Abstract
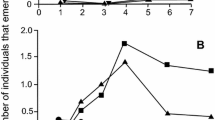
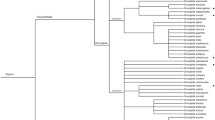
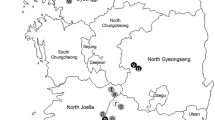
Ganaspis individuals parasitizing Drosophila suzukii (Matsumura), a pest of fruit crops, were examined for host use and molecular and morphological differences from those attacking D. lutescens Okada and some other Drosophila species that breed on fermenting fruits. Wild cherry fruits were collected in the suburbs of Tokyo, and drosophilid pupae obtained from these fruits were examined for parasitism. Drosophila suzukii was the only drosophilid species infesting fresh wild cherry fruits, and Ganaspis individuals were the major parasitoids attacking D. suzukii in wild cherry fruits. In parasitism experiments, these Ganaspis individuals parasitized D. suzukii larvae in fresh cherry fruits, but did not parasitize those in Drosophila medium. In addition, they did not parasitize larvae of some other fruit-feeding Drosophila species even when these occurred in fresh cherry fruit. These Ganaspis individuals parasitizing D. suzukii were different from those parasitizing D. lutescens and some other drosophilids in nucleotide sequences of the COI gene, as well as in ITS1 and ITS2. They were also different in forewing and antenna morphology, although they showed some overlap in morphological traits. They are tentatively assigned as the suzukii- and lutescens-associated types of G. xanthopoda Ashmead. In the present field survey, Leptopilina japonica Novković & Kimura and some Asobara species were also observed to attack D. suzukii larvae in wild cherry fruit.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashmead WH (1896) Report on the parasitic Hymenoptera of the Island of Grenada, comprising the families Cynipidae, Ichneumonidae, Braconidae, and Proctotrypidae. Proc Zool Soc London 1895:742–812
Calabria G, Máca J, Bächli G, Serra L, Pascual M (2012) First records of the potential pest species Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae) in Europe. J Appl Entomol 136:139–147
Carton Y, Boulétreau M, van Alphen JJM, van Lenteren JC (1986) The Drosophila parasitic wasps. In: Ashburner M, Carson HL, Thompson JN (eds) The genetics and biology of Drosophila, 3e. Academic press, New York, pp 347–394
Chabert S, Allemand R, Poyet M, Eslin P, Gilbert P (2012) Ability of European parasitoids (Hymenoptera) to control a new invasive Asiatic pest, Drosophila suzukii. Biol Control 63:40–47
Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Luiz R, Vrijenhoek R (1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol Mar Biol Biotech 3:294–299
Hauser M, Gaimari S, Damus M (2009) Drosophila suzukii new to North America. http://www.nadsdiptera.org/News/FlyTimes/issue43.pdf
Ideo S, Watada M, Mitsui H, Kimura MT (2008) Host range of Asobara japonica (Hymenoptera: Brachonidae), a larval parasitoid of drosophilid flies. Entomol Sci 11:1–6
Kanzawa T (1939) Studies on Drosophila suzukii Mats. Yamanashi Agri Exp Sta Rep Kofu, Japan (In Japanese)
Kimura MT, Toda MJ, Beppu A, Watabe H (1977) Breeding sites of drosophilid flies in and near Sapporo, northern Japan, with supplementary notes on adult feeding habits. Kontyû 45:571–582
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Lee JC, Bruck DJ, Curry H, Edwards D, Haviland DR, Van Steenwyk RA, Yorgey BM (2011) The susceptibility of small fruits and cherries to the spotted-wing drosophila, Drosophila suzukii. Pest Manag Sci 67:1358–1367
Lemeunier F, Tsacas L, David J, Ashburner M (1986) The melanogaster species group. In: Ashburner M, Carson HL, Thompson JN (eds) The genetics and biology of Drosophila, 3e. Academic press, New York, pp 147–256
Mitsui H, Kimura MT (2010) Distribution, abundance and host association of two parasitoid species attacking frugivorous drosophilid larvae in central Japan. Eur J Entomol 107:535–540
Mitsui H, Takahashi KH, Kimura MT (2006) Spatial distributions and clutch sizes of Drosophila species ovipositing on cherry fruits of different stages. Popul Ecol 48:233–237
Mitsui H, van Achterberg K, Nordlander G, Kimura MT (2007) Geographical distribution and host associations of larval parasitoids of frugivorous Drosophilidae in Japan. J Nat Hist 41:1731–1738
Mitsui H, Beppu K, Kimura MT (2010) Seasonal life cycles and resource uses of flower- and fruit-feeding drosophilid flies (Diptera: Drosophilidae) in central Japan. Entomol Sci 13:60–67
Nishiharu S (1980) A study of ecology and evolution of drosophilid flies with special regard to imaginal and larval feeding habits and seasonal population fluctuations. Doctor of Science Thesis, Tokyo Metropolitan University, Tokyo
Novković B, Mitui H, Suwito A, Kimura MT (2011) Taxonomy and phylogeny of Leptopilina species (Hymenoptera: Cynipoidea: Figitidae) attacking frugivorous drosophilid flies in Japan, with description of three new species. Entomol Sci 14:333–346
Rohlf FJ (2008a) tpsDig—Thin Plate Spline Digitizer, version 2.12. State University of New York at Stony Brook. New York. http://life.bio.sunysb.edu/morph/
Rohlf FJ (2008b) tpsRelw—Thin Plate Spline Relative Warp, ver. 1.46. State University of New York at Stony Brook. New York. http://life.bio.sunysb.edu/morph/
Rohlf FJ, Slice D (1990) Extensions of the procrustes method for the optimal superimposition of landmarks. Syst Zool 39:40–59
Rohlf FJ, Loy A, Corti M (1996) Morphometric analysis of old world talpidae (Mammalia, Insectivora) using partial-warp scores. Syst Biol 45:344–362
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining methods: new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Tamura K, Petersen D, Petersen N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Van Alphen JJM, Janssen ARM (1982) Host selection by Asobara tabida Nees (Braconidae; Alysiinae) a larval parasitoid of fruit inhabiting drosophilid species. II. Host species selection. Neth J Zool 32:194–214
Walsh DB, Bolda MP, Goodhue RE, Dreves AJ, Lee J, Bruck DJ, Walton VM, O’Neal SD, Zalom FG (2011) Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae): invasive pest of ripening soft fruit expanding its geographic range and damage potential. J Integr Pest Manag 2:G1–G7
Acknowledgments
We thank Y. Murata and B. Novković for their assistance in the molecular studies. This work was partly supported by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan (No. 23370005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kasuya, N., Mitsui, H., Ideo, S. et al. Ecological, morphological and molecular studies on Ganaspis individuals (Hymenoptera: Figitidae) attacking Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Appl Entomol Zool 48, 87–92 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-012-0156-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-012-0156-0