Abstract
To evaluate the infection risk of Anoplophora malasiaca (Thomson) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in two species of Japanese pine bonsais (Japanese black pine and Japanese white pine), feeding and oviposition preferences of female A. malasiaca to pine bonsai and mandarin orange were examined. A female was released into a net cage together with a pair of one pine bonsai and one mandarin orange. All mandarin oranges used in preference tests were damaged by feeding and deep biting scars from females, and larval frass ejection from the trunk was found in some mandarin oranges within 4 months of observation. However, these scars were found on only a few pine bonsais, and frass ejection was not found in any pine bonsais. No A. malasiaca larvae were detected in these pine bonsais. Therefore, frass ejection from trunks might be indicative of the presence of larvae. In field surveys at bonsai nurseries, no A. malasiaca adults were found on the pine bonsais and no pine bonsais exhibited frass ejection. Statistical analyses of these results suggested that the risk of A. malasiaca infestation in pine bonsais could be ruled out as a negligible level by confirming an absence from the trunk of frass ejection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi I (1988) Reproductive biology of the white-spotted longicorn beetle, Anoplophora malasiaca Thomson (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae), in citrus trees. Appl Entomol Zool 23:256–264. https://doi.org/10.1303/aez.23.256
Aono N, Murakoshi S (1980) Investigation and control of white spotted longicorn beetle (Anoplophora malasiaca THOMSON) which injure Japanese pear trees. Bull Kanagawa Hortic Exp Sta 27:28–34 (in Japanese)
European Union (2012) Commission implementing decision of 1 March 2012 as regards emergency measures to prevent the introduction into and the spread within the Union of Anoplophora chinensis (Forster). https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2012:064:0038:0047:EN:PDF. Accessed 22 July 2019
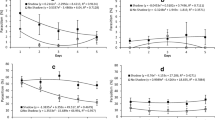
Fujiwara-Tsujii N, Yasui H, Yasuda T (2019) Fecundity and feeding preferences of adult Anoplophora malasiaca (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) females fed on Japanese black and white pines. Tree Forest Health 23:1–6
Haack R, Hérard F, Sun J, Turgeon J (2010) Managing invasive populations of Asian longhorned beetle and citrus longhorned beetle: a worldwide perspective. Annu Rev Entomol 55:521–546. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-112408-085427
Hay CJ (1968) Frass of some wood-boring insects in living oak (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae; Lepidoptera: Cossidae and Aegeriidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 61:255–258. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/61.2.255
Hérard F, Ciampitti M, Maspero M, Krehan H, Benker U, Boegel C, Schrage R, Bouhot-Delduc L, Bialooki P (2006) Anoplophora spp. in Europe: infestations and management process. Bull OEPP 36:470–474. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2338.2006.01046.x
International Plant Protection Convention (2016) The ISPM 37 on Determination of host status of fruit to fruit flies (Tephritidae) https://www.ippc.int/en/core-activities/standards-setting/ispms/. Accessed 9 Dec 2019
Ito Y, Kitamura T, Hagiwara Y (1980) The seasonal occurrence and control of withe spotted longicorn and thin-winged longicorn of apple trees in Nagano district. Proc Kanto-Tosan Plant Prot Soc 27:148–149. https://doi.org/10.11337/ktpps1954.1980.148(in Japanese)
Iwaizumi R, Arimoto M, Kurauchi T (2014) A Study on the occurrence and fecundity of white spotted longicorn, Anoplophora malasiaca (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Res Bull Plant Prot Jpn 50:9–15. https://www.maff.go.jp/pps/j/guidance/r_bulletin/pdf/rb050_002.pdf. Accessed 9 Dec 2019
Iwasaki M, Yoshida K (2005) Statistical Inference for the occurrence probability of rare events—rule of three and related topics. Jpn J Biometrics 26:53–63. https://doi.org/10.5691/jjb.26.53(in Japanese with English summary)
JETRO Kagawa (2015) A survey of bonsai exportability in Europe. https://www.jetro.go.jp/ext_images/jfile/report/07000186/bonsai.pdf. Accessed 9 Dec 2019. (in Japanese)
Kagawa Prefecture Bonsai Production Promotion Council, Kagawa Prefecture (2017) Bookmark of bonsai cultivation for export. https://www.pref.kagawa.lg.jp/agrinet/dougubako/kongetu/shin_gijyutsu/bonsai_shiori.pdf. Accessed 22 July 2019. (in Japanese)
