Abstract
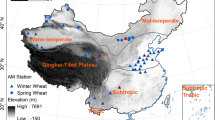
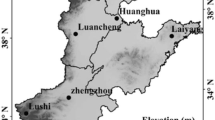
The aim of this study is to compare the impacts of climate change on the potential productivity and potential productivity gaps of sunflower (Helianthus annuus), potato (Solanum tuberosum), and spring wheat (Triticumaestivum Linn) in the agro-pastoral ecotone (APE) of North China. A crop growth dynamics statistical method was used to calculate the potential productivity affected by light, temperature, precipitation, and soil fertility. The growing season average temperature increased by 0.47, 0.48, and 0.52°C per decade (p < 0.05) for sunflower, potato, and spring wheat, respectively, from 1981 to 2010. Meanwhile, the growing season solar radiation showed a decreasing trend (p < 0.05) and the growing season precipitation changed non-significantly across APE. The light–temperature potential productivity increased by 4.48% per decade for sunflower but decreased by 1.58% and 0.59% per decade for potato and spring wheat. The climate–soil potential productivity reached only 31.20%, 27.79%, and 20.62% of the light–temperature potential productivity for sunflower, potato, and spring wheat, respectively. The gaps between the light–temperature and climate–soil potential productivity increased by 6.41%, 0.97%, and 1.29% per decade for sunflower, potato, and spring wheat, respectively. The increasing suitability of the climate for sunflower suggested that the sown area of sunflower should be increased compared with potato and spring wheat in APE under future climate warming.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albersen, P., G. Fischer, M. A. Keyzer, et al., 2002: Estimation of Agricultural Production Relations in the LUC Model for China. International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis Press, Laxenburg, Austria, 60 pp.
Allen, R. G., L. S. Pereira, D. Rates, et al., 1998: Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56, Rome, FAO, 1–300.
Dong Zhiqiang, Pan Zhihua, An Pingli, et al., 2012: Responses of growth period of spring wheat in northern ecotone to climate change: A case of Wuchuan County, Inner Mongolia, China. Progressus Inquisitiones de Mutatione Climatis, 8, 265–271. (in Chinese)
Du Bin, Qu Zhongyi, Yu Jian, et al., 2014: Experimental study on crop coefficient under mulched drip irrigation in Hetao Irrigation District of Inner Mongolia. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 33, 16–20. (in Chinese)
Duan Yu, Tuo Debao, Zhao Peiyi, et al., 2013: Crops caloric value and adjustment of planting structure in rainfed farmland of North Yinshan Mountian area, Inner Mongolia. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 27, 153–157. (in Chinese)
Gou Fang, Zhang Lizhen, Dong Wanlin, et al., 2012: Simulation model for the crop development stages in sunflower–potato intercropping. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23, 2773–2778. (in Chinese)
Grassini, P., J. Thorburn, C. Burr, et al., 2011: Highyield irrigated maize in the western U.S. Corn Belt. I: On-farm yield, yield potential, and impact of agronomic practices. Field Crops Research, 120, 142–150.
Harrison, P. A., and R. E. Butterfield, 1996: Effects of climate change on Europe-wide winter wheat and sunflower productivity. Climate Res., 7, 225–241.
Haverkort, A. J., P. Sandaña, and J. Kalazich, 2014: Yield gaps and ecological footprints of potato production systems in Chile. Potato Research, 57, 13–31.
He, W., P. C. Struik, J. Wang, et al., 1998: Potential and actual yields of potato at different elevations and in different seasons in subtropical Southwest China. J. Agronomy Crop Sci., 180, 93–99.
He Di, Wang Jing, Dai Tong, et al., 2014: Impact of climate change on maize potential productivity and the potential productivity gap in Southwest China. J. Meteor. Res., 28, 1155–1167.
