2833–2932 (1993)
Pan, J., Konermann, L.: Calcium-induced structural transitions of the calmodulin-melittin system studied by electrospray mass spectrometry: conformational subpopulations and metal-unsaturated intermediates. Biochemistry 49, 3477–3486 (2010)
Veenstra, T.D., Johnson, K.L., Tomlinson, A.J., Kumar, R., Naylor, S.: Correlation of fluorescence and circular dichroism spectroscopy with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry in the determination of tertiary conformational changes in calcium-binding proteins. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom 12, 613–619 (1998)
Nemirovskiy, O., Giblin, D.E., Gross, M.L.: Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and hydrogen/deuterium exchange for probing the interaction of calmodulin with calcium. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom 10, 711–718 (1999)
Zhu, M.M., Rempel, D.L., Zhao, J., Giblin, D.E., Gross, M.L.: Probing Ca2+-induced conformational changes in porcine calmodulin by H/D exchange and ESI-MS: effect of cations and ionic strength. Biochemistry 42, 15388–15397 (2003)
Novak, P., Havlicek, V., Derrick, P.J., Beran, K.A., Bashir, S., Giannakopulos, A.E.: Monitoring conformational changes in protein complexes using chemical cross-linking and Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry: The effect of calcium binding on the calmodulin–melittin complex. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom 13, 281–290 (2007)
Ly, T., Julian, R.R.: Protein–metal interactions of calmodulin and alpha-synuclein monitored by selective noncovalent adduct protein probing mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom 19, 1663–1672 (2008)
Taraszka, J.A., Li, J., Clemmer, D.E.: Metal-mediated peptide ion conformations in the gas phase. J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 4545–4551 (2000)
Wyttenbach, T., Grabenauer, M., Thalassinos, K., Scrivens, J.H., Bowers, M.T.: The effect of calcium ions and peptide ligands on the relative stabilities of the calmodulin dumbbell and compact structures. J. Phys. Chem. B 114, 437–447 (2010)
Kohtani, M., Jarrold, M.F., Wee, S., O'Hair, R.A.J.: Metal ion interactions with polyalanine peptides. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 6093–6097 (2004)
Kohtani, M., Kinnear, B.S., Jarrold, M.F.: Metal-ion enhanced helicity in the gas phase. J. Am. Chem. Soc 122, 12377–12378 (2000)
Seo, Y.J., Schenauer, M.R., Leary, J.A.: Biologically relevant metal-cation binding induces conformational changes in heparin oligosaccharides as measured by ion mobility mass spectrometry. Int. J. Mass Spectrom 303, 191–198 (2011)
Leavell, M.D., Gaucher, S.P., Leary, J.A., Taraszka, J.A., Clemmer, D.E.: Conformational studies of Zn-Ligand-hexose diastereomers using ion mobility measurements and density functional theory calculations. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom 13, 284–293 (2002)
Prell, J.S., Demireva, M., Oomens, J., Williams, E.R.: Role of sequence in salt-bridge formation for alkali metal cationized GlyArg and ArgGly investigated with IRMPD spectroscopy and theory. J. Am. Chem. Soc 131, 1232–1242 (2009)
Prell, J.S., Flick, T.G., Oomens, J., Berden, G., Williams, E.R.: Coordination of trivalent metal cations to peptides: results from IRMPD spectroscopy and theory. J. Phys. Chem. A 114, 854–860 (2010)
Rodgers, M.T., Armentrout, P.B.: A thermodynamic “vocabulary” for metal ion interactions in biological systems. Acc. Chem. Res. 37, 989–998 (2004)
Polfer, N.C., Oomens, J., Dunbar, R.C.: Alkali metal complexes of the dipeptides PheAla and AlaPhe: IRMPD spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Chem 9, 579–589 (2008)
Ye, S.J., Armentrout, P.B.: Absolute thermodynamic measurements of alkali metal cation interactions with a simple dipeptide and tripeptide. J. Phys. Chem. A 112, 3587–3596 (2008)
Loo, J.A., Hu, P., Smith, R.D.: Interaction of angiotensin peptides with zinc metal ions probed by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom 5, 959–965 (1994)
Wyttenbach, T., von Helden, G., Bowers, M.T.: Gas-phase conformation of biological molecules: bradykinin. J. Am. Chem. Soc 118, 8355–8364 (1996)
