Abstract
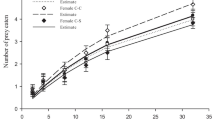
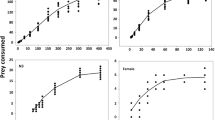
The predation potential of a generalist predator Rhynocoris marginatus (Fab.) (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) against three important mealybug pests of cotton, Phenacoccus solenopsis Tinsley, Maconellicoccus hirsutus Green, and Coccidohystrix insolita Green (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) was evaluated under laboratory conditions. The specific objective of the study was to determine the prey capturing time, prey handling time, and prey preference among the three mealybug species for different developmental stages of R. marginatus. The number of prey consumed/predator/24 h by R. marginatus was dependent on the mealybug species and the predator developmental stage. Rhynocoris marginatus showed a decrease in prey capturing time and handling time as the predator grew older. After evaluating the prey stage preference, results indicated that the developmental stages of R. marginatus preferred adult mealybugs over the younger stages. In a choice-test bioassay including the three mealybug species, no significant difference in prey species selection was observed for the various R. marginatus developmental stages. However, the mortality of P. solenopsis was observed to be highest among the mealybugs, followed by M. hirsutus and C. insolita. This supports the idea that R. marginatus can be effectively utilized for the management of one of the most destructive mealybug pests of cotton, P. solenopsis. Results from this study are important for the development of a knowledge-based management program for cotton agroecosystems affected by various mealybug pests.


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
14 September 2018
In the original publication of the article, the name of the corresponding author was published incorrectly as “Sahayaraj Kitherian”. The correct name is “Kitherian Sahayaraj”.
References
Ambrose DP (1999) Assassin bugs. Science, Enfield
Antony J, Daniel M, Kurian C, Pillai GB (1979) Attempts on introduction and colonization of the exotic reduviid predator, Platymeris laevicollis Distant for the biological suppression of the coconut rhinoceros beetle, Oryctes rhinoceros L. Placrosym II:445–454
Arif MI, Rafiq M, Wazir Mehmood S, Ghaffar N (2012) Studies on cotton mealybug, Phenacoccus solenopsis (Pseudococcidae: Homoptera) and its natural enemies in Punjab, Pakistan. Int J Agric Biol 14:557–562
Atodaria MN (1998) Biology and chemical control of mealybug Ferrisia virgata Cockerell (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae) on custard apple (Annona squamosa). MSc thesis. Gujarat Agriculture University, Sadarkrushinagar
Biswas B, Mitra B (2011) Check list of Indian assassin bugs (Insecta: Hemiptera: Reduviidae). Zoological Survey of India, New Alipore
Butler C, O’Neil R (2006) Defensive response of soybean aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to predation by insidious flower bug (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 99:317–320
CABI (2017) Datasheets on Phenacoccus solenopsis (cotton mealybug), Maconellicoccus hirsutus (pink hibiscus mealybug) and Coccidohystrix insolita (eggplant mealybug). Invasive species compendium. http://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/109097; http://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/40171; http://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/11716. Accessed: 16 July 2017
Chailleux A, Bearez P, Pizzol J, Amiens-Desneux E, Ramirez-Romero R (2013) Potential for combined use of parasitoids and generalist predators for biological control of the key invasive tomato pest, Tuta absoluta. J Pest Sci 86:533–541
Cisneros JJ, Rosenheim JA (1997) Ontogenetic change of prey preference in the generalist predator Zelus renardii and its influence on predator–predator interactions. Ecol Entomol 22:399–407
