Abstract
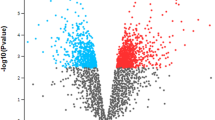
Mastitis, an inflammatory response of mammary glands to invading bacteria, is one of the most economically costly diseases affecting dairy animals. Escherichia coli can be introduced as a major etiological agent of bovine mastitis in well-managed dairy farms. It is of great significance to understand the regulatory mechanisms by which the disease can be controlled. High-throughput technologies combined with novel computational systems biology tools have provided new opportunities for a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms that underlie disease. In the current study, the results of microarray meta-analysis research were used to perform a network analysis to potentially identify molecular mechanisms that regulate gene expression profile in response to E. coli mastitis. In our result, transcription factors, TP53, SP1, ligands, INS, IFNG, EGF, and protein kinases, MAPK1, MAPK14, AKT1, were identified as the key upstream regulators whereas protein kinases, MAPK3, MAPK8, MAPK14, ligands, VEGFA, IL10, an extracellular protein, MMP2, and a mitochondrial membrane protein, BCL2, were identified as the key downstream targets of differentially expressed genes. The results of this research revealed important genes that have the key functions in immune response, inflammation, or mastitis which can provide the basis for strategies to improve the diagnosis and treatment of mastitis in dairy cows.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelrahim M, Safe S (2005) Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors decrease vascular endothelial growth factor expression in colon cancer cells by enhanced degradation of Sp1 and Sp4 proteins. Mol Pharmacol 68:317–329. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.105.011825
Alanazi IO, Ebrahimie E (2016) Computational systems biology approach predicts regulators and targets of microRNAs and their genomic hotspots in apoptosis process. Mol Biotechnol 58:460–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-016-9938-x
Androulidaki A et al (2009) The kinase Akt1 controls macrophage response to lipopolysaccharide by regulating microRNAs. Immunity 31:220–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2009.06.024
Arranz A et al (2012) Akt1 and Akt2 protein kinases differentially contribute to macrophage polarization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:9517–9522. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1119038109
Ashburner M et al. (2000) Gene ontology. Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium http://www.geneontology.org. Accessed November 2017
Bader GD, Christopher DB, Hogue WV (2003) BIND. The biomolecular interaction network database. http://bind.ca
Bakhtiarizadeh MR, Moradi-Shahrbabak M, Ebrahimie E (2013) Underlying functional genomics of fat deposition in adipose tissue. Gene 521:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2013.03.045
Bannerman DD, Paape MJ, Jai-Wei L, Xin Z, Hope JC, Pascal R (2004) Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus Elicit Differential Innate Immune Responses following Intramammary Infection. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 11(3):463–472
Bar D et al (2008) The cost of generic clinical mastitis in dairy cows as estimated by using dynamic programming. J Dairy Sci 91:2205–2214. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2007-0573
Beishline K, Azizkhan-Clifford J (2015) Sp1 and the ‘hallmarks of cancer’. FEBS J 282:224–258. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13148
Black AR, Black JD, Azizkhan-Clifford J (2001) Sp1 and kruppel-like factor family of transcription factors in cell growth regulation and cancer. J Cell Physiol 188:143–160. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.1111
Bradley A (2002) Bovine mastitis: an evolving disease. Vet J 164:116–128
Busca A, Saxena M, Kryworuchko M, Kumar A (2009a) Anti-apoptotic genes in the survival of monocytic cells during infection. Curr Genomics 10:306–317. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920209788920967
Busca A, Saxena M, Kryworuchko M, Kumar A (2009b) Anti-apoptotic genes in the survival of monocytic cells during infection. Curr Genomics 10:306–317
Centola M et al (2013) Development of a multi-biomarker disease activity test for rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One 8:e60635. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060635
Cooks T et al (2013) Mutant p53 prolongs NF-kappaB activation and promotes chronic inflammation and inflammation-associated colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell 23:634–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2013.03.022
Dandona P, Aljada A, Mohanty P, Ghanim H, Hamouda W, Assian E, Ahmad S (2001) Insulin inhibits intranuclear nuclear factor kappaB and stimulates IkappaB in mononuclear cells in obese subjects: evidence for an anti-inflammatory effect? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:3257–3265. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.86.7.7623
