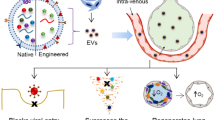
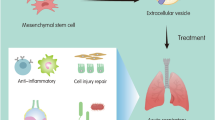
Abstract
Acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) are common clinical critical diseases with high morbidity and mortality. Especially since the COVID-19 outbreak, the mortality rates of critically ill patients with ARDS can be as high as 60%. Therefore, this problem has become a matter of concern to respiratory critical care. To date, the main clinical measures for ALI/ARDS are mechanical ventilation and drug therapy. Although ventilation treatment reduces mortality, it increases the risk of hyperxemia, and drug treatment lacks safe and effective delivery methods. Therefore, novel therapeutic strategies for ALI/ARDS are urgently needed. Developments in nanotechnology have allowed the construction of a safe, efficient, precise, and controllable drug delivery system. However, problems still encounter in the treatment of ALI/ARDS, such as the toxicity, poor targeting ability, and immunogenicity of nanomaterials. Cell-derived biomimetic nanodelivery drug systems have the advantages of low toxicity, long circulation, high targeting, and high bioavailability and show great therapeutic promises for ALI/ARDS owing to their acquired cellular biological features and some functions. This paper reviews ALI/ARDS treatments based on cell membrane biomimetic technology and extracellular vesicle biomimetic technology, aiming to achieve a significant breakthrough in ALI/ARDS treatments.
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Matthay MA, Ware LB, Zimmerman GA. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2019;122:2731–40. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0069-0.
Warren MA, Zhao Z, Koyama T, Bastarache JA, Shaver CM, Semler MW, Rice TW, Matthay MA, Calfee CS, Ware LB. Severity scoring of lung oedema on the chest radiograph is associated with clinical outcomes in ARDS. Thorax. 2018;73:840–6. https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2017-211280.
Baron RM, Levy BD. Recent advances in understanding and treating ARDS. F1000Research. 2016;5:725. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.7646.1.
Yang SC, Tsai YF, Pan YL, Hwang TL. Understanding the role of neutrophils in acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Biomed Sci. 2021;44:439–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bj.2020.09.001.
Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, Fan E, Brochard L, Esteban A, Gattinoni L, van Haren F, Larsson A, McAuley DF, Ranieri M, Rubenfeld G, Thompson BT, Wrigge H, Slutsky AS, Pesenti A. Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care units in 50 countries. JAMA. 2016;315:788–800. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.0291.
Silva PL, Pelosi P, Rocco PRM. Personalized pharmacological therapy for ARDS: a light at the end of the tunnel. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020;29:49–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/13543784.2020.1699531.
Wu C, Chen X, Cai Y, Xia J, Zhou X, Xu S, Huang H, Zhang L, Zhou X, Du C, Zhang Y, Song J, Wang S, Chao Y, Yang Z, Xu J, Zhou X, Chen D, Xiong W, Xu L, Zhou F, Jiang J, Bai C, Zheng J, Song Y. Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern Med. 2020;180:934–43. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994.
Murgia X, Cristiane D, Lehr CM. Overcoming the pulmonary barrier: new insights to improve the efficiency of inhaled therapeutics. Eur J Nanomed. 2014;6. https://doi.org/10.1515/ejnm-2014-0019.
Torchilin VP. Multifunctional nanocarriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006;58:1532–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2006.09.009.
Okeke EB, Louttit C, Fry C, Najafabadi AH, Han K, Nemzek J, Moon JJ. Inhibition of neutrophil elastase prevents neutrophil extracellular trap formation and rescues mice from endotoxic shock. Biomaterials. 2020;238:119836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.119836.
Li SJ, Wang XJ, Hu JB, Kang XQ, Chen L, Xu XL, Ying XY, Jiang SP, Du YZ. Targeting delivery of simvastatin using ICAM-1 antibody-conjugated nanostructured lipid carriers for acute lung injury therapy. Drug Deliv. 2017;24:402–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2016.1259369.
Prasanna P, Rathee S, Upadhyay A, Sulakshana S. Nanotherapeutics in the treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Life Sci. 2021;276:119428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119428.
