Abstract
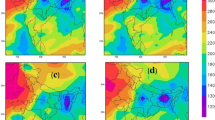
Outgoing longwave radiation (OLR) at the top of the atmosphere (TOA) is a key parameter for understanding and interpreting the relationship between clouds, radiation, and climate interactions. It has been one of the operational products of the Fengyun (FY) meteorological satellites. OLR accuracy has gradually improved with advancements in satellite payload performance and the OLR retrieval algorithm. Supported by the National Key R&D Program Retrospective Calibration of Historical Chinese Earth Observation Satellite data (Richceos) project, a long-term OLR climate data record (CDR) was reprocessed based on the recalibrated Level 1 data of FY series satellites using the latest OLR retrieval algorithm. In this study, Fengyun-3B (FY-3B)’s reprocessed global OLR data from 2010 to 2018 were evaluated by using the Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System (CERES) global daily OLR data. The results showed that there was a high consistency between the FY-3B instantaneous OLR and CERES Single Scanner Footprint (SSF) OLR. Globally, between the two CDR datasets, the correlation coefficient reached 0.98, and the root-mean-square error (RMSE) was approximately 8–9 W m−2. The bias mainly came from the edge regions of the satellite orbit, which may be related to the satellite zenith angle and cloud cover distribution. It was shown that the long-term FY-3B OLR had temporal stability compared to CERES OLR long-term data. In terms of spatial distribution, the mean deviations showed zonal and seasonal characteristics, although seasonal fluctuations were observed in the differences between the two datasets. Effects of FY-3B OLR application to the South China Sea monsoon region and ENSO were demonstrated and analyzed, and the results showed that the seasonal deviation of FY-3B’s OLR comes mainly from the retrieval algorithm. However, it has little effect on the analysis of climate events.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowman, K. W., D. T. Shindell, H. M. Worden, et al., 2013: Evaluation of ACCMIP outgoing longwave radiation from tropospheric ozone using TES satellite observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 13, 4057–4072, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-4057-2013.
Chen, Y., 2006: A study of the southeast Asian summer monsoon onset, evolution and its influence on the weather and climate over the southwest of China. Ph.D. dissertation, Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, Nanjing, 152 pp. (in Chinese)
Chiodi, A. M., and D. E. Harrison, 2013: El Niño impacts on seasonal U.S. atmospheric circulation, temperature, and precipitation anomalies: The OLR-event perspective. J. Climate, 26, 822–837, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00097.1.
Chiodi, A. M., and D. E. Harrison, 2015: Global seasonal precipitation anomalies robustly associated with El Niño and La Niña events—An OLR perspective. J. Climate, 28, 6133–6159, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00387.1.
Clerbaux, N., S. Dewitte, L. Gonzalez, et al., 2003: Outgoing longwave flux estimation: improvement of angular modelling using spectral information. Remote Sens. Environ., 85, 389–395, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(03)00015-4.
Clerbaux, N., T. Akkermans, E. Baudrez, et al., 2020: The climate monitoring SAF outgoing longwave radiation from AVHRR. Remote Sens., 12, 929, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12060929.
Gruber, A., and A. F. Krueger, 1984: The status of the NOAA outgoing longwave radiation data set. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 65, 958–962, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1984)065<0958:TSOTNO>2.0.CO;2.
Hu, X. Q., 2012: Unified radiometric recalibration study on long-term historical data record of meteorological satellite sensors. Ph.D. dissertation, Institute of Remote Sensing Applications, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 262 pp. (in Chinese)
Huang, M., J. D. Li, G. Zeng, et al., 2020: Regional characteristics of cloud radiative effects before and after the South China Sea summer monsoon onset. J. Meteor. Res., 34, 1167–1182, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-020-0018-6.
Inoue, T., and S. A. Ackerman, 2002: Radiative effects of various cloud types as classified by the split window technique over the eastern sub-tropical Pacific derived from collocated ERBE and AVHRR data. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 80, 1383–1394, doi: https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.80.1383.
Kiladis, G. N., J. Dias, K. H. Straub, et al., 2014: A comparison of OLR and circulation-based indices for tracking the MJO. Mon. Wea. Rev., 142, 1697–1715, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-13-00301.1.
Kim, B.-Y., and K.-T. Lee, 2019: Using the Himawari-8 AHI multi-channel to improve the calculation accuracy of outgoing longwave radiation at the top of the atmosphere. Remote Sens., 11, 589, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050589.
Kim, B.-Y., K.-T. Lee, J.-B. Jee, et al., 2018: Retrieval of outgoing longwave radiation at top-of-atmosphere using Himawari-8 AHI data. Remote Sens. Environ., 204, 498–508, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2017.10.006.
Knapp, K. R., S. Ansari, C. L. Bain, et al., 2011: Globally gridded satellite observations for climate studies. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 92, 893–907, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/2011BAMS3039.1.
Lee, H.-T., 2014: Climate Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (C-ATBD): Outgoing Longwave Radiation (OLR)-Daily. NOAA’s Climate Data Record (CDR) Program, CDRP-AT-BD-0526, 46 pp. Available online at https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/pub/data/sds/cdr/CDRs/Outgoing%20Longwave%20Radiation%20-%20Daily/AlgorithmDescription_01B-21.pdf. Accessed on 16 May 2022.
Lee, H.-T., A. Gruber, R. G. Ellingson, et al., 2007: Development of the HIRS outgoing longwave radiation climate dataset. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 24, 2029–2047, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/2007JTECHA989.1.
Liebmann, B., and C. A. Smith, 1996: Description of a complete (interpolated) outgoing longwave radiation dataset. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77, 1275–1277.
