Abstract
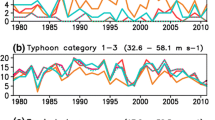
This study investigates the impact of low-frequency (intraseasonal and interannual) steering flows on straight northward-moving (defined as a meridional displacement two times greater than the zonal displacement) typhoons over the western North Pacific using observational data. The year-to-year change in the northward-moving tracks is affected by the interannual change in the location and intensity of the subtropical high. A strengthened northward steering flow east of 120°E and a weakened easterly steering flow south of the subtropical high favor more frequent straight northward tracks. Examining each of the individual northward-moving typhoons shows that they interact with three types of intraseasonal (10–60-day) background flows during their northward journey. The first type is the monsoon gyre pattern, in which the northward-moving typhoon is embedded in a closed cyclonic monsoon gyre circulation. The second type is the wave train pattern, where a cyclonic (anticyclonic) vorticity circulation is located to the west (east) of the northward-moving typhoon center. The third type is the mid-latitude trough pattern, in which the northward-moving typhoon center is located in the maximum vorticity region of the trough.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anthes R. A., 1982: Tropical Cyclones: Their Evolution, Structure and Effects. American Meteorological Society, Boston, 208 pp.
Bi M. Y., T. Li, M. Peng, et al., 2015: Interactions between typhoon Megi (2010) and a low-frequency monsoon gyre. J. Atmos. Sci., 72, 2682–2702, doi: 10.1175/JAS-D-14-0269.1.
Brand S., C. A. Buenafe, and H. D. Hamilton, 1981: Comparison of tropical cyclone motion and environmental steering. Mon. Wea. Rev., 109, 908–909, doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1981)109<0908:COTCMA>2.0.CO;2.
Cao X., T. Li, M. Peng, et al., 2014: Effects of monsoon trough intraseasonal oscillation on tropical cyclogenesis over the western North Pacific. J. Atmos. Sci., 71, 4639–4660, doi: 10.1175/JAS-D-13-0407.1.
Carr L. E., and R. L. Elsberry, 1995: Monsoonal interactions leading to sudden tropical cyclone track changes. Mon. Wea. Rev., 123, 265–290, doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1995)123<0265:MILTST>2.0.CO;2.
Chan J. C. L., and W. M. Gray, 1982: Tropical cyclone movement and surrounding flow relationships. Mon. Wea. Rev., 110, 1354–1374, doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1982)110<1354:TCMASF>2.0.CO;2.
Chen L. S., and Z. Y. Meng, 2001: An overview on tropical cyclone research progress in China during the past 10 years. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 25, 420–432, doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2001.03.11. (in Chinese)
Duchon C. E., 1979: Lanczos filtering in one and two dimensions. J. Appl. Meteor., 18, 1016–1022, doi: 10.1175/1520-0450(1979)018<1016:LFIOAT>2.0.CO;2.
Fiorino M., and R. L. Elsberry, 1989: Some aspects of vortex structure related to tropical cyclone motion. J. Atmos. Sci., 46, 975–990, doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1989)046<0975:SAOVSR>2.0.CO;2.
Fovell R. G., Y. P. Bu, K. L. Corbosiero, et al, 2016: Influence of cloud microphysics and radiation on tropical cyclone structure and motion. Meteor. Monogr., 56, 11.1–11.27, doi: 10.1175/AMSMONOGRAPHS-D-15-0006.1.
Fu B., T. Li, M. S. Peng, et al, 2007: Analysis of tropical cyclogenesis in the western North Pacific for 2000 and 2001. Wea. Forecasting, 22, 763–780, doi: 10.1175/WAF1013.1.
Gao S. Y., T. T. Zhao, L. L. Song, et al., 2017: Study of northward moving tropical cyclones in 1949–2015. Meteor. Sci. Technol., 45, 313–323, doi: 10.19517/j.1671-6345.20160229. (in Chinese)
Holland G. J., 1984: Tropical cyclone motion: A comparison of theory and observation. J. Atmos. Sci., 41, 68–75, doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1984)041<0068:TCMACO>2.0.CO;2.
Hsu P. C., T. Li, and C. H. Tsou, 2011: Interactions between boreal summer intraseasonal oscillations and synoptic-scale disturbances over the western North Pacific. Part I: Energetics diagnosis. J. Climate, 24, 927–941, doi: 10.1175/2010JCLI3833.1.
Jiang X. A., D. E. Waliser, P. K. Xavier, et al., 2015: Vertical structure and physical processes of the Madden–Julian oscillation: Exploring key model physics in climate simulations. J. Geophys. Res., 120, 4718–4748, doi: 10.1002/2014JD022375.
Kasahara A., 1957: The numerical prediction of hurricane movement with the barotropic model. J. Atmos. Sci., 14, 386–402, doi:1 0.1175/15200469(1957)014<0386:TNPOHM>2.0.CO;2.
Kasahara A., 1960: The numerical prediction of hurricane movement with a two-level baroclinic model. J. Atmos. Sci., 17, 357–370, doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1960)017<0357:TNPOHM>2.0.CO;2.
Kurihara Y., M. A. Bender, and R. J. Ross, 1993: An initialization scheme of hurricane models by vortex specification. Mon. Wea. Rev., 121, 2030–2045, doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1993)121<2030:AISOHM>2.0.CO;2.
Lander M. A., 1994: Description of a monsoon gyre and its effects on the tropical cyclones in the western North Pacific during August 1991. Wea. Forecasting, 9, 640–654, doi: 10.1175/1520-0434(1994)009<0640:DOAMGA>2.0.CO;2.