Xu H, Wang KQ, Deng YH, Chen DW. Effects of cleavable PEG-cholesterol derivatives on the accelerated blood clearance of PEGylated liposomes. Biomaterials. 2010;31:4757–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.02.049.
Li YJ, Wu JY, Liu J, Xu W, Qiu X, Huang S, Hu XB, Xiang DX. Artificial exosomes for translational nanomedicine. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19:242. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-021-00986-2.
Qiao Q, Liu X, Yang T, Cui K, Kong L, Yang C, Zhang Z. Nanomedicine for acute respiratory distress syndrome: the latest application, targeting strategy, and rational design. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11:3060–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2021.04.023.
Bose RJ, Paulmurugan R, Moon J, Lee SH, Park H. Cell membrane-coated nanocarriers: the emerging targeted delivery system for cancer theranostics. Drug Discov Today. 2018;23:891–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2018.02.001.
Liu Y, Luo J, Chen X, Liu W, Chen T. Cell membrane coating technology: a promising strategy for biomedical applications. Nanomicro Lett. 2019;11:100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-019-0330-9.
Hu CM, Zhang L, Aryal S, Cheung C, Fang RH, Zhang L. Erythrocyte membrane-camouflaged polymeric nanoparticles as a biomimetic delivery platform. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:10980–5. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1106634108.
Liu G, Zhao X, Zhang Y, Xu J, Xu J, Li Y, Min H, Shi J, Zhao Y, Wei J, Wang J, Nie G. Engineering biomimetic platesomes for pH-responsive drug delivery and enhanced antitumor activity. Adv Mater. 2019;31:e1900795. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201900795.
Sun T, Kwong CHT, Gao C, Wei J, Yue L, Zhang J, Ye RD, Wang R. Amelioration of ulcerative colitis via inflammatory regulation by macrophage-biomimetic nanomedicine. Theranostics. 2020;10:10106–19. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.48448.
Zhou K, Yang C, Shi K, Liu Y, Hu D, He X, Yang Y, Chu B, Peng J, Zhou Z, Qian Z. Activated macrophage membrane-coated nanoparticles relieve osteoarthritis-induced synovitis and joint damage. Biomaterials. 2023;295:122036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122036.
Yang F, Cabe MH, Ogle SD, Sanchez V, Langert KA. Optimization of critical parameters for coating of polymeric nanoparticles with plasma membrane vesicles by sonication. Sci Rep. 2021;11:23996. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-03422-5.
Zou S, Wang B, Wang C, Wang Q, Zhang L. Cell membrane-coated nanoparticles: research advances. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2020;15:625–41. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm-2019-0388.
Liu C, Zhang W, Li Y, Chang J, Tian F, Zhao F, Ma Y, Sun J. Microfluidic sonication to assemble exosome membrane-coated nanoparticles for immune evasion-mediated targeting. Nano Lett. 2019;19:7836–44. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b02841.
Rao L, Cai B, Bu LL, Liao QQ, Guo SS, Zhao XZ, Dong WF, Liu W. Microfluidic electroporation-facilitated synthesis of erythrocyte membrane-coated magnetic nanoparticles for enhanced imaging-guided cancer therapy. ACS Nano. 2017;11:3496–505. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b00133.
Bose RJ, Lee SH, Park H. Biofunctionalized nanoparticles: an emerging drug delivery platform for various disease treatments. Drug Discov Today. 2016;21:1303–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2016.06.005.
Tauro BJ, Greening DW, Mathias RA, Ji H, Mathivanan S, Scott AM, Simpson RJ. Comparison of ultracentrifugation, density gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods for isolating human colon cancer cell line LIM1863-derived exosomes. Methods. 2012;56:293–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.01.002.
Mao L, Jiang Y, Ouyang H, Feng Y, Li R, Zhang X. Revealing the distribution of aggregation-induced emission nanoparticles via dual-modality imaging with fluorescence and mass spectrometry. Research (Wash DC). 2021;2021:9784053. https://doi.org/10.34133/2021/9784053.
