Abstract
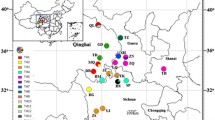
The chloroplast genomes of five Fritillaria ussuriensis materials from different production areas were comparatively analyzed, atpF and petB were screened as specific DNA barcodes, and the population identification and genetic diversity of F. ussuriensis were analyzed based on them. The F. ussuriensis chloroplast genome showed a total length of 151 515–151 548 bp with a typical tetrad structure and encoded 130 genes. atpF and petB were used to amplify 183 samples from 13 populations, and they could identify 6 and 9 haplotypes, respectively. Joint analysis of the two sequences revealed 18 haplotypes, named H1–H18, with the most widely distributed and most abundant being H4. Ten haplotypes were unique for 7 populations that they could be used to distinguish from others. Haplotype diversity and nucleotide diversity were 0.99 and 2.09 × 10−3, respectively, indicating the genetic diversity was relatively rich. The results of the intermediary adjacency network showed that H5 was the oldest haplotype, and stellate radiation was centered around it, indicating that population expansion occurred in genuine production areas. This study lays a theoretical foundation for the population identification, genetic evolution, and breed selection of F. ussuriensis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
cpDNA sequences determined in this study were deposited in NCBI GenBank under the accession numbers OR723982-OR723986. atpF sequences determined in this study were deposited in NCBI GenBank under the accession numbers OR767291-OR767296. petB sequences determined in this study were deposited in NCBI GenBank under the accession numbers OR767298-OR767306.
References
Bazin E, Glémin S, Galtier N (2006) Population size does not influence mitochondrial genetic diversity in animals. Science 312(5773):570–572. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1122033
Beier S, Thiel T, Münch T, Scholz U, Mascher M, Valencia A (2017) MISA-web: a web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 33(16):2583–2585. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx198
Coart E, Van Glabeke S, De Loose M, Larsen AS, Roldan-Ruiz I (2006) Chloroplast diversity in the genus Malus: new insights into the relationship between the European wild apple (Malus sylvestris (L.) Mill.) and the domesticated apple (Malus domestica Borkh.). Mol Ecol 15(8):2171–2182. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2006.02924.x
de Vere N, Rich Tc Fau - Trinder, Sarah A, Trinder Sa Fau - Long, Charlotte, Long C (2015) DNA barcoding for plants, Methods Mol Biol, 1245 (1940–6029 (Electronic)): 101–118.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-1966-6_8
Fagen L, Nianhe X (2005) Population structure and genetic diversity of an endangered species, Glyptostrobus pensilis (Cupressaceae). J Bot Bull Acad Sin 46:155–162
Huang J, Yu Y, Liu Y-M, Xie D-F, He X-J, Zhou S-D (2020) Comparative chloroplast genomics of Fritillaria (Liliaceae), inferences for phylogenetic relationships between Fritillaria and Lilium and plastome evolution. Plants 9(2):133–147. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9020133
Jiang D, Zhao Z, Zhang T, Zhong W, Liu C, Yuan Q, Huang L (2017) The chloroplast genome sequence of Scutellaria baicalensis provides insight into intraspecific and interspecific chloroplast genome diversity in Scutellaria. Genes 8(9):227–239. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8090227
Kehie M, Kumaria S, Devi KS, Tandon P (2016) Genetic diversity and molecular evolution of Naga King Chili inferred from internal transcribed spacer sequence of nuclear ribosomal DNA. Meta Gene 7:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mgene.2015.11.006
Kim JH, Jung J-Y, Choi H-I, Kim N-H, Park JY, Lee Yi, Yang T-J (2012) Diversity and evolution of major Panax species revealed by scanning the entire chloroplast intergenic spacer sequences. Genet Resour Crop Evol 60(2):413–425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-012-9844-4
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23(21):2947–2948. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Li Y, Zhang Z, Yang J, Lv G (2018) Complete chloroplast genome of seven Fritillaria species, variable DNA markers identification and phylogenetic relationships within the genus. PLoS One 13(3):e0194613. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0194613
Li J, Xie D-F, Guo X-L, Zheng Z-Y, He X-J, Zhou S-D (2020) Comparative analysis of the complete plastid genome of five Bupleurum species and new insights into DNA barcoding and phylogenetic relationship. Plants 9(4):543–562. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9040543
Liu C, Chang J Fau - Zhang, Li, Zhang L Fau - Zhang, Jie, Zhang J Fau - Li, Shengyu, Li S (2012) Purification and antioxidant activity of a polysaccharide from bulbs of Fritillaria ussuriensis Maxim. Int J Biol Macromol 50(4):1075-1080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2012.03.006
Lynch M, Conery JS (2003) The origins of genome complexity. Science 302(5649):1401–1404. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1089370
Meng J, Li X, Li H, Yang J, Wang H, He J (2018) Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes of four Aconitum medicinal species. Molecules 23(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051015
Nock CJ, Waters DL, Edwards MA, Bowen SG, Rice N, Cordeiro GM, Henry RJ (2011) Chloroplast genome sequences from total DNA for plant identification. Plant Biotechnol J 9(3):328–333. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2010.00558.x
Park I, Kim W, Yeo S-M, Choi G, Kang Y-M, Piao R, Moon B (2017) The complete chloroplast genome sequences of Fritillaria ussuriensis Maxim. and Fritillaria cirrhosa D. Don, and comparative analysis with other Fritillaria species. Molecules 22(6):982–996. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22060982
