Abstract
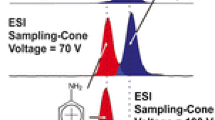
Structural elucidation and distinction of isomeric neurotoxic agents remain a challenge. Tandem mass spectrometry can be used for this purpose in particular if a “diagnostic” product ion is observed. Different vibrational activation methods were investigated to enhance formation of diagnostic ions through consecutive processes from O,O-dialkyl alkylphosphonates. Resonant and non-resonant collisional activation and infrared multiphoton dissociation (IRMPD) were used with different mass spectrometers: a hybrid quadrupole Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (Qh-FTICR) and a hybrid linear ion trap-Orbitrap (LTQ/Orbitrap). Double resonance (DR) experiments, in ion cyclotron resonance (ICR) cell, were used for unambiguous determination of direct intermediate yielding diagnostic ions. From protonated n-propyl and isopropyl O-O-dialkyl-phosphonates, a diagnostic m/z 83 ion characterizes the isopropyl isomer. This ion is produced through consecutive dissociation processes. Conditions to favor its formation and observation using different activation methods were investigated. It was shown that with the LTQ, consecutive experimental steps of isolation/activation with modified trapping conditions limiting the low mass cut off (LMCO) effect were required, whereas with FT-ICR by CID and IRMPD the diagnostic ion detection was provided only by one activation step. Among the different investigated activation methods it was shown that by using low-pressure conditions or using non-resonant methods, efficient and fast differentiation of isomeric neurotoxic agents was obtained. This work constitutes a unique comparison of different activation modes for distinction of isomers showing the instrumental dependence characteristic of the consecutive processes. New insights in the dissociation pathways were obtained based on double-resonance IRMPD experiments using a FT-ICR instrument with limitation at low mass values.

ᅟ









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Creasy, W.R., Stuff, J.R., Williams, B., Morrissey, K., Mays, J., Duevel, R., Durst, H.D.: Identification of chemical weapons-related compounds in decontamination solutions and other matrixes by multiple chromatographic techniques. J. Chromatogr. A 774, 253–263 (1997)
Kim, K., Tsay, O.G., Atwood, D.A., Churchill, D.G.: Destruction and detection of chemical warfare agents. Chem. Rev. 111, 5345–5403 (2011)
Owens, J., Koester, C.: Quantitative analysis of chemical warfare agent degradation products in beverages by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57, 8227–8235 (2009)
Tsuge, K., Seto, Y.: Mass spectrometric identification of chemical warfare agent adducts with biological macromolecule for verification of their exposure. J. Health Sci. 55, 879–886 (2009)
Van Baar, B.L.M., Hulst, A.G., Wils, E.R.J.: Identification of the C3H7 moiety of isopropyl- and propylphosphonates by electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 33, 1104–1108 (1998)
Desoubries, C., Chapuis-Hugon, F., Bossee, A., Pichon, V.: Three-phase hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction of organophosphorous nerve agent degradation products from complex samples. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 900, 48–58 (2012)
Mechin, N., Plomley, J., March, R.E., Blasco, T., Tabet, J.C.: Formation of protonated phosphonates in the ion-trap mass spectrometer under electron impact conditions. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 9, 5–8 (1995)
Lagarrigue, M., Bossee, A., Begos, A., Varenne, A., Gareil, P., Bellier, B.: Separation and identification of isomeric acidic degradation products of organophosphorus chemical warfare agents by capillary electrophoresis-ion trap mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1137, 110–118 (2006)
Petersson, F., Sulzer, P., Mayhew, C.A., Watts, P., Jordan, A., Maerk, L., Maerk, T.D.: Real-time trace detection and identification of chemical warfare agent simulants using recent advances in proton transfer reaction time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 23, 3875–3880 (2009)
Cordell, R.L., Willis, K.A., Wyche, K.P., Blake, R.S., Ellis, A.M., Monks, P.S.: Detection of chemical weapon agents and simulants using chemical ionization reaction time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 79, 8359–8366 (2007)
Steiner, W.E., Klopsch, S.J., English, W.A., Clowers, B.H., Hill, H.H.: Detection of a chemical warfare agent simulant in various aerosol matrixes by ion mobility time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 77, 4792–4799 (2005)
Ferreira, D.E.C., Florentino, B.P.D., Rocha, W.R., Nome, F.: Quantum mechanical/effective fragment potential (qm/efp) study of phosphate monoester aminolysis in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 113, 14831–14836 (2009)
Cooper, D.B., Read, R.W., Timperley, C.M., Williams, N.H., Black, R.M.: Identification of iso- and n-propylphosphonates using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and gas chromatography-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Chromatogr. A 1040, 83–95 (2004)