Lu C, Zheng J, Ding Y, Meng Y, Tan F, Gong W, Chu X, Kong X, Gao C. Cepharanthine loaded nanoparticles coated with macrophage membranes for lung inflammation therapy. Drug Deliv. 2021;28:2582–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2021.2009936.
Wang Y, Zhang K, Li T, Maruf A, Qin X, Luo L, Zhong Y, Qiu J, McGinty S, Pontrelli G, Liao X, Wu W, Wang G. Macrophage membrane functionalized biomimetic nanoparticles for targeted anti-atherosclerosis applications. Theranostics. 2021;11:164–80. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.47841.
Huang Z, Wang H, Long J, Lu Z, Chun C, Li X. Neutrophil membrane-coated therapeutic liposomes for targeted treatment in acute lung injury. Int J Pharm. 2022;624:121971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121971.
Park JH, Jiang Y, Zhou J, Gong H. Genetically engineered cell membrane-coated nanoparticles for targeted delivery of dexamethasone to inflamed lungs. Sci Adv. 2021;7:eabf7820. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abf7820.
Li B, Wang W, Song W, Zhao Z, Tan Q, Zhao Z, Tang L, Zhu T, Yin J, Bai J. Antiviral and anti-inflammatory treatment with multifunctional alveolar macrophage-like nanoparticles in a surrogate mouse model of COVID-19. Adv Sci. 2021;8:2002556. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202003556.
Wang K, Lei Y, Xia D, Xu P, Zhu T, Jiang Z, Ma Y. Neutrophil membranes coated, antibiotic agent loaded nanoparticles targeting to the lung inflammation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;188:110755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110755.
Shen S, Han F, Yuan A, Wu L, Cao J, Qian J, Qi X, Yan Y, Ge Y. Engineered nanoparticles disguised as macrophages for trapping lipopolysaccharide and preventing endotoxemia. Biomaterials. 2019;189:60–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.10.029.
Tan Q, He L, Meng X, Wang W, Pan H, Yin W, Zhu T, Huang X. Macrophage biomimetic nanocarriers for anti-inflammation and targeted antiviral treatment in COVID-19. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19:173. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-021-00926-0.
Li Y, Guo C, Chen Q, Su Y, Guo H, Liu R, Sun C, Mi S, Wang J, Chen D. Improvement of pneumonia by curcumin-loaded bionanosystems based on platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharides via calming cytokine storm. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;202:691–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.01.194.
Wei X, Ran D, Campeau A, Xiao C, Zhou J, Dehaini D, Jiang Y, Kroll AV, Zhang Q, Gao W, Gonzalez DJ, Fang RH, Zhang L. Multiantigenic nanotoxoids for antivirulence vaccination against antibiotic-resistant gram-negative bacteria. Nano Lett. 2019;19:4760–9. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b01844.
Zhang Q, Honko A, Zhou J, Gong H, Downs SN, Vasquez JH, Fang RH, Gao W, Griffiths A, Zhang L. Cellular nanosponges inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infectivity. Nano Lett. 2020;20:5570–4. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c02278.
Zhang F, Zhuang J, Li Z, Gong H, de Ávila BE, Duan Y, Zhang Q, Zhou J. Nanoparticle-modified microrobots for in vivo antibiotic delivery to treat acute bacterial pneumonia. Nat Mater. 2022;21:1324–32. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-022-01360-9.
Zhou J, Ventura CJ. Biomimetic neutrophil nanotoxoids elicit potent immunity against Acinetobacter baumannii in multiple models of infection. Nano Lett. 2022;22:7057–65. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c01948.
Gao J, Wang S, Dong X, Leanse LG, Dai T. Co-delivery of resolvin D1 and antibiotics with nanovesicles to lungs resolves inflammation and clears bacteria in mice. Commun Biol. 2020;3:680. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-020-01410-5.
Huang R, Cai GQ, Li J, Li XS, Liu HT, Shang XL, Zhou JD, Nie XM. Platelet membrane-camouflaged silver metal-organic framework drug system against infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19:278. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-021-00978-2.