Posada D, Fau - Crandall KA, Crandall KA (2001) Intraspecific gene genealogies: trees grafting into networks, Trends Ecol Evol, 16 (1872–8383 (Electronic)): 37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-5347(00)02026-7
Reusch TB, Ehlers A, Hämmerli A, Worm B (2005) Ecosystem recovery after climatic extremes enhanced by genotypic diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(8):2826–2831. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0500008102
Rozas J, Ferrer-Mata A, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Guirao-Rico S, Librado P, Ramos-Onsins SE, Sánchez-Gracia A (2017) DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol Biol Evol 34(12):3299–3302. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx248
Sally Rahayu YY (2023) Assessing adoption of DNA barcoding in herbal value chain: a multistakeholder analysis. Nat Prod J 13(6):54–62. https://doi.org/10.2174/2210315513666220928112238
Seo J-Y, Kim J-S, Kim K-L (2018) Anti-inflammatory effects and innate immunity suppression by Fritillaria ussuriensis extracts. Asian J Beauty Cosmetol 16(1):10–19. https://doi.org/10.20402/ajbc.2017.0145
Stenfan Kurtz, Choudhuri JV, Ohlebusch E, Schleiermacher C, Stoye J, Giegerich R (2001) REPuter the manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res 29:4633–4642. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.22.4633
Vladimir M, Pierre L, Yves D (2004) Modelling phylogenetic relationships using reticulated networks. Zool Scr 33:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-6409.2004.00141.x
Wang S-H, Bao L, Wang T-M, Wang H-F, Ge J-P (2016) Contrasting genetic patterns between two coexisting Eleutherococcus species in northern China. Ecol Evol 6(10):3311–3324. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.2118
Wang Z, Cao F, Chen Y, Tang Z, Wang Z (2018) Simultaneous determination and pharmacokinetics of peimine and peiminine in beagle dog plasma by UPLC-MS/MS after the oral administration of Fritillariae ussuriensis Maxim and Fritillariae thunbergii Miq powder. Molecules 23(7):1573–1586. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071573
Whittall JB, Syring J Fau - Parks M, Parks M Fau - Buenrostro J, Buenrostro J Fau - Dick C, Dick C Fau - Liston A, Liston A Fau - Cronn R, Cronn R (2010) Finding a (pine) needle in a haystack: chloroplast genome sequence divergence in rare and widespread pines, Mol Ecol, 19 (1365–294X (Electronic)): 100–114.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2009.04474.x
Yang L, Zhang M, Yang T, Ming W, Tse WG, Kathy T, Ye B (2021) LC–MS/MS coupled with chemometric analysis as an approach for the differentiation of bulbus Fritillaria unibracteata and Fritillaria ussuriensis. Phytochem Anal 32(6):957–969. https://doi.org/10.1002/pca.3038
Yi D-K, Lee H-L, Sun B-Y, Chung MY, Kim K-J (2012) The complete chloroplast DNA sequence of Eleutherococcus senticosus (Araliaceae); comparative evolutionary analyses with other three asterids. Mol Cells 33(5):497–508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-012-2281-6
Zhang X, Liu Y, Gu X, Guo Z, Li L, Song X, Liu S, Zang Y, Li Y, Liu C, Wei S (2014) Genetic diversity and population structure of Rheum tanguticum (Dahuang) in China. Chin Med 9(1):26. https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-8546-9-26
Zhang T, Huang S, Song S, Zou M, Yang T, Wang W, Zhou J, Liao H (2021) Identification of evolutionary relationships and DNA markers in the medicinally important genus Fritillaria based on chloroplast genomics. PeerJ 9:e12612. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.12612
Zhong Y, Wang H, Wei Q, Cao R, Zhang H, He Y, Wang L (2019) Combining DNA barcoding and HPLC fingerprints to trace species of an important traditional Chinese medicine Fritillariae Bulbus. Molecules 24(18):3269–3280. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183269
Zhou Z, Wang J, Pu T, Dong J, Guan Q, Qian J, Shi L, Duan B (2022) Comparative analysis of medicinal plant Isodon rubescens and its common adulterants based on chloroplast genome sequencing. Front Plant Sci 13:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.1036277
Zhu S, Niu Z, Xue Q, Wang H, Xie X, Ding X (2018) Accurate authentication of Dendrobium officinale and its closely related species by comparative analysis of complete plastomes. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 8(6):969–980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2018.05.009
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our special thanks to Shengli Wei and Xiaohui Wang for conceiving and designing the research. Xin Wang and Zhifei Zhang conducted experiments and wrote the manuscript. Gaojie He, Kelu An, Laha Amu, Wenqin Chen, and Ziqi Liu collected the samples. Jinhui Man, Yue Shi, Yuying Huang, Xiaoqin Zhang, and Shanhu LIU analyzed the data.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from study on breeding and cultivation technology of precision medicine Bupleurum bupleurum based on molecular anti-counterfeiting technology (20221156), research project on molecular anti-counterfeiting technology of 4 precision medicinal materials such as Platycodon grandiflorus (2020110031009385), and National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFC3501505).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: Izabela Pawłowicz
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Xin Wang and Zhifei Zhang are first authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Zhang, Z., Shi, Y. et al. Population identification and genetic diversity analysis of Fritillaria ussuriensis (Fritillaria) based on chloroplast genes atpF and petB. J Appl Genetics (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-024-00874-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-024-00874-z