Li C. Y., J. Pan, H. Tian, et al., 2012: Typhoon activities over the western north Pacific and atmospheric intraseasonal oscillation. Meteor. Mon., 38, 1–16, doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2012.1.001. (in Chinese)
Li R. C. Y., and W. Zhou, 2013a: Modulation of western North Pacific tropical cyclone activity by the ISO. Part I: Genesis and intensity. J. Climate, 26, 2904–2918, doi: 10.1175/JCLID-12-00210.1.
Li R. C. Y., and W. Zhou, 2013b: Modulation of western North Pacific tropical cyclone activity by the ISO. Part II: Tracks and landfalls. J. Climate, 26, 2919–2930, doi: 10.1175/JCLID-12-00211.1.
Li T., 2010: Monsoon climate variabilities. Climate Dynamics: Why Does Climate Vary? D. Z. Sun, and F. Bryan, Eds., American Geophysical Union, Washington DC, doi: 10.1029/2008GM000782.
Li T., 2012: Synoptic and climatic aspects of tropical cyclogenesis in western North Pacific. Cyclones: Formation, Triggers and Control. K. Oouchi, and H. Fudeyasu, Eds., Nova Science Publishers Inc., New York, NY, USA, 276 pp.
Li T., 2014: Recent advance in understanding the dynamics of the Madden–Julian oscillation. J. Meteor. Res., 28, 1–33, doi: 10.1007/s13351-014-3087-6.
Li T., and B. Wang, 2005: A review on the western North Pacific monsoon: Synoptic-to-interannual variabilities. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci., 16, 285–314, doi: 10.3319/TAO.2005.16.2.285(A).
Li T. M., and Y. Zhu, 1991: Analysis and modelling of tropical cyclone motion (I)—The axiasymmetric structure and the sudden change of tracks. Sci. China (Ser. B), 34, 222–233, doi: 10.1360/yb1991-34-2-222.
Liebmann B., H. H. Hendon, and J. D. Glick, 1994: The relationship between tropical cyclones of the western Pacific and Indian Oceans and the Madden–Julian oscillation. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 72, 401–412, doi: 10.2151/jmsj1965.72.3_401.
Maloney E. D., and D. L. Hartmann, 1998: Frictional moisture convergence in a composite life cycle of the Madden–Julian oscillation. J. Climate, 11, 2387–2403, doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1998)011<2387:FMCIAC>2.0.CO;2.
Ren S. L., Y. M. Liu, and G. X. Wu, 2007: Interactions between typhoon and subtropical anticyclone over western Pacific revealed by numerical experiments. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 65, 329–340, doi: 10.11676/qxxb2007.032. (in Chinese)
Tao L., S. J. Li, Y. Han, et al., 2012: Impact of intraseasonal oscillations of tropical atmosphere on TC track change over the western North Pacific. J. Trop. Meteor., 28, 698–706, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4965.2012.05.009. (in Chinese)
Tian H., C. Y. Li, and H. Yang, 2010: Modulation of typhoon tracks over the western North Pacific by the intraseasonal oscillation. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 34, 559–579, doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2010.03.09. (in Chinese)
Wang B., R. L. Elsberry, Y. Q. Wang, et al., 1998: Dynamics in tropical cyclone motion: A review. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 22, 535–547, doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1998.04.15. (in Chinese)
Xu X. D., L. Xie, X. J. Zhang, et al., 2006: A mathematical model for forecasting tropical cyclone tracks. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl., 7, 211–224, doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2004.04.004.
Xu Y. M., T. Li, and M. Peng, 2013: Tropical cyclogenesis in the western North Pacific as revealed by the 2008–09 YOTC data. Wea. Forecasting, 28, 1038–1056, doi: 10.1175/WAFD-12-00104.1.
Xu Y. M., T. Li, and M. Peng, 2014: Roles of the synoptic-scale wave train, the intraseasonal oscillation, and high-frequency eddies in the genesis of Typhoon Manyi (2001). J. Atmos. Sci., 71, 3706–3722, doi: 10.1175/JAS-D-13-0406.1.
Yamada H., T. Nasuno, W. Yanase, et al., 2016: Role of the vertical structure of a simulated tropical cyclone in its motion: A case study of Typhoon Fengshen (2008). SOLA, 12, 203–208, doi: 10.2151/sola.2016-041.
Yang L., Y. Du, D. X. Wang, et al., 2015: Impact of intraseasonal oscillation on the tropical cyclone track in the South China Sea. Climate Dyn., 44, 1505–1519, doi: 10.1007/s00382-014-2180-y.
Yoshida R., Y. Kajikawa, and H. Ishikawa, 2014: Impact of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation on environment of tropical cyclone genesis over the western North Pacific. SOLA, 10, 15–18, doi: 10.2151/sola.2014-004.
Zhu Z. W., T. Li, P. C. Hsu, et al., 2015: A spatial-temporal projection model for extended-range forecast in the tropics. Climate Dyn., 45, 1085–1098, doi: 10.1007/s00382-014-2353-8.
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate the constructive comments from the anonymous reviewers and Dr. Mingyu Bi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National (Key) Basic Research and Development (973) Program of China (2017YFA0603802 and 2015CB453200), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41630423, 41475084, 41575043, and 41375095), US National Science Foundation (AGS-1643297), NRL grant (N00173-16-1-G906), Jiangsu Projects (BK20150062 and R2014SCT001), and Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD). This is SOEST contribution number 10297, IPRC contribution number 1305, and ESMC contribution 203.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Li, T. & Zhou, W. Impact of 10–60-Day Low-Frequency Steering Flows on Straight Northward-Moving Typhoon Tracks over the Western North Pacific. J Meteorol Res 32, 394–409 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-018-7035-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-018-7035-8