Cohen AC, Tang R (1997) Relative prey weight influences handling time and biomass extraction in Sinea confusa and Zelus renardii (Heteroptera: Reduviidae). Environ Entomol 26:559–565
Culik MP, Gullan PS (2005) A new pest of tomato and other records of mealybugs from Espírito Santo, Brazil. Zootaxa 964:1–8
Dhawan AK, Joginder S, Sindhu AS (1980) Maconellicoccus sp. attacking arboretum cotton in Punjab. Sci Cult 46:258
Farehan IN, Syarafina R, Idris AB (2013) Toxicity of three insecticides on the predator of oil palm leaf-eater pests Sycanus dichotomus Stål. (Hemiptera: Reduviidae). Acad J Entomol 6:11–19
Grundy P, Maelzer D (2000) Predation by the assassin bug Pristhesancus plagipennis (Walker) (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and Nezara viridula (L.) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in the laboratory. Aust J Entomol 39:280–282
Grundy PR, Maelzer DA (2002) Augmentation of the assassin bug Pristhesancus plagipennis (Walker) (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) as a biological control agent for Helicoverpa spp. in cotton. Aust J Entomol 41:192–196
Guershon M, Gerling D (1999) Predatory behavior of Delphastus pusillus in relation to the phenotypic plasticity of Bemisia tabaci nymphs. Entomol Exp Appl 92:239–248
Hodgson CJ, Abbas G, Arif MJ, Saeed S, Karar H (2008) Phenacoccus solenopsis Tinsley (Sternorrhyncha: Coccoidea: Pseudococcidae), an invasive mealybug damaging cotton in Pakistan and India, with a discussion on seasonal morphological variation. Zootaxa 1913:1–35
Jhala RC, Bharpoda TM, Patil MG (2006) Occurrence of mealybugs, Phenococcus solenopsis Tinsley and Phenacoccus solani Ferris on cotton in Gujarat. Insect Environ 13:13–16
Kalidas S, Sahayaraj K (2012) Survey of reduviids in cotton agro-ecosystem of Tamil Nadu. Middle East J Sci Res 12:1216–1223
Kannan K, Uthamasamy S, Mohan S (2004) Impact of insecticides on sucking pests and natural enemy complex of transgenic cotton. Curr Sci 86:727–729
Kaur H, Virk JS (2012) Feeding potential of Cryptolaemus montrouzieri against the mealybug Phenacoccus solenopsis. Phytoparasitica 40:131–136
Larraín P (2002) Incidencia de insectos y ácaros plagas en pepino dulce (Solanum muricatum Ait.) cultivado en la IV región. Chile Agric Tech 62:15–26
McMahan EA (1983) Adaptations, feeding preferences, and biometrics of a termite-baiting assassin bug (Hemiptera: Reduviidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 76:483–486
Mohan S, Monga D, Kumar R, Nagrare V, Gokte-Narkhedkar Nandini, Vennila S, Tanwar R, Sharma OP, Someshwar B, Meenu A, Chattopadhyay C, Rakesh K, Ajanta B, Amaresan N, Amar Singh S, Sushil N, Ram AK, Kapoo S, Jeyakumar P, Satyagopal K (2014) Integrated pest management package for cotton. National Centre for Integrated Pest Management, New Delhi
Moore A, Watson G, Bamba J (2014) First record of eggplant mealybug, Coccidohystrix insolita (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae), on Guam: potentially a major pest. Biodivers Data J 2:e1042. https://doi.org/10.3897/BDJ.2.e1042
Muralidharan CM, Badaya SN (2000) Mealy bug (Maconellicoccus hirsutus) (Pseudococcidae: Hemiptera) out break on herbaceum cotton (Gossypium herbaceum) in Wagad cotton belt of Kachchh. Indian J Agric Sci 70:705–706
Nagrare VS, Kranthi S, Biradar VK, Zade NN, Sangode V, Kakde G, Kranthi KR (2009) Widespread infestation of the exotic mealybug species, Phenacoccus solenopsis (Tinsley) (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae), on cotton in India. Bull Entomol Res 99:537–541
OEPP/EPPO (2005) Data sheets on quarantine pests Maconellicoccus hirsutus (Green). Bulletin 35:413–415
Pereira AIA, Zanuncio JC, Gil-Santana HR, Ramalho FS, Leite GLD, Serrão JE (2009) Harpactor angulosus (Reduviidae: Harpactorinae): a predator of neotropical saturniids, Hylesia spp. Entomol News 120:206–221
Sahayaraj K (1994) Capturing success by reduviid predators Rhynocoris marginatus and Rhynocoris kumari on different age groups of Spodoptura litura, a polyphagous pest (Heteroptera: Reduviidae). J Ecobiol 6:221–224
