Abstract
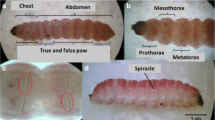
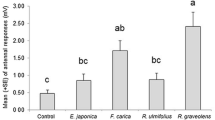
The brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) is an agricultural pest with a unique odor, aggregating near human habitats during the cold season. In the present study, we evaluated the suitability of H. halys as an edible insect. We observed that the one-time administration of 2000 mg/kg raw stink bugs to female rats via oral gavage did not affect their weight or cause mortality, suggesting that the medium lethal dose of H. halys adults was > 2000 mg/kg for female rats. Moreover, the presence of microorganisms or heavy metals was not observed in heated and raw insects, respectively, except for cadmium, suggesting that they met food hygiene and safety standards. Nutrient composition analysis revealed that the levels of useful compounds in H. halys were comparable to those in general hemipterans. The ratio of polyunsaturated fatty acids in H. halys adults was 44.3%, whereas that of saturated fatty acids was 16.8%. Moreover, H. halys was rich in β-carotene, astaxanthin, lutein, and zeaxanthin. Therefore, H. halys is a potential edible carotenoid source. Consumption of this insect would become a solution to managing the pest and nuisance. Further studies are needed to ensure food safety and human consumption.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ambati RR, Moi PS, Ravi S, Aswathanarayana RG (2014) Astaxanthin: sources, extraction, stability, biological activities and its commercial applications—a review. Mar Drugs 12:128–152. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12010128
Britton G, Goodwin TW, Harriman GE, Lockley WJ (1977) Carotenoids of the ladybird beetle, Coccinella septempunctata. Insect Biochem 7:337–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-1790(77)90035-X
Calvo MM (2005) Lutein: a valuable ingredient of fruit and vegetables. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 45:671–696. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408690590957034
Ding BY, Xie XC, Shang F, Smagghe G, Niu JZ, Wang JJ (2022) Characterization of carotenoid biosynthetic pathway genes in the pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum) revealed by heterologous complementation and RNA interference assays. Insect Sci 29:645–656. https://doi.org/10.1111/1744-7917.12958
EFSA Nda Panel (EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens) (2021a) Scientific opinion on the safety of dried yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor larva) as a novel food pursuant to regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J 19:6343. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2021.6343
EFSA Nda Panel (EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens) (2021b) Scientific opinion on the safety of frozen and dried formulations from migratory locust (Locusta migratoria) as a novel food pursuant to regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J 19:6667. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2021.6667
EFSA Nda Panel (EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens) (2021c) Scientific opinion on the safety of frozen and dried formulations from whole house crickets (Acheta domesticus) as a novel food pursuant to regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J 19:6779. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2021.6779
EFSA Nda Panel (EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens) (2022) Scientific opinion on the safety of frozen and freeze-dried formulations of the lesser mealworm (Alphitobius diaperinus larva) as a novel food pursuant to regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J 20:7325. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2022.7325
Feng Y, Chen X, Wang S, Ye S, Chen Y (2000) The common edible insects of Hemiptera and their nutritive value. For Res 13:608–612 (in Chinese with English abstract)
FAO (2010) Fats and fatty acids in human nutrition. Report of an expert consultation. FAO Food Nutr Pap 91:1–166
FAO (2021) Looking at edible insects from a food safety perspective. Challenges and Opportunities for the Sector, Rome. https://doi.org/10.4060/cb4094en
Han SR, Yun EY, Kim JY, Hwang JS, Jeong EJ, Moon KS (2014) Evaluation of genotoxicity and 28-day oral dose toxicity on freeze-dried powder of Tenebrio molitor larvae (Yellow Mealworm). Toxicol Res 30:121–130. https://doi.org/10.5487/TR.2014.30.2.121
Han SR, Lee BS, Jung KJ, Yu HJ, Yun EY, Hwang JS, Moon KS (2016) Safety assessment of freeze-dried powdered Tenebrio molitor larvae (yellow mealworm) as novel food source: evaluation of 90-day toxicity in Sprague–Dawley rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 77:206–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2016.03.006
Hanboonsong Y (2010) Edible insects and associated food habits in Thailand. In: DPB, JDV, LRN, SK (eds) Forest insects as food: humans bite back. Bangkok, Thailand, pp 173–182
Higuera-Ciapara I, Félix-Valenzuela L, Goycoolea FM (2006) Astaxanthin: a review of its chemistry and applications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 46:185–196. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408690590957188
Honda M, Watanabe Y, Murakami K, Hoang NN, Wahyudiono KH, Goto M (2018) Enhanced lycopene extraction from gac (Momordica cochinchinensis Spreng.) by the Z-isomerization induced with microwave irradiation pre-treatment. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 120:1700293. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejlt.201700293