Rodgers, M.T., Armentrout, P.B., Oomens, J., Steill, J.D.: Infrared multiphoton dissociation spectroscopy of cationized threonine: effects of alkali-metal cation size on gas-phase conformation. J. Phys. Chem A 112, 2258–2267 (2008)
Loo, J.A.: Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: a technology for studying noncovalent macromolecular complexes. Int. J. Mass Spectrom 200, 175–186 (2000)
Heck, A.J.R., van den Heuvel, R.H.H.: Investigation of intact protein complexes by mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev 23, 368–389 (2004)
Sterling, H.J., Batchelor, J.D., Wemmer, D.E., Williams, E.R.: Effects of buffer loading for electrospray ionization mass spectrometry of a noncovalent protein complex that requires high concentrations of essential salts. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom 21, 1045–1049 (2010)
Han, L.J., Hyung, S.J., Mayers, J.J.S., Ruotolo, B.T.: Bound anions differentially stabilize multiprotein complexes in the absence of bulk solvent. J. Am. Chem. Soc 133, 11358–11367 (2011)
Merenbloom, S.I., Flick, T.G., Daly, M.P., Williams, E.R.: Effects of select anions from the Hofmeister series on the gas-phase conformations of protein ions measured with traveling-wave ion mobility spectrometry/mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom 22, 1978–1990 (2011)
Ruotolo, B.T., Benesch, J.L.P., Sandercock, A.M., Hyung, S.J., Robinson, C.V.: Ion mobility-mass spectrometry analysis of large protein complexes. Nat. Prot 3, 1139–1152 (2008)
Bush, M.F., Hall, Z., Giles, K., Hoyes, J., Robinson, C.V., Ruotolo, B.T.: Collision Cross sections of proteins and their complexes: a calibration framework and database for gas-phase structural biology. Anal. Chem 82, 9557–9565 (2010)
Myung, S., Badman, E.R., Young Jin, L., Clemmer, D.E.: Structural transitions of electrosprayed ubiquitin ions stored in an ion trap over ~10 ms to 30 s. J. Phys. Chem. A 106, 9976–9982 (2002)
Hoaglund, C.S., Valentine, S.J., Sporleder, C.R., Reilly, J.P., Clemmer, D.E.: Three-dimensional ion mobility/TOFMS analysis of electrosprayed biomolecules. Anal. Chem 70, 2236–2242 (1998)
Badman, E.R., Hoaglund-Hyzer, C.S., Clemmer, D.E.: Monitoring structural changes of proteins in an ion trap ~10–200 ms: unfolding transitions in cytochrome c ions. Anal. Chem 73, 6000–6007 (2001)
Bush, M.F., Campuzano, I.D.G., Robinson, C.V.: Ion mobility mass spectrometry of peptide ions: effects of drift gas and calibration strategies. Anal. Chem 84, 7124–7130 (2012)
Iavarone, A.T., Udekwu, O.A., Williams, E.R.: Buffer loading for counteracting metal salt-induced signal suppression in electrospray ionization. Anal. Chem 76, 3944–3950 (2004)
Pan, P., Gunawardena, H.P., Xia, Y., McLuckey, S.A.: Nanoelectrospray ionization of protein mixtures: solution pH and protein pI. Anal. Chem 76, 1165–1174 (2004)
Flick, T.G., Williams, E.R.: Supercharging with trivalent metal ions in native mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom 23, 1885–1895 (2012)
Merenbloom, S.I., Flick, T.G., Willams, E.R.: How hot are your ions in TWAVE ion mobility spectrometry? J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom 23, 553–562 (2012)
Griko, Y.V., Remeta, D.P.: Energetics of solvent and ligand-induced conformational changes in alpha-lactalbumin. Protein Sci 8, 554–561 (1999)
Chrysina, E.D., Brew, K., Acharya, K.R.: Crystal structures of Apo- and Holo-bovine α-lactalbumin at 2.2-Å resolution reveal an effect of calcium on inter-lobe interactions. J. Biol. Chem 275, 37021–37029 (2000)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Institutes of Health (grants no. R01GM096097 and no. 5F32GM093593-02 for fellowship support for S.I.M.). The authors also thank Dr. Haichuan Liu and Professor Ewa Witkowska of the UCSF Sandler-Moore Mass Spectrometry Core Facility for the use of their Synapt G2 instrument.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 303 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flick, T.G., Merenbloom, S.I. & Williams, E.R. Effects of Metal Ion Adduction on the Gas-Phase Conformations of Protein Ions. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 24, 1654–1662 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-013-0664-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-013-0664-3