Sahayaraj K (1999) Effect of prey and their ages on the feeding preference of Rhynocoris marginatus (Fab). Int Arch Newsl 19:39–41
Sahayaraj K (2008) Approaching behaviour of Rhynocoris marginatus (Fab.) (Heteroptera: Reduviidae) on three prey kairomones. Bull Insectol 61:233–237
Sahayaraj K (2012) Artificial rearing on the nymphal developmental time and survival of three reduviid predators of Western Ghats, Tamil Nadu. J Biopest 5:218–221
Sahayaraj K (2014) Reduviids and their merits in biological control. In: Sahayaraj K (ed) Basic and applied aspects of biopesticides. Springer, New Delhi, pp 195–214
Sahayaraj K, Ambrose DP (1993) Population dynamics of five reduviids from Kaipathai scrub jungles, South India. J Soil Biol Ecol 13:122–129
Sahayaraj K, Ambrose DP (1994) Stage and host preference and functional response of a reduviid predator Acanthspis pedastris Stal to four cotton pests. J Biol Control 8:23–26
Sahayaraj K, Muthukumar SM (2011) Zootoxic effects of reduviid Rhynocoris marginatus (Fab.) (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) venomous saliva on Spodoptera litura (Fab.). Toxicon 58:415
Sahayaraj K, Raju G (2006) Assessing the intraguild predation of Rhynocoris marginatus (Fab.) (Heteroptera: Reduviidae: Harpactorinae) and Menochiluss exmaculatus (Fab.) of cotton pest Aphis craccivora. Hexapoda 13:62–65
Sahayaraj K, Delma JCR, Martin P (2003) Biological control potential of aphidophagous reduviid predator Rhynocoris marginatus. Int Arch Newsl 23:29–30
Sahayaraj K, Martin P, Selvaraj P, Raju G (2006) Feeding behaviour of reduviid predators on meat and insect-based artificial diets. Belg J Entomol 8:55–65
Sahayaraj K, Kalidas S, Majesh T (2012) Stage preference and functional response of Rhynocoris longifrons (Stål) (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) on three hemipteran cotton pests. Braz Arch Biol Technol 55:733–740
Sahayaraj K, Kumar V, Avery PB (2015) Functional response of Rhynocoris kumarii (Heteroptera: Reduviidae) on Phenacoccus solenopsis (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) in the laboratory. Eur J Entomol 112:69–74
Sahayaraj K, Kumar SM, Enkegaard A (2016) Response of the reduviid bug, Rhynocoris marginatus (Heteroptera: Reduviidae) to six different species of cotton pests. Eur J Entomol 113:29–36
Schaefer PW (1983) Natural enemies and host plants of species in the Epilachninae (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): a world list. Bull Agric Exp Stn Univ Del 445:1–42
SAS Institute Inc (2012) Base SAS® 9.3 Procedures Guide. Cary, SAS Institute Inc., NC
Vennila S, Ramamurthy VV, Deshmukh A, Pinjarkar DB, Agarwal M, Pagar PC, Prasad YG, Prabhakar M, Kranthi KR, Bambawale OM (2010) A treatise on mealybugs of central Indian cotton production system. Technical bulletin, vol 24. National Centre for Integrated Pest Management, New Delhi
Vijay A, Suresh S (2013) Coccid pests of flower and medicinal crops in Tamil Nadu. Karnataka J Agric Sci 26:46–53
Williams DJ (1996) A brief account of hibiscus mealybug, Maconellicoccus hirsutus, a pest of agriculture and horticulture, with description of two related species from South Asia. Bull Entomol Res 86:617–628
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to MEF, New Delhi (ref. no.23-1/2008-RE) for their financial assistance, and to the management of the St. Xavier’s College (Autonomous), Palayamkottai, for providing the necessary laboratory facilities and support to complete this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitherian, S., Kumar, V., Banu, N. et al. Predation potential of Rhynocoris marginatus (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) against three mealybug species of agricultural importance. Appl Entomol Zool 53, 475–482 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-018-0576-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-018-0576-6