Abstract
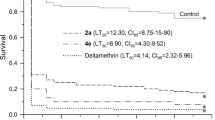
The effects of sublethal concentrations of indoxacarb on Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae) were examined. In comparison with the control, sublethal concentrations led to a significant decrease in adult emergence, the percentage of pupation and pupal weight of the parent generation, fecundity, and adult longevity. They also significantly decreased the net reproductive rate (R 0), intrinsic rate of increase (r m), finite rate of increase (λ), and gross reproduction rate (GRR), and had significantly increased egg developmental time and doubling time (Dt) of P. xylostella. However, sublethal concentrations of indoxacarb had no significant affect on adult emergence, percentage of pupation, larva, prepupa and pupa developmental periods, hatchability, and sex ratio of offspring. The results of this study indicated that sublethal concentrations can decrease the biological parameters of P. xylostella.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alyokhin A, Sewell G, Choban R (2008) Reduced viability of Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata, eggs exposed to novaluron. Pest Manag Sci 64:94–99
Capinera JL (2001) Handbook of vegetable pests. Academic Press, New York, p 729
Cutler GC, Scott-Dupree CD, Tolman JH, Harris CR (2005) Acute and sublethal toxicity of novaluron, a novel chitin synthesis inhibitor, to Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Pest Manag Sci 61:1060–1068
Delpuech JM, Meyet J (2003) Reduction in the sex ratio of the progeny of a parasitoid wasp (Trichogramma brassicae) surviving the insecticide chlorpyrifos. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 45:203–208
Dinter A, Wiles JA (2000) Safety of the new DuPont insecticide indoxacarb to beneficial arthropods: an overview. IOBC Bull 23:149–156
Ergin E, Er A, Uçkan F, Rivers DB (2007) Effect of cypermethrin exposed hosts on egg-adult developmental time, number of offspring, sex ratio, longevity, and size of Apanteles galleriae Wilkinson (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Belg J Zool 137:27–31
Eziah VY, Rose HA, Clift AD, Mansfield S (2008) Susceptibility of four field populations of the diamondback moth Plutella xylostella L. (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae) to six insecticides in the Sydney region, New South Wales. Aust. J. Entomol. 47:355–360
Fujiwara Y, Takahashi T, Yoshioka T, Nakasuji F (2002) Changes in egg size of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae) treated with fenvalerate at sublethal doses and viability of the eggs. Appl Entomol Zool 37:103–109
Galvan TL, Koch RL, Hutchison WD (2005) Effects of spinosad and indoxacarb on survival, development and reproduction of the multicolored Asian lady beetle (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biol Control 34:108–114
Golmohammadi Gh, Hejazi M, Iranipour Sh, Mohammadi SA (2009) Lethal and sublethal effects of endosulfan, imidacloprid and indoxacarb on first instar larvae of Chrysoperla carnea (Neu.: Chrysopidae) under laboratory conditions. J Entomol Soc Iran 28:37–47
Gupta PR, Chandel RS (1995) Effects of diflubenzuron and penfluron on workers of Apis cerana indica F. and Apis mellifera L. Apidologie 26:3–10
Harder HH, Riley SL, MacCann SS and Irving SN (1996) DPX-MP062: a novel broad-spectrum, environmentally soft, insect control compound. In: Proceeding of the 1996 Brighton Crop Protection Conference. 5A-a, pp 449–454
Haseeb M, Amano H (2002) Effects of contact, oral and persistent toxicity of selected pesticides on Cotesia plutellae (Hym., Braconidae), a potential parasitoid of Plutella xylostella (Lep., Plutellidae). J Appl Entomol 126:8–13
Haynes KF (1988) Sublethal effects of neurotoxic insecticides on insect behavior. Ann Rev Entomol 33:149–168
Kerns DL, Stewart SD (2000) Sublethal effects of insecticides on the intrinsic rate of increase of cotton aphid. Entomol Exp Appl 94:41–49
Lashkari MR, Sahragard A, Ghadamyari M (2007) Sublethal effects of imidacloprid and pymetrozine on population growth parameters of cabbage aphid, Brevicoryne brassicae on rapeseed, Brassica napus L. Insect Sci 14:207–212
Luckey TD (1968) Insecticide hormoligosis. J Econ Entomol 61:7–12