Dandona P, Ghanim H, Bandyopadhyay A, Korzeniewski K, Ling Sia C, Dhindsa S, Chaudhuri A (2010) Insulin suppresses endotoxin-induced oxidative, nitrosative, and inflammatory stress in humans. Diabetes Care 33:2416–2423. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc10-0929
Dong C, Davis RJ, Flavell RA (2002) MAP kinases in the immune response. Annu Rev Immunol 20:55–72. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.20.091301.131133
Endo K, Takino T, Miyamori H, Kinsen H, Yoshizaki T, Furukawa M, Sato H (2003) Cleavage of syndecan-1 by membrane type matrix metalloproteinase-1 stimulates cell migration. J Biol Chem 278:40764–40770. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M306736200
Genini S et al (2011) Strengthening insights into host responses to mastitis infection in ruminants by combining heterogeneous microarray data sources. BMC Genomics 12:225. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-225
Ghanim H et al (2008) Acute modulation of toll-like receptors by insulin. Diabetes Care 31:1827–1831. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc08-0561
Gholizadeh-Ghaleh Aziz S, Pashaei-Asl F, Fardyazar Z, Pashaiasl M (2016) Isolation, characterization, cryopreservation of human amniotic stem cells and differentiation to osteogenic and adipogenic cells. PLoS One 11:e0158281. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0158281
He X, Wei Z, Zhou E, Chen L, Kou J, Wang J, Yang Z (2015) Baicalein attenuates inflammatory responses by suppressing TLR4 mediated NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-induced mastitis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 28:470–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2015.07.012
Hogan J, Larry Smith K (2003) Coliform mastitis. Vet Res 34:507–519. https://doi.org/10.1051/vetres:2003022
Hogeveen H, Huijps K, Lam TJ (2011) Economic aspects of mastitis: new developments. N Z Vet J 59:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/00480169.2011.547165
Kanehisa M (2008) KEGG. Metabolic database. http://www.genome.ad.jp/kegg/. Accessed November 2017
Kargarfard F, Sami A, Ebrahimie E (2015) Knowledge discovery and sequence-based prediction of pandemic influenza using an integrated classification and association rule mining (CBA) algorithm. J Biomed Inform 57:181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2015.07.018
Lamb DJ, Modjtahedi H, Plant NJ, Ferns GA (2004) EGF mediates monocyte chemotaxis and macrophage proliferation and EGF receptor is expressed in atherosclerotic plaques. Atherosclerosis 176:21–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2004.04.012
Lee WR et al (2013) Effects of chimeric decoy oligodeoxynucleotide in the regulation of transcription factors NF-kappaB and Sp1 in an animal model of atherosclerosis. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 112:236–243. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.12029
Lewis JD (2011) The utility of biomarkers in the diagnosis and therapy of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 140:1817–1826 e1812. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2010.11.058
Li D et al (2013) Emodin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis in mice by inhibiting activation of NF-kappaB and MAPKs signal pathways. Eur J Pharmacol 705:79–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.02.021
Malarstig A, Eriksson P, Hamsten A, Lindahl B, Wallentin L, Siegbahn A (2008) Raised interleukin-10 is an indicator of poor outcome and enhanced systemic inflammation in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Heart 94:724–729. https://doi.org/10.1136/hrt.2007.119271
McGuire JK, Li Q, Parks WC (2003) Matrilysin (matrix metalloproteinase-7) mediates E-cadherin ectodomain shedding in injured lung epithelium. Am J Pathol 162:1831–1843. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64318-0
Mimoso C, Lee DD, Zavadil J, Tomic-Canic M, Blumenberg M (2014) Analysis and meta-analysis of transcriptional profiling in human epidermis. Methods Mol Biol 1195:61–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/7651_2013_60
Minuti A et al (2015) Acute mammary and liver transcriptome responses after an intramammary Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide challenge in postpartal dairy cows. Phys Rep 3. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.12388
Mizia-Stec K, Gasior Z, Zahorska-Markiewicz B, Janowska J, Szulc A, Jastrzebska-Maj E, Kobielusz-Gembala I (2003) Serum tumour necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-2 and interleukin-10 activation in stable angina and acute coronary syndromes. Coron Artery Dis 14:431–438. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mca.0000085707.34267.70
Mohammadi A, Saraee MH, Salehi M (2011) Identification of disease-causing genes using microarray data mining and gene ontology. BMC Med Genet 4:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1755-8794-4-12
Nikitin A, Egorov S, Daraselia N, Mazo I (2003) Pathway studio--the analysis and navigation of molecular networks. Bioinformatics 19:2155–2157