Bowers, M.T., Elleman, D.D., Beauchamp, J.L.: Ion cyclotron resonance of olefins. I. Study of the ion–molecule reactions in electron-impacted ethylene. J. Phys. Chem. 72, 3599–3612 (1968)
Freiser, B.S., McMahon, T.B., Beauchamp, J.L.: Ion ejection phenomena in ion cyclotron double resonance experiments. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Phys. 12, 249–255 (1973)
Bourgoin-Voillard, S., Zins, E.L., Fournier, F., Jacquot, Y., Afonso, C., Pepe, C., Leclercq, G., Tabet, J.C.: Stereochemical Effects During M-H (−) Dissociations of epimeric 11-OH-17 beta-estradiols and distant electronic effects of substituents at C-(11) position on gas phase acidity. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 20, 2318–2333 (2009)
McLuckey, S.A., Goeringer, D.E.: Slow heating methods in tandem mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 32, 461–474 (1997)
Vekey, K.: Internal energy effects in mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 31, 445–463 (1996)
Liere, P., Blasco, T., March, R.E., Tabet, J.C.: Influence of cooling time on the internal energy of ion subjected to resonance excitation in a quadrupole ion trap. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 8, 953–956 (1994)
Liere, P., Bouchonnet, S., March, R.E., Tabet, J.C.: Cooling time and pressure effects on competitive thermalization/activation processes by resonance excitation on ITMS. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 9, 1594–1598 (1995)
Liere, P., Steiner, V., Jennings, K.R., March, R.E., Tabet, J.C.: Influence of ion activation and thermalization effects on reaction rate constants in a quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometer. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Processes 167/168, 735–751 (1997)
Wu, H.F., Brodbelt, J.S.: Effects of collisional cooling on ion detection in a quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometer. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Processes 115, 67–81 (1992)
Black, D.M., Payne, A.H., Glish, G.L.: Determination of cooling rates in a quadrupole ion trap. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 17, 932–938 (2006)
Steiner, V., Daoust-Maleval, I., Tabet, J.C.: Study of gas-phase reactivity of positive and negative even-electron ions prepared from diethylmethyl phosphonate ester in an external chemical ionization source of orthogonal tandem quadrupole/ion trap instrument. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 195/196, 121–138 (2000)
March, R.E.: An introduction to quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 32, 351–369 (1997)
Laskin, J., Futrell, J.H.: Activation of large lons in FT-ICR mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 24, 135–167 (2005)
Herrmann, K.A., Somogyi, A., Wysocki, V.H., Drahos, L., Vekey, K.: Combination of sustained off-resonance irradiation and on-resonance excitation in FT-ICR. Anal. Chem. 77, 7626–7638 (2005)
Laskin, J., Futrell, J.: Internal energy distributions resulting from sustained off-resonance excitation in fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. II. Fragmentation of the 1-bromonaphthalene radical cation. J. Phys. Chem. A 104, 5484–5494 (2000)
Tonner, D.S., McMahon, T.B.: Consecutive infrared multiphoton dissociations in a Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 69, 4735–4740 (1997)
Olsen, J.V., Macek, B., Lange, O., Makarov, A., Horning, S., Mann, M.: Higher-energy C-trap dissociation for peptide modification analysis. Nat. Methods 4, 709–712 (2007)
Crowe, M.C., Brodbelt, J.S.: Infrared multiphoton dissociation (IRMPD) and collisionally activated dissociation of peptides in a quadrupole ion trap with selective IRMPD of phosphopeptides. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 15, 1581–1592 (2004)
Nguyen, V.H., Afonso, C., Tabet, J.-C.: Concomitant EDD and EID of DNA evidenced by MSn and double resonance experiments. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 301, 224–233 (2011)
Perot-Taillandier, M., Zirah, S., Rebuffat, S., Linne, U., Marahiel, M.A., Cole, R.B., Tabet, J.C., Afonso, C.: Determination of peptide topology through time-resolved double-resonance under electron capture dissociation conditions. Anal. Chem. 84, 4957–4964 (2012)
Afonso, C., Lesage, D., Fournier, F., Mancel, V., Tabet, J.-C.: Origin of enantioselective reduction of quaternary copper d, l amino acid complexes under vibrational activation conditions. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 312, 185–194 (2012)
Lioe, H., O'Hair, R.A.J.: Neighbouring group processes in the deamination of protonated phenylalanine derivatives. Org. Biomol. Chem. 3, 3618–3628 (2005)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the Délégation Général de l’Armement (DGA) and the CNRS and the university Pierre and Marie Curie. The SM3P platform is also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bennaceur, C., Afonso, C., Alves, S. et al. Instrumental Dependent Dissociations of n-Propyl/Isopropyl Phosphonate Isomers: Evaluation of Resonant and Non-Resonant Vibrational Activations. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 24, 1260–1270 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-013-0656-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-013-0656-3