Maia AHN, Luiz AJB, Canpanhola C (2000) Statistical influence on associated fertility life table parameters using jackknife technique, computational aspect. J Econ Entomol 93:511–518
Meier GA, Silverman R, Ray PS, Cullen TG, Ali SF, Mared FL, Webster CA (1992) Insecticidal dihydropyrazoles with reduced lipophilicity. In: Baker DR, Fenyes JG, Steffens JJ (eds) Synthesis and chemistry of agrochemicals. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 313–326
Michaud JP, Grant AK (2003) IPM-compatibility of foliar insecticides for citrus: indices derived from toxicity to beneficial insects from four orders. J Insect Sci 3:n18
Morse JG, Zareh N (1991) Pesticide-induced hormoligosis of citrus thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) fecundity. J Econ Entomol 84:1169–1174
Nadda G, Saxena PN, Srivstava G (2005) Effects of sublethal doses of beta-cyfluthrin on mutant Drosophila melanogaster (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Appl Entomol Zool 40:265–271
Nemoto H (1993) Mechanism of resurgence of the diamondback moth. Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae). JARQ 27:27–32
Rezaei M, Talebi K, Hosseini Naveh V, Kavousi A (2007) Impacts of the pesticides imidacloprid, propargite and pymetrozine on Chrysoperla carnea (Stephens) (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae): IOBC and life table. Biol Control 5:385–398
Ripper WE (1956) Effect of pesticides on balance of arthropod populations. Annu Rev Entomol 1:403–438
SAS Institute (1997) SAS/STAT guide for personal computers. Ver. 6.12. SAS Institute, Cary, NC
Sayyed AH, Attique NMR, Khaliq A, Wright DJ (2005) Inheritance of resistance and cross-resistance to deltamethrin in Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) from Pakistan. Pest Manag Sci 61:636–642
Sota N, Motoyama N, Fujisaki K, Nakasuji F (1998) Possible amplification of insecticide hormoligosis from resistance in the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae). Appl Entomol Zool 33:435–440
Sun CN, Wu TK, Chen JS and Lee WT (1986) Insecticide resistance in diamondback moth, Management. In: Talekar NS and Griggs TD (eds.). Diamondback moth management. Proceedings of the First International Workshop. Asian Vegetable Research and Development Center, Taiwan, pp. 359–371
Tabashnik BE, Cushing NL (1987) Leaf residue vs. topical bioassays for assessing insecticide resistance in the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella L. FAO Plant Prot Bull 35:11–14
Talekar NS, Shelton AM (1993) Biology, ecology and management of the diamondback moth. Annu Rev Entomol 38:275–301
Wang XY, Yang ZQ, Shen ZR, Lu J, Xu WB (2008) Sublethal effects of selected insecticides on fecundity and wing dimorphism of green peach aphid (Hom., Aphididae). J Appl Entomol 132:135–142
Wang DX, Qiu H, Ren XX, Zhang WZ, Wang KY (2009) Sublethal effects of spinosad on survival, growth and reproduction of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pest Manag Sci 65:223–227
Wing KD, Schnee ME, Sacher M, Connair M (1998) A novel oxadiazine insecticide is bioactivated in lepidopteran larvae. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 37:91–103
Yin XH, Wu QJ, Li XF, Zhang YJ, Xu BY (2008) Sublethal effects of spinosad on Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae). Crop Prot 27:1385–1391
Zanuncio TV, Zanuncio JC, Serrao JE, Medeiros RS, Pinon TB, Sediyama CA (2005) Fertility and life expectancy of the predator Supputius cincticeps (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) exposed to sublethal doses of permethrin. Biol Res 38:31–39
Acknowledgments
We thank the Agricultural Entomology section of the Iranian Research Institute of Plant Protection, Tehran, Iran, and the Entomology Section of the Department of Plant Protection of Shahed University, Tehran, Iran. We also thank Dr. Edward. A. Ueckermann from North-West University, South Africa, for his review and excellent comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoudvand, M., Abbasipour, H., Garjan, A.S. et al. Sublethal effects of indoxacarb on the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae). Appl Entomol Zool 46, 75–80 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-010-0010-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-010-0010-1