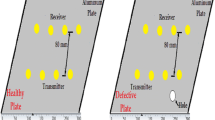
Abstract
In the current study, a new structural damage detection algorithm is presented using the modified Hilbert–Huang transform and support vector machine. The modified Hilbert–Huang transform is an adaptive time–frequency analysis tool that alleviates the mode mixing issue encountered with Hilbert–Huang transform. On the other hand, since the measured vibration responses are generally nonlinear and non-stationary signals, the Fourier transform utilizing the sinusoidal functions is inadequate for their processing. Thus, the modified Hilbert–Huang transform is utilized to study the measured signals. The structural damage features are constructed with the Hilbert spectrum energy of selected intrinsic mode function obtained by decomposing the measured vibration signals with modified ensemble empirical mode decomposition. The support vector machine’s classification and regression algorithms are utilized to detect the location and extent of the damage, respectively. The offshore platform's experiment model is utilized for theoretical and experimental validation of the presented method's effectiveness.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Worden K, Farrar CR, Haywood J, Todd M (2008) A review of nonlinear dynamics applications to structural health monitoring. Struct Control Heal Monit 15:540–567. https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.215
Doebling SW, Farrar CR, Prime MB (1998) A summary review of vibration-based damage identification methods. Shock Vib Dig 30:91–105. https://doi.org/10.1177/058310249803000201
Alvandi A, Cremona C (2006) Assessment of vibration-based damage identification techniques. J Sound Vib 292:179–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2005.07.036
Banerjee TP, Das S (2012) Multi-sensor data fusion using support vector machine for motor fault detection. Inf Sci (NY) 217:96–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2012.06.016
Walter GG, Shen X (1994) Wavelets and other orthogonal systems. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315273716
Chui CK (1997) Wavelets: a mathematical tool for signal analysis. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004.
Huang NE, Shen Z, Long SR, Wu MC, Snin HH, Zheng Q, Yen NC, Tung CC, Liu HH (1998) The empirical mode decomposition and the Hubert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 454:903–995. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1998.0193
Ren WX, Sun ZS (2008) Structural damage identification by using wavelet entropy. Eng Struct 30:2840–2849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2008.03.013
Yun GJ, Lee SG, Carletta J, Nagayama T (2011) Decentralized damage identification using wavelet signal analysis embedded on wireless smart sensors. Eng Struct 33:2162–2172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2011.03.007
Lee SG, Yun GJ, Shang S (2014) Reference-free damage detection for truss bridge structures by continuous relative wavelet entropy method. Struct Heal Monit 13:307–320. https://doi.org/10.1177/1475921714522845
Chen B, Zhao SL, Li PY (2014) Application of hilbert-huang transform in structural health monitoring: a state-of-the-art review. Math Probl Eng 2014:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/317954
Yang JN, Lin S, Pan S (2022) Damage detection of a health monitoring benchmark building using Hilbert–Huang spectral analysis. Adv Build Technol 2002:1017–1024. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-008044100-9/50128-5
Lin S, Yang JN, Zhou L (2005) Damage identification of a benchmark building for structural health monitoring. Smart Mater Struct 14:S162–S169. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/14/3/019
Xu YL, Chen J (2004) Structural damage detection using empirical mode decomposition: experimental investigation. J Eng Mech 130:1279–1288. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(2004)130:11(1279)
Wu S, Qin G, Zou J (2009) Structure health monitoring based on HHT of vibration response from unknown excitation. In: 8th Int. Symp. Test Meas., pp. 490–493
Dong Y, Li Y, Lai M (2010) Structural damage detection using empirical-mode decomposition and vector autoregressive moving average model. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 30:133–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2009.10.002
Banerji S, Roy TB, Sabamehr A, Bagchi A (2017) Experimental validation of a structural damage detection method based on marginal Hilbert spectrum. Health Monit Struct Biol Syst. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2260298
Ghazi RM, Buyukozturk O (2014) Assessment and localization of active discontinuities using energy distribution between intrinsic modes. Struct Health Monit. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-04570-2-1
Mohammadi Ghazi R, Büyüköztürk O (2016) Damage detection with small data set using energy-based nonlinear features. Struct Control Health Monit 23:333–348. https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.1774
Han DY, Wei SM, Shi PM, Zhang Y, Gao K, Tian NY (2017) Damage identification of a derrick steel structure based on the HHT marginal spectrum amplitude curvature difference. Shock Vib 2:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1062949
Bandara S, Rajeev P, Gad E, Sriskantharajah B, Flatley I (2019) Damage detection of in service timber poles using Hilbert–Huang transform. NDT and E Int 107:102141
Xu Q (2019) Investigation of damage diagnosis of retaining wall structures based on the Hilbert damage feature vector spectrum. Shock Vib. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3509470
Banjara NK, Sasmal S, Srinivas V (2019) Damage progression study in fibre reinforced concrete using acoustic emission technique. Smart Struct Syst 23:173–184
Xu J, Wang WX, Han QH, Liu X (2020) Damage pattern recognition and damage evolution analysis of unidirectional CFRP tendons under tensile loading using acoustic emission technology. Compos Struct 238:111948