Panahi B, Mohammadi SA, Ebrahimi Khaksefidi R, Fallah Mehrabadi J, Ebrahimie E (2015) Genome-wide analysis of alternative splicing events in Hordeum vulgare: highlighting retention of intron-based splicing and its possible function through network analysis. FEBS Lett 589:3564–3575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2015.09.023
Papageorgiou AP, Heymans S (2012) Interactions between the extracellular matrix and inflammation during viral myocarditis. Immunobiology 217:503–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imbio.2011.07.011
Parks WC, Wilson CL, Lopez-Boado YS (2004) Matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 4:617–629. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1418
Pathi S, Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, Nair V, Lee SO, Safe S (2012) Aspirin inhibits colon cancer cell and tumor growth and downregulates specificity protein (Sp) transcription factors. PLoS One 7:e48208. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048208
Portt L, Norman G, Clapp C, Greenwood M, Greenwood MT (2011) Anti-apoptosis and cell survival: a review. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:238–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.10.010
Ramasamy A, Mondry A, Holmes CC, Altman DG (2008) Key issues in conducting a meta-analysis of gene expression microarray datasets. PLoS Med 5:e184. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0050184
Rech J et al (2016) Prediction of disease relapses by multibiomarker disease activity and autoantibody status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis on tapering DMARD treatment. Ann Rheum Dis 75:1637–1644. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207900
Rinaldi M, Li RW, Capuco AV (2010) Mastitis associated transcriptomic disruptions in cattle. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 138:267–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetimm.2010.10.005
Shafi S, Lamb D, Modjtahedi H, Ferns G (2010) Periadventitial delivery of anti-EGF receptor antibody inhibits neointimal macrophage accumulation after angioplasty in a hypercholesterolaemic rabbit. Int J Exp Pathol 91:224–234. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2613.2009.00700.x
Sharifi S, Pakdel A, Ebrahimi M, Reecy JM, Fazeli Farsani S, Ebrahimie E (2018) Integration of machine learning and meta-analysis identifies the transcriptomic bio-signature of mastitis disease in cattle. PLoS One 13:e0191227. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0191227
Sipka A, Klaessig S, Duhamel GE, Swinkels J, Rainard P, Schukken Y (2014) Impact of intramammary treatment on gene expression profiles in bovine Escherichia coli mastitis. PLoS One 9:e85579. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085579
Soehnlein O et al (2010) Anesthesia aggravates lung damage and precipitates hypotension in endotoxemic sheep. Shock 34:412–419. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181d8e4f5
Song X, Guo M, Wang T, Wang W, Cao Y, Zhang N (2014) Geniposide inhibited lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis by modulating TLR4 and apoptosis-related factors in mouse mammary glands. Life Sci 119:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2014.10.006
Subramanian A et al (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:15545–15550. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506580102
Tan KW et al (2013) Neutrophils contribute to inflammatory lymphangiogenesis by increasing VEGF-A bioavailability and secreting VEGF-D. Blood 122:3666–3677. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-11-466532
Turner MD, Nedjai B, Tara Hurst T, Pennington DJ (2014) Cytokines and chemokines: at the crossroads of cell signalling and inflammatory disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1843:2563–2582
Younis S, Javed Q, Blumenberg M (2016) Meta-analysis of transcriptional responses to mastitis-causing Escherichia coli. PLoS One 11:e0148562. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0148562
Zhang WR et al (2015) Plasma IL-6 and IL-10 concentrations predict AKI and long-term mortality in adults after cardiac surgery. J Am Soc Nephrol 26:3123–3132. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2014080764
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Research does not involve human participants and/or animals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by: Maciej Szydlowski
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Online Resource 1
Differentially expressed genes identified after meta-analysis (one-tailed q < 0.005). (XLSX 44 kb)
Online Resource 2
The network constructed by the Common Regulator algorithm. (PNG 8041 kb)
Online Resource 3
The details of applying of Common Regulator algorithms on meta-genes. (XLSX 269 kb)
Online Resource 4
The network constructed by the Common Targets algorithm. (PNG 7031 kb)
Online Resource 5
The details of applying of Common Target algorithms on meta-genes. (XLSX 176 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharifi, S., Pakdel, A., Ebrahimie, E. et al. Prediction of key regulators and downstream targets of E. coli induced mastitis. J Appl Genetics 60, 367–373 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-019-00499-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-019-00499-7