Liu, J., Y. Q. Da, T. Li, et al., 2020: Impact of ENSO on MJO pattern evolution over the Maritime Continent. J. Meteor. Res., 34, 1151–1166, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-020-0046-2.
Liu, L., W. C. Zhang, W. Chen, et al., 2021: Evaluation of FY-3B reprocessed OLR data in the Asian-Australian monsoon region during 2011–2019: Comparison with NOAA OLR. J. Meteor. Res., 35, 964–974, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-021-1086-y.
Matthews, A. J., 2008: Primary and successive events in the Madden-Julian Oscillation. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 134, 439–453, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.224.
Nakazawa, T., 2006: Madden-Julian Oscillation activity and typhoon landfall on Japan in 2004. SOLA, 2, 136–139, doi: https://doi.org/10.2151/sola.2006-035.
Ohring, G., A. Gruber, and R. Ellingson, 1984: Satellite determinations of the relationship between total longwave radiation flux and infrared window radiance. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol., 23, 416–425, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(1984)023<0416:SDOTRB>2.0.CO;2.
Priestley, K. J., G. L. Smith, S. Thomas, et al., 2007: Validation protocol for climate quality CERES measurements. Proceedings of SPIE 6678, Infrared Spaceborne Remote Sensing and Instrumentation XV, SPIE, San Diego, USA, 66781I, doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.735312.
Ren, S. L., Y. Li, X. Fang, et al., 2018: The South China Sea summer monsoon onset index using FY satellite derived data. J. Trop. Meteor., 34, 587–597, doi: https://doi.org/10.16032/j.issn.1004-4965.2018.05.002. (in Chinese)
Schmetz, J., and Q. H. Liu, 1988: Outgoing longwave radiation and its diurnal variation at regional scales derived from Meteosat. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 93, 11,192–11,204, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/JD093iD09p11192.
Short, D. A., and R. F. Cahalan, 1983: Interannual variability and climatic noise in satellite-observed outgoing longwave radiation. Mon. Wea. Rev., 111, 572–577, doi:https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1983)111<0572:IVACNI>2.0.CO;2.
Singh, A., U. C. Mohanty, and G. Mishra, 2014: Long-lead prediction skill of Indian summer monsoon rainfall using outgoing longwave radiation (OLR): an application of canonical correlation analysis. Pure Appl. Geophys., 171, 1519–1530, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-013-0689-3.
Stechmann, S. N., and H. R. Ogrosky, 2014: The Walker circulation, diabatic heating, and outgoing longwave radiation. Geophys. Res. Lett., 41, 9097–9105, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/2014GL062257.
Stowe, L. L., H. Jacobowitz, G. Ohring, et al., 2002: The Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) Pathfinder Atmosphere (PATMOS) climate dataset: Initial analyses and evaluations. J. Climate, 15, 1243–1260, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015<1243:TAVHRR>2.0.CO;2.
Susskind, J., G. Molnar, L. Iredell, et al., 2012: Interannual variability of outgoing longwave radiation as observed by AIRS and CERES. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 117, D23107, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JD017997.
Taylor, P. C., 2012: Tropical outgoing longwave radiation and longwave cloud forcing diurnal cycles from CERES. J. Atmos. Sci., 69, 3652–3669, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-12-088.1.
Wang, C. Z., R. H. Weisberg, and J. I. Virmani, 1999: Western Pacific interannual variability associated with the El Niño—Southern Oscillation. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans, 104, 5131–5149, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/1998JC900090.
Weickmann, K. M., G. R. Lussky, and J. E. Kutzbach, 1985: Intraseasonal (30–60 day) fluctuations of outgoing longwave radiation and 250 mb streamfunction during northern winter. Mon. Wea. Rev., 113, 941–961, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1985)113<0941:IDFOOL>2.0.CO;2.
Whitburn, S., L. Clarisse, S. Bauduin, et al., 2020: Spectrally resolved fluxes from IASI data: Retrieval algorithm for clear-sky measurements. J. Climate, 33, 6971–6988, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-19-0523.1.
Wu, X., and J. J. Yan, 2011: Estimating the outgoing longwave radiation from the FY-3B satellite visible infrared radiometer Channel 5 radiance observations. Chinese Sci. Bull., 56, 3480–3485, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-011-4686-6.
Yang, G.-Y., and J. Slingo, 2001: The diurnal cycle in the tropics. Mon. Wea. Rev., 129, 784–801, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(2001)129<0784:TDCITT>2.0.CO;2.
Yang, J., C. H. Dong, N. M. Lu, et al., 2009: FY-3A: The new generation polar-orbiting meteorological satellite of China. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 67, 501–509, doi: https://doi.org/10.11676/qxxb2009.050. (in Chinese)
Yang, J., Z. Q. Zhang, C. Y. Wei, et al., 2017: Introducing the new generation of Chinese geostationary weather satellites, Fengyun-4. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 98, 1637–1658, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-16-0065.1.
Zhang, P., Q. F. Lu, X. Q. Hu, et al., 2019: Latest progress of the Chinese meteorological satellite program and core data processing technologies. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 36, 1027–1045, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-019-8215-x.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the LARC data center (https://ceres.larc.nasa.gov/) and the ECMWF (https://www.ecmwf.int/) for providing the CERES data and the ERA5 data used in this work. The authors wish to acknowledge the Editor Dr. Jun Li and two anonymous reviewers for their comments that have helped improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFB0504900 and 2018YFB0504905) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (41801278).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Liu, J., Zhang, P. et al. Evaluation of Reprocessed Fengyun-3B Global Outgoing Longwave Radiation Data: Comparison with CERES OLR. J Meteorol Res 36, 417–428 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-022-1132-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-022-1132-4