Jin H, Li J, Zhang M, Luo R, Lu P, Zhang W, Zhang J, Pi J, Zheng W, Mai Z, Ding X, Liu X, Ouyang S, Huang G. Berberine-loaded biomimetic nanoparticles attenuate inflammation of experimental allergic asthma via enhancing IL-12 expression. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:724525. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.724525.
Jin H, Luo R, Li J, Zhao H, Ouyang S, Yao Y, Chen D, Ling Z, Zhu W, Chen M, Liao X, Pi J, Huang G. Inhaled platelet vesicle-decoyed biomimetic nanoparticles attenuate inflammatory lung injury. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1050224. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1050224.
Wang F, Hou W, Xiao C, Hao Y, Su N, Deng Y, Wang J, Yu L, Xie JM, Xiong JW, Luo Y. Endothelial cell membrane-based biosurface for targeted delivery to acute injury: analysis of leukocyte-mediated nanoparticle transportation. Nanoscale. 2021;13:14636–43. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1nr04181a.
Koo J, Escajadillo T, Zhang L, Nizet V, Lawrence SM. Erythrocyte-coated nanoparticles block cytotoxic effects of group B Streptococcus β-hemolysin/cytolysin. Front Pediatr. 2019;7:410. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2019.00410.
Batrakova EV, Li S, Reynolds AD, Mosley RL, Bronich TK, Kabanov AV, Gendelman HE. A macrophage-nanozyme delivery system for Parkinson’s disease. Bioconjug Chem. 2007;18:1498–506. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc700184b.
Wang Z, Li J, Cho J, Malik AB. Prevention of vascular inflammation by nanoparticle targeting of adherent neutrophils. Nat Nanotechnol. 2014;9:204–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2014.17.
Liu R, An Y, Jia W, Wang Y, Wu Y, Zhen Y, Cao J, Gao H. Macrophage-mimic shape changeable nanomedicine retained in tumor for multimodal therapy of breast cancer. J Control Release. 2020;321:589–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.02.043.
Summers C, Rankin SM, Condliffe AM, Singh N, Peters AM, Chilvers ER. Neutrophil kinetics in health and disease. Trends Immunol. 2010;31:318–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2010.05.006.
Ley K, Laudanna C, Cybulsky MI, Nourshargh S. Getting to the site of inflammation: the leukocyte adhesion cascade updated. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:678–89. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2156.
Craig A, Mai J, Cai S, Jeyaseelan S. Neutrophil recruitment to the lungs during bacterial pneumonia. Infect Immun. 2009;77:568–75. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.00832-08.
Wu JC, Huang WC, Chen YC, Tu TH, Tsai YA, Huang SF, Huang HC, Cheng H. Acidic fibroblast growth factor for repair of human spinal cord injury: a clinical trial. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011;15:216–27. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.4.spine10404.
Huang ZW, Shi Y, Zhai YY, Du CC, Zhai J, Yu RJ, Kou L, Xiao J, Zhao YZ, Yao Q. Hyaluronic acid coated bilirubin nanoparticles attenuate ischemia reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. J Control Release. 2021;334:275–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.04.033.
Wang Q, He Y, Zhao Y, Xie H. A thermosensitive heparin-poloxamer hydrogel bridges aFGF to treat spinal cord injury. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:6725–45. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b13155.
Zinger A, Sushnitha M, Naoi T, Baudo G, De Rosa E. Enhancing inflammation targeting using tunable leukocyte-based biomimetic nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2021;15:6326–39. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c05792.
Wiklander OPB, Brennan M, Lötvall J. Advances in therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11:eaav8521. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aav8521.
Looney MR, Nguyen JX, Hu Y, Van Ziffle JA, Lowell CA, Matthay MA. Platelet depletion and aspirin treatment protect mice in a two-event model of transfusion-related acute lung injury. J Clin Invest. 2009;119:3450–61. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci38432.
Mujtaba MA, Akhter MH, Alam MS, Ali MD, Hussain A. An updated review on therapeutic potential and recent advances in drug delivery of berberine: current status and future prospect. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2022;23:60–71. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389201022666210208152113.