Kawamura M (1985) Development of the white-spotted longicorn beetle, Anoplophora malasiaca Thomson, on Satsuma mandarin. Bull Kochi Inst Agric Forest Sci 17:23–36 (in Japanese)
Kojima K, Nakamura S (2011) Food plants of cerambycid beetles (Cerambycidae, Coleoptera) in Japan (Revised and enlarged edition). Hiba Society of Natural History Press, Hiroshima, pp 223–227. (in Japanese)
Lingafelter SW, Hoebeke ER (2002) Revision of the genus Anoplophora (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). The Entomological Society of Washington, Washington, DC
Linsley EG (1959) Ecology of Cerambycidae. Annu Rev Entomol 4:99–138. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.en.04.010159.000531
Makihara H (2007) Genus Anoplophora Hope, 1839. In: Ohbayashi N, Niisato T (eds) Longicorn beetles of Japan. Tokai University Press, Hiratsuka, pp 583–585 (in Japanese)
Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (2017) Estimating the amounts of shipment (export) and export values of bonsais. https://www.maff.go.jp/j/seisan/kaki/flower/attach/pdf/index-38.pdf. Accessed 9 Dec 2019. (in Japanese)
Mitomi M, Kuroda E, Okamoto H (1990) Ecological study of the white-spotted longicorn beetle, Anoplophora malasiaca Thomson (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) I. Investigation of adult emergence holes in citrus orchards in Kagawa Prefecture. Jpn J Appl Entomol Zool 34:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1303/jjaez.34.7(in Japanese with English summary)
Muraji M, Wakamura S, Yasui H, Arakaki N, Sadoyama Y, Ohno S, Matsuhira K (2011) Genetic variation of the white-spotted longicorn beetle Anoplophora spp. (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in Japan detected by mitochondrial DNA sequence. Appl Entomol Zool 46:363–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-011-0056-8
Ohbayashi N (1992) Genus Anoplophora Hope, 1839. In: Ohbayashi N, Satô M, Kojima K (eds) An illustrated guide to identification of longicorn beetles of Japan. Tokai University Press, Tokyo, pp 583–584 (in Japanese)
Ohbayashi N, Ogawa J (2009) Phylogenetic analysis of the Lamiine genus Anoplophora and its relatives (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae) based on the mitochondrial COI gene. Spec Bull Jpn Soc Coleopterol, Tokyo 7:309–324
Xu T, Yasui H, Teale SA, Fujiwara-Tsujii N, Wickham JD, Fukaya M, Hansen L, Kiriyama S, Hao D, Nakano A, Zhang L, Watanabe T, Tokoro M, Millar JG (2017) Identification of a male-produced sex-aggregation pheromone for a highly invasive cerambycid beetle Aromia bungii. Sci Rep 7:7330. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07520-1
Yamamura K, Katsumata H, Yoshioka J, Yuda T, Kasugai K (2016) Sampling inspection to prevent the invasion of alien pests: statistical theory of import plant quarantine systems in Japan. Popul Ecol 58:63–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10144-015-0521-2
Yasuoka T (2017) Efficacy of insecticides against larvae of red necked longhorn beetle, Aromia bungii (Faldermann) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Res Bull Plant Prot Jpn 53:51–62 (in Japanese with English summary)
Yoshida K, Iwasaki M (2013) A new testing procedure for the probability of rare events. J Fac Sci Tech Seikei Univ 50 (2):11–16. https://hdl.handle.net/10928/461
Acknowledgements
We thank Kagawa Prefecture Bonsai Production Promotion Council and Takamatsu Bonsai Export Organization for supporting this project. We also thank Kumiko Ebihara, Mitsue Fukuda, and Ayako Komatsu for assistance with the bonsai cultivation, and Ikuko Hashimoto and Yukiko Tsushima for assistance with the insect rearing. We would like to thank Enago (www.enago.jp) for the English language review. This research was supported by grants from the Project of the NARO Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Institution (the special scheme project on vitalizing management entities of agriculture, forestry, and fisheries).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasuda, T., Mishiro, K., Kusunoki, M. et al. Inspection of frass ejection could decrease the risk of white-spotted longicorn beetle Anoplophora malasiaca (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) infestation of Japanese pine bonsais to negligible levels. Appl Entomol Zool 55, 205–212 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-020-00670-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-020-00670-1