Honda M, Kageyama H, Hibino T, Sowa T, Kawashima Y (2020) Efficient and environmentally friendly method for carotenoid extraction from Paracoccus carotinifaciens utilizing naturally occurring Z-isomerization-accelerating catalysts. Process Biochem 89:146–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2019.10.005
Honda M, Murakami K, Osawa Y, Kawashima Y, Hirasawa K, Kuroda I (2021) Z-Isomers of astaxanthin exhibit greater bioavailability and tissue accumulation efficiency than the all-E-isomer. J Agric Food Chem 69:3489–3495. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c00087
Honda M, Hirota K, Zhang Y, Hayashi Y, Sugahara R (2023) Effect of astaxanthin isomer supplementation on their accumulation in edible orthopterans: migratory locusts and two-spotted crickets. J Insects Food Feed 9:955–964. https://doi.org/10.3920/JIFF2022.0129
Inkley DB (2012) Characteristics of home invasion by the brown marmorated stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J Entomol Sci 47:125–130. https://doi.org/10.18474/0749-8004-47.2.125
Kim IS, Ahn MY, Ryu KS, Lee BM (2002) Acute oral toxicity of G. bimaculatus in rats. J Toxicol Pub Health 18:397–400
Lee DH, Short BD, Joseph SV, Bergh JC, Leskey TC (2013) Review of the biology, ecology, and management of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in China, Japan, and the Republic of Korea. Environ Entomol 42:627–641. https://doi.org/10.1603/EN13006
Leskey T, Nielsen L (2018) Impact of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug in North America and Europe: history, biology, ecology, and management. Annu Rev Entomol 63:599–618. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-020117-043226
Leskey TC, Lee D-H, Short BD, Wright SE (2012a) Impact of insecticides on the invasive Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae): analysis of insecticide lethality. J Econ Entomol 105:1726–1735. https://doi.org/10.1603/EC12096
Leskey TC, Short BD, Butler BR, Wright SE (2012b) Impact of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål), in mid-Atlantic tree fruit orchards in the United States: case studies of commercial management. Psyche 2012:535062. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/535062
Maoka T, Kawase N, Hironaka M, Nishida R (2021) Carotenoids of hemipteran insects, from the perspective of chemo-systematic and chemical ecological studies. Biochem Syst Ecol 95:104241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2021.104241
Meyer-Rochow VB (2010) Entomophagy and its impact on world cultures: the need for a multidisciplinary approach. In: DPB, JDV, LRN, SK (eds) Forest insects as food: humans bite back. Bangkok, Thailand, pp 23–36
Niva CC, Takeda M (2002) Color changes in Halyomorpha brevis (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) correlated with distribution of pteridines: regulation by environmental and physiological factors. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 132:653–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1096-4959(02)00081-7
Ochiai M, Inada M, Horiguchi S (2020) Nutritional and safety evaluation of locust (Caelifera) powder as a novel food material. J Food Sci 85:279–288. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15024
Pyo SJ, Kang DG, Jung C, Sohn HY (2020) Anti-thrombotic, anti-oxidant and haemolysis activities of six edible insect species. Foods 9:401. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040401
Remold H (1963) Scent-glands of land-bugs, their physiology and biological function. Nature 198:764–768. https://doi.org/10.1038/198764a0
Rumpold BA, Schlüter OK (2013) Nutritional composition and safety aspects of edible insects. Mol Nutr Food Res 57:802–823. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201200735
Ryu HY, Lee S, Ahn KS, Kim HJ, Lee SS, Ko HJ, Lee JK, Cho MH, Ahn MY, Kim EM, Lim JH, Song KS (2016) Oral toxicity study and skin sensitization test of a cricket. Toxicol Res 32:159–173. https://doi.org/10.5487/TR.2016.32.2.159
Sobhani Z, Mohtashami L, Amiri MS, Ramezani M, Emami SA, Simal-Gandara J (2022) Ethnobotanical and phytochemical aspects of the edible herb Coriandrum sativum L. J Food Sci 87:1386–1422. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.16085
Su F, Xu H, Yang N, Liu W, Liu J (2018) Hydrolytic efficiency and isomerization during de-esterification of natural astaxanthin esters by saponification and enzymolysis. Electron J Biotechnol 34:37–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt.2018.05.002
Uchibayashi M (2001) The Coriander Story Yakushigaku Zasshi 36:56–57 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Van Huis A, Itterbeeck JV, Klunder H, Mertens E, Halloran A, Muir G, Vantomme P (2013) Edible insects: future prospects for food and feed security. FAO Pap 171:1–187
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Takeyuki Nakamura (Hirosaki University), Mr. Keiryu Hirota (Hirosaki University), and Mr. Tomoharu Saito (Aone Shirakami Juniko) for collecting the insects for this study. We thank Dr. Harutoshi Tsuda (Hirosaki University) for critically reviewing the manuscript. The manuscript was greatly improved by two reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sugahara, R., Honda, M. & Mitsuhashi, R. Immature Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) adults are potential edible insects rich in carotenoids. Appl Entomol Zool 59, 13–20 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-023-00845-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-023-00845-6