He Ling, He Wenshou, Ren Rang, et al., 2015: Effect of water-fertilizer coupling on oilseed sunflower in the drought region of Ningxia. Water Saving Irrigation, 16–20. (in Chinese)
Higgins, G. M., A. H. Kassam, L. Naiken, et al., 1982: Potential Population Supporting Capacities of Lands in the Developing World. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Roma, 139 pp.
Hou Qiong, Guo Ruiqing, and Yang Litao, 2009: Climate change and its impact on main crops in Inner Mongolia. Chinese J. Agrometeor., 30, 560–564. (in Chinese)
Hou Xuehui, Niu Zheng, Gao Shuai, et al., 2013: Monitoring vegetation phenology in farming-pastoral zone using SPOT-VGT NDVI data. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 29, 142–150. (in Chinese)
Hu Qi, Pan Xuebiao, and Yang Ning, 2015: Suitability of rainwater harvesting technology for potato farmland ridge and furrow in northern agro-pastoral zone of China. Arid Land Geography, 38, 585–591. (in Chinese)
Huang Bingwei, 1985: Agricultural Productive Potentiality-Photosynthetic Potential in China. Science Press, Beijing, China, 15–22. (in Chinese)
Lacatusu, R., and A. R. Lacatusu, 2011: Complex indicator for assessing soil fertility. Res. J. Agricult. Sci., 43, 95–101.
Li Kenan, Yang Xiaoguang, Liu Zhijuan, et al., 2010: Analysis of the potential influence of global climate change on cropping systems in China. III: The change characteristics of climatic resources in northern China and its potential influence on cropping systems. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 43, 2088–2097. (in Chinese)
Liu Honglai, Wang Yimeng, Dou Xiao, et al., 2009: Progress and perspective of agro-pasturage ecotone. Acta Ecologiva Sinica, 29, 4420–4425. (in Chinese)
Liu, L. L., Y. Zhu, L. Tang, et al., 2013: Impacts of climate changes, soil nutrients, variety types and management practices on rice yield in East China: A case study in the Taihu region. Field Crops Research, 149, 40–48.
Liu, Z. J., K. G. Hubbard, X. M. Lin, et al., 2013: Negative effects of climate warming on maize yield are reversed by the changing of sowing date and cultivar selection in Northeast China. Global Change Biology, 19, 3481–3492.
Lobell, D. B., and J. I. Ortiz-Monasterio, 2006: Regional importance of crop yield constraints: Linking simulation models and geostatistics to interpret spatial patterns. Ecological Modelling, 196, 173–182.
Lobell, D. B., K. G. Gassman, and C. B. Field, 2009: Crop yield gaps: Their importance, magnitudes, and causes. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 34, 179–204.
Lv, S., X. G. Yang, X. M. Lin, et al., 2015: Yield gap simulations using ten maize cultivars commonly planted in Northeast China during the past five decades. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 205, 1–10.
Ma Shuqing and Guo Shunji, 1995: The analysis of the potential productivity, exploitation, and utilization of climate–soil resources in Northeast China. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 15, 243–252. (in Chinese)
Mi Jian, Luo Qiyou, Gao Mingjie, et al., 2015: A supply and demand equilibrium forecast of potato in medium and long term. Chinese J. Agricult. Resour. Regional Planning, 36, 27–34. (in Chinese)
Pan Zhihua, An Pingli, Liu Yaling, et al., 2003: Study on natural environment condition changes in the ecological system at the crossing belt (Wuchuan County) of agriculture and animal husbandry in northern China. Journal of China Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 24, 37–41. (in Chinese)
Pan Zhihua, Zhang Luyang, Chen Dongdong, et al., 2010: Research progress and thoughts about proper exploitation of field water potential productivity in farming-pastoral ecotone of Northern China. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 12, 40–45. (in Chinese)
Porter, J. R., and M. Gawith, 1999: Temperatures and the growth and development of wheat: A review. European Journal of Agronomy, 10, 23–26.