Li Z, Zheng J, Zhang N, Li C. Berberine improves airway inflammation and inhibits NF-κB signaling pathway in an ovalbumin-induced rat model of asthma. J Asthma. 2016;53:999–1005. https://doi.org/10.1080/02770903.2016.1180530.
Shakeri A, Cicero AFG. Curcumin: a naturally occurring autophagy modulator. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:5643–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27404.
Zhang LX, Li CX, Kakar MU, Khan MS, Wu PF, Amir RM, Dai DF, Naveed M, Li QY, Saeed M, Shen JQ, Rajput SA, Li JH. Resveratrol (RV): a pharmacological review and call for further research. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;143:112164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112164.
Wu T, Zhang D, Zhang Z. Dendritic cells derived extracellular vesicles for the combinational immunotherapy against tumor. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Nanomedicine of China. Shanghai, China; 2018.
Quan C, Wang M, Chen H, Zhang H. Extracellular vesicles in acute respiratory distress syndrome: Recent developments from bench to bedside. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;100:108118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108118.
Monsel A, Zhu YG, Gennai S, Hao Q, Hu S, Rouby JJ, Rosenzwajg M, Matthay MA, Lee JW. Therapeutic effects of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles in severe pneumonia in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;192:324–36. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201410-1765OC.
Hu S, Park J, Liu A, Lee J, Zhang X, Hao Q, Lee JW. Mesenchymal stem cell microvesicles restore protein permeability across primary cultures of injured human lung microvascular endothelial cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018;7:615–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/sctm.17-0278.
Khatri M, Richardson LA, Meulia T. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate influenza virus-induced acute lung injury in a pig model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-018-0774-8.
Zhao R, Wang L, Wang T, Xian P, Wang H, Long Q. Inhalation of MSC-EVs is a noninvasive strategy for ameliorating acute lung injury. J Control Release. 2022;345:214–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.03.025.
Ahn SY, Park WS, Kim YE, Sung DK, Sung SI, Ahn JY, Chang YS. Vascular endothelial growth factor mediates the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles against neonatal hyperoxic lung injury. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-018-0055-8.
Potter DR, Miyazawa BY, Gibb SL, Deng X, Togaratti PP, Croze RH, Srivastava AK, Trivedi A, Matthay M, Holcomb JB, Schreiber MA, Pati S. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate pulmonary vascular permeability and lung injury induced by hemorrhagic shock and trauma. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018;84:245–56. https://doi.org/10.1097/ta.0000000000001744.
Lee C, Mitsialis SA, Aslam M, Vitali SH, Vergadi E, Konstantinou G, Sdrimas K, Fernandez-Gonzalez A, Kourembanas S. Exosomes mediate the cytoprotective action of mesenchymal stromal cells on hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 2012;126:2601–11. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.112.114173.
Shah T, Qin S, Vashi M, Predescu DN, Jeganathan N, Bardita C, Ganesh B, diBartolo S, Fogg LF, Balk RA, Predescu SA. Alk5/Runx1 signaling mediated by extracellular vesicles promotes vascular repair in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Clin Transl Med. 2018;7:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40169-018-0197-2.
Phinney DG, Di Giuseppe M, Njah J, Sala E, Shiva S, St Croix CM, Stolz DB, Watkins SC, Di YP, Leikauf GD, Kolls J, Riches DW, Deiuliis G, Kaminski N. Mesenchymal stem cells use extracellular vesicles to outsource mitophagy and shuttle microRNAs. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8472. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9472.
Ma Q, Fan Q, Xu J, Bai J, Han X, Dong Z, Zhou X, Liu Z, Gu Z, Wang C. Calming cytokine storm in pneumonia by targeted delivery of TPCA-1 using platelet-derived extracellular vesicles. Matter. 2020;3:287–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2020.05.017.
Ma Q, Yao C, Shi H, Xu J, Dai H, Fei Z, Wu Y, Lu T, Wang C. Targeted delivery of dexamethasone in acute pneumonia. Biomater Sci. 2021;9:5569–76. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1bm00924a.