Mousavi AA, Zhang CW, Masri SF, Gholipour G (2020) Structural damage localization and quantification based on a CEEMDAN Hilbert transform neural network approach: a model steel truss bridge case study. Sensors 20:1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051271
Wu Z, Huang NE (2009) Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv Adapt Data Anal 1:41. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793536909000047
Zheng X, Hao Z, Jin Y, Lu Z (2012) Studying noise contributions of IC engine via MEEMD method. Zhejiang Univ 46:954–960
Masri SF, Smyth AW, Chassiakos AG, Caughey TK, Hunter NF (2000) Application of neural networks for detection of changes in nonlinear systems. J Eng Mech 126:666–676. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(2000)126:7(666)
Zang C, Imregun M (2001) Structural damage detection using artificial neural networks and measured FRF data reduced via principal component projection. J Sound Vib 242:813–839. https://doi.org/10.1006/jsvi.2000.3390
Oh CK, Sohn H (2009) Damage diagnosis under environmental and operational variations using unsupervised support vector machine. J Sound Vib 325:224–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2009.03.014
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support-vector networks. Mach Learn 20:273–297. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022627411411
Khoa NLD, Zhang B, Wang Y, Chen F, Mustapha S (2014) Robust dimensionality reduction and damage detection approaches in structural health monitoring. Struct Health Monit 13:406–417. https://doi.org/10.1177/1475921714532989
Yu Y, Dackermann U, Li JC, Niederleithinger E (2018) Wavelet packet energy–based damage identification of wood utility poles using support vector machine multi-classifier and evidence theory. Struct Health Monit 18:123–142
Kim JW, Tola KD, Tran DQ, Park S (2019) MFL-based local damage diagnosis and SVM-based damage type classification for wire rope NDE. Materials 12:2894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12182894
Liu CF, Liu CW, Liu CX, Huang XH, Miao JJ, Xu WL (2019) Fire Damage Identification in RC Beams based on support vector machines considering vibration test. KSCE J Civ Eng 23:4407–4416
Kohiyama M, Oka K, Yamashita T (2020) Detection method of unlearned pattern using support vector machine in damage classification based on deep neural network. Struct Control Health Monit 27:1–23
Luts J, Molenberghs G, Verbeke G, Van Huffel S, Suykens JAK (2012) A mixed effects least squares support vector machine model for classification of longitudinal data. Comput Stat Data Anal 56:611–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csda.2011.09.008
Kim Y, Chong JW, Chon KH, Kim J (2013) Wavelet-based AR-SVM for health monitoring of smart structures. Smart Mater Struct 22:015003. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/22/1/015003
Khatibinia M, Javad-Fadaee M, Salajegheh J, Salajegheh E (2013) Seismic reliability assessment of RC structures including soil-structure interaction using wavelet weighted least squares support vector machine. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 110:22–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2012.09.006
Chong JW, Kim Y, Chon KH (2014) Nonlinear multiclass support vector machine-based health monitoring system for buildings employing magnetorheological dampers. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 25:1456–1468. https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X13507343
Dushyanth ND, Suma MN, Latte MV (2016) Detection and localization of damage using empirical mode decomposition and multilevel support vector machine. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 122:250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-9753-z
Gui G, Pan H, Lin Z, Li Y, Yuan Z (2017) Data-driven support vector machine with optimization techniques for structural health monitoring and damage detection. KSCE J Civ Eng 21:523–534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-1518-5
Keshtan MN, Nouri-Khajavi M (2016) Bearings fault diagnosis using vibrational signal analysis by EMD method. Res Nondestruct Eval 27:155–174. https://doi.org/10.1080/09349847.2015.1103921
Wang G, Chen XY, Qiao FL, Wu Z, Huang NE (2010) On intrinsic mode function. Adv Adapt Data Anal 2:277–293. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793536910000549
Vapnik VN (1995) The nature of statistical learning theory. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-2440-0
Burges CJC (1998) A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Min Knowl Discov 2:121–167. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009715923555
Smola AJ, Schölkopf B (2004) A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat Comput 14:199–222. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:STCO.0000035301.49549.88
Worden K, Lane AJ (2001) Damage identification using support vector machines. Smart Mater Struct 10:540–547. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/10/3/317
Chang CC, Lin CJ (2011) LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol 2:2157–6904. https://doi.org/10.1145/1961189.1961199
Diao Y, Zhang X, Sun Z, Guo K, Wang Y (2018) Wavelet entropy based structural damage identification under seismic excitation. Smart Mater Struct. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665X/aadaaa
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the financial support by the Shandong Provincial Key Research and Development Program (Special Project of Public Welfare) (2019GHY112039).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diao, Y., Jia, D., Liu, G. et al. Structural damage identification using modified Hilbert–Huang transform and support vector machine. J Civil Struct Health Monit 11, 1155–1174 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13349-021-00509-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13349-021-00509-5