Qiu Guowang, Zhao Yanxia, and Wang Shili, 2001: Studies on development of the interlock area of farmingpastoral region in northern China. China Population, Resources and Environment, 11, 49–50. (in Chinese)
Sun Jingsheng, Liu Zugui, Zhang Jiyang, et al., 2002: Crop coefficients of spring wheat in Windy Dust Area. Transactions of the CSAE, 18, 55–58. (in Chinese)
Supit, I., C. A. van Diepen, A. J. W. de Wit, et al., 2010: Recent changes in the climatic yield potential of various crops in Europe. Agriculture Systems, 103, 683–694.
Wang Jing’ai, Xu Xia, and Liu Peifang, 1999: Land use and land carrying capacity in ecotone between agriculture and animal husbandry in northern China. Resources Science, 21, 19–24, 8. (in Chinese)
Wang Zongming, Zhang Bo, Zhang Shuqing, et al., 2005: Studies on agricultural climatic potential productivity and natural resources utilization ratio in Songnen Plain of Heilongjiang Province. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 26, 1–6. (in Chinese)
Wang, J., E. L. Wang, X. G. Yang, et al., 2012: Increased yield potential of wheat–maize cropping system in the North China Plain by climate change adaptation. Climatic Change, 113, 825–840.
Wang, J., E. L. Wang, H. Yin, et al., 2014: Declining yield potential and shrinking yield gaps of maize in the North China Plain. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 195–196, 89–101.
Wang, J., E. L. Wang, H. Yin, et al., 2015: Differences between observed and calculated solar radiations and their impact on simulated crop yields. Field Crops Research, 176, 1–10.
Wu Guishu, 2003: Research advance on the farminggrazing transitional zone in China. Journal of Sichuan Normal University (Natural Science), 26, 108–110. (in Chinese)
Xia Zhechao, Pan Zhihua, Zhang Luyang, et al., 2010: Examining mechanisms of vegetation ecosystems degradation based on water in northern farmingpastoral zone: A case study on Wuchuan Country. Resources Science, 32, 317–322. (in Chinese)
Xiong, W, I. P. Holman, L. Z. You, et al., 2014: Impacts of observed growing-season warming trends since 1980 on crop yields in China. Regional Environmental Change, 14, 7–16.
Yang Xiaoguang and Liu Zhijuan, 2014: Advances in research on crop yield gaps. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 47, 2731–2741. (in Chinese)
Yuan Bin, Guo Jianping, Ye Mingzhu, et al., 2012: Variety distribution pattern and climatic potential productivity of spring maize in Northeast China under climate change. Chin. Sci. Bull., 57, 3497–3508.
Zhang Fuchun and Zhu Zhihui, 1990: Harvest index for various crops in China. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 23, 83–87. (in Chinese)
Zhang Shuyuan, Li Jing, and Ren Zhiyuan, 2011: Study on soil nutrients effect of grassland ecosystem in the farming-grazing ecotone in North Shaanxi. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 39, 75–80. (in Chinese)
Zhao Yanxia and Qiu Guowang, 2001: A study of climate change impact on northern farming-pastoral region. Meteor. Mon., 27, 3–7. (in Chinese)
Zhao Feng, Qian Huaisui, and Jiao Shixing, 2003: The climatic suitability model of crop: A case study of winter wheat in Henan Province. Resources Science, 26, 77–82. (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank China Meteorological Administration for providing the historical climate data and agro-meteorological data. The authors acknowledge the anonymous referees for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the China Meteorological Administration Special PublicWelfare Research Fund (GYHY201506016), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2015ZH002), National Support Plan (2012BAD09B02), and National Agricultural Intelligence Tendering Platform (2015Z007).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, J., Wang, J., He, D. et al. Comparison of the impacts of climate change on potential productivity of different staple crops in the agro-pastoral ecotone of North China. J Meteorol Res 30, 983–997 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-016-6023-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-016-6023-0