Wu X, Liu Z, Hu L, Gu W, Zhu L. Exosomes derived from endothelial progenitor cells ameliorate acute lung injury by transferring miR-126. Exp Cell Res. 2018;370:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.06.003.
Zhou Y, Li P, Goodwin AJ, Cook JA, Halushka PV, Chang E, Zingarelli B, Fan H. Exosomes from endothelial progenitor cells improve outcomes of the lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Crit Care. 2019;23:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-019-2339-3.
Wang H, He JQ. Preparation of nanocesicle preparations for functional pluripotent stem cells and their use in preventing pneumonia [M]. 2020.
Pan RL, Zhang Q, Wu ZT, Dai LH, Wang FJ. Application of an endometrial stem cell-derived exossome in treating acute lung injury [M]. 2019.
Quan Y, Wang Z, Gong L, Peng X, Richard MA, Zhang J, Fornage M, Alcorn JL, Wang D. Exosome miR-371b-5p promotes proliferation of lung alveolar progenitor type II cells by using PTEN to orchestrate the PI3K/Akt signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8:138. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-017-0586-2.
Gao J, Wang S, Wang Z. High yield, scalable and remotely drug-loaded neutrophil-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) for anti-inflammation therapy. Biomaterials. 2017;135:62–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.05.003.
Lee JW, Fang X, Gupta N, Serikov V, Matthay MA. Allogeneic human mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of E. coli endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in the ex vivo perfused human lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:16357–62. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0907996106.
Tögel F, Hu Z, Weiss K, Isaac J, Lange C, Westenfelder C. Administered mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischemic acute renal failure through differentiation-independent mechanisms. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005;289:F31-42. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00007.2005.
Volarevic V, Markovic BS, Gazdic M, Volarevic A, Jovicic N, Arsenijevic N, Armstrong L, Djonov V, Lako M, Stojkovic M. Ethical and safety issues of stem cell-based therapy. Int J Med Sci. 2018;15:36–45. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.21666.
Najar M, Raicevic G, Fayyad-Kazan H, Bron D, Toungouz M, Lagneaux L. Mesenchymal stromal cells and immunomodulation: a gathering of regulatory immune cells. Cytotherapy. 2016;18:160–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcyt.2015.10.011.
Harrell CR, Jovicic N. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes and other extracellular vesicles as new remedies in the therapy of inflammatory diseases. Cells. 2019;8:1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121605.
Seo Y, Kim HS. Stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles as immunomodulatory therapeutics. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:5126156. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5126156.
Zhu X, Badawi M, Pomeroy S, Sutaria DS, Xie Z, Baek A, Jiang J, Elgamal OA, Mo X, Perle K, Chalmers J, Schmittgen TD, Phelps MA. Comprehensive toxicity and immunogenicity studies reveal minimal effects in mice following sustained dosing of extracellular vesicles derived from HEK293T cells. J Extracell Vesicles. 2017;6:1324730. https://doi.org/10.1080/20013078.2017.1324730.
Zhu YG, Feng XM, Abbott J, Fang XH, Hao Q, Monsel A, Qu JM, Matthay MA, Lee JW. Human mesenchymal stem cell microvesicles for treatment of Escherichia coli endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. Stem Cells. 2014;32:116–25. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.1504.
Guo SC, Tao SC, Yin WJ, Qi X, Yuan T, Zhang CQ. Exosomes derived from platelet-rich plasma promote the re-epithelization of chronic cutaneous wounds via activation of YAP in a diabetic rat model. Theranostics. 2017;7:81–96. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.16803.
Zaldivia MTK, McFadyen JD, Lim B, Wang X, Peter K. Platelet-derived microvesicles in cardiovascular diseases. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2017;4:74. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2017.00074.
Hansson GK, Libby P, Tabas I. Inflammation and plaque vulnerability. J Intern Med. 2015;278:483–93. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12406.
Song Y, Huang Z, Liu X, Pang Z, Chen J, Yang H, Zhang N, Cao Z, Liu M, Cao J, Li C, Yang X, Gong H, Qian J, Ge J. Platelet membrane-coated nanoparticle-mediated targeting delivery of Rapamycin blocks atherosclerotic plaque development and stabilizes plaque in apolipoprotein E-deficient (ApoE(-/-)) mice. Nanomedicine. 2019;15:13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2018.08.002.
Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200:373–83. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201211138.
Rafat N, Tönshoff B, Bierhaus A, Beck GC. Endothelial progenitor cells in regeneration after acute lung injury: do they play a role? Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013;48:399–405. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2011-0132TR.
Yamada M, Kubo H, Kobayashi S, Ishizawa K, Numasaki M, Ueda S, Suzuki T, Sasaki H. Bone marrow-derived progenitor cells are important for lung repair after lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury. J Immunol. 2004;172:1266–72. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.172.2.1266.
Mao M, Wang SN, Lv XJ, Wang Y, Xu JC. Intravenous delivery of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells improves survival and attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in rats. Shock. 2010;34:196–204. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181d49457.
Kawasaki T, Nishiwaki T, Sekine A, Nishimura R, Suda R, Urushibara T, Suzuki T, Takayanagi S, Terada J, Sakao S, Tatsumi K. Vascular repair by tissue-resident endothelial progenitor cells in endotoxin-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015;53:500–12. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2014-0185OC.
Buesing KL, Densmore JC, Kaul S, Pritchard KA, Jr., Jarzembowski JA, Gourlay DM, Oldham KT. Endothelial microparticles induce inflammation in acute lung injury. J Surg Res. 2011;166:32–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2010.05.036.
Densmore JC, Signorino PR, Ou J, Hatoum OA, Rowe JJ, Shi Y, Kaul S, Jones DW, Sabina RE, Pritchard KA, Jr., Guice KS, Oldham KT. Endothelium-derived microparticles induce endothelial dysfunction and acute lung injury. Shock. 2006;26:464–71. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.shk.0000228791.10550.36.
Ingato D, Edson JA, Zakharian M, Kwon YJ. Cancer cell-derived, drug-loaded nanovesicles induced by sulfhydryl-blocking for effective and safe cancer therapy. ACS Nano. 2018;12:9568–77. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b05377.
Sezgin E, Kaiser HJ, Baumgart T, Schwille P, Simons K, Levental I. Elucidating membrane structure and protein behavior using giant plasma membrane vesicles. Nat Protoc. 2012;7:1042–51. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2012.059.
Zhu L, Gangadaran P, Kalimuthu S, Oh JM, Baek SH, Jeong SY, Lee SW, Lee J, Ahn BC. Novel alternatives to extracellular vesicle-based immunotherapy - exosome mimetics derived from natural killer cells. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46:S166–79. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1489824.
Liu L, Bai X, Martikainen MV, Kårlund A, Roponen M, Xu W. Cell membrane coating integrity affects the internalization mechanism of biomimetic nanoparticles. Nat Commun. 2021;12:5726. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-26052-x.
Tian T, Zhang HX, He CP, Fan S, Zhu YL, Qi C, Huang NP, Xiao ZD, Lu ZH, Tannous BA, Gao J. Surface functionalized exosomes as targeted drug delivery vehicles for cerebral ischemia therapy. Biomaterials. 2018;150:137–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.10.012.
Funding
This work was supported by the Huadong Medicine Joint Funds of the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. LHDMZ22H300009, Key Research Projects of Hangzhou Medical College under Grant No. KYZD202106, Education of Zhejiang Province under Grant No. Y202146052, and Key Laboratory of Neuropsychiatric Drug Research of Zhejiang Province under Grant No. 2019E10021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W. Y.: conceptualization, funding acquisition, supervision. X. P.: supervision. R. G.: writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. P. L.: writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. Z. F.: writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. W. Y.: table. W. G.: Investigation. F. W.: table.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, R., Lin, P., Fang, Z. et al. Cell-derived biomimetic nanoparticles for the targeted therapy of ALI/ARDS. Drug Deliv. and Transl. Res. 14, 1432–1457 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-023-01494-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-023-01494-6