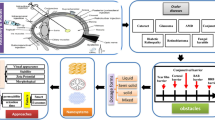
Abstract
Fluconazole (FLZ) has been widely used in the treatment of infection caused by Candida albicans, including the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC). However, when delivered orally, FLZ faces numerous limitations due to its poor solubility and undergoes the symptoms of first-pass metabolism. In this study, we developed the combinatorial approach of nanocrystals (NCs) and dissolving microneedles (DMNs) for effective local vaginal delivery of FLZ. The formulation containing 1.0% w/v PVA as stabilizer with 12 h of milling time process was found to be an optimal combination to fabricate FLZ as NCs (FLZ-NCs) with optimum size particle and PDI value (less than 0.25). Furthermore, the in vitro release study also showed a superior percentage of FLZ release up to 89.51 ± 7.52%. In combination with the DMNs, the FLZ recovery was 96.45 ± 2.38% with the insertion percentage in average of 76.14 ± 2.28% and height decreased percentage was only 7.53 ± 0.56%. Moreover, the ex vivo investigation and anti-candidiasis activity of DMNs-FLZ-NCs in vaginal model showed better results compared to other conventional preparations, such as film patch and hydrogel containing FLZ.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not available.
References
Denning DW, Kneale M, Sobel JD, Rautemaa-Richardson R. Global burden of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis: A systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis [Internet]. 2018;18:e339–47. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30103-8
Senthilganesh J, Ravichandran S, Durairajan R, BalaSubramaniyan S, Krishnasamy L, Veerappan A, et al. Metal sulfide nanoparticles based phytolectin scaffolds inhibit vulvovaginal candidiasis causing Candida albicans. J Clust Sci [Internet]. 2022;33:1361–72. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02061-0
Samimi MS, Mahboobian MM, Mohammadi M. Ocular toxicity assessment of nanoemulsion in-situ gel formulation of fluconazole. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021;40:2039–47.
Al Hujran TA, Magharbeh MK, Habashneh AY, Al-Dmour RS, Aboelela A, Tawfeek HM. Insight into the inclusion complexation of fluconazole with sulfonatocalix[4]naphthalene in aqueous solution, solid-state, and its antimycotic activity. Molecules. 2022;27.
Ferreira-da-silva C, Fernandes AR, Silva M, Severino P, Martins-gomes C. Drug nanocrystals: Present, past and future 11. 2018;
Permana AD, Paredes AJ, Zanutto FV, Amir MN, Ismail I, Bahar MA, et al. Albendazole nanocrystal-based dissolving microneedles with improved pharmacokinetic performance for enhanced treatment of cystic echinococcosis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13:38745–60.
Nagaraj S, Manivannan S, Narayan S. Potent antifungal agents and use of nanocarriers to improve delivery to the infected site: A systematic review. J Basic Microbiol. 2021;61:849–73.
Yang H, Kang G, Jang M, Um DJ, Shin J, Kim H, et al. Development of lidocaine-loaded dissolving microneedle for rapid and efficient local anesthesia. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12:1–13.
Wang C, Jiang X, Zeng Y, Terry RN, Li W. Rapidly separable microneedle patches for controlled release of therapeutics for long-acting therapies. Med Drug Discov [Internet]. 2022;13:100118. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medidd.2021.100118
Sartawi Z, Blackshields C, Faisal W. Dissolving microneedles: Applications and growing therapeutic potential. J Control Release [Internet]. 2022;348:186–205. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.05.045
Aziz AYR, Hasir NA, Imran NBP, Hamdan MF, Mahfufah U, Wafiah N, et al. Development of hydrogel-forming microneedles for transdermal delivery of albendazole from liquid reservoir. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed [Internet]. 2022;0:000. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/09205063.2022.2157671
Ananda PWR, Elim D, Zaman HS, Muslimin W, Tunggeng MGR, Permana AD. Combination of transdermal patches and solid microneedles for improved transdermal delivery of primaquine. Int J Pharm. 2021;609: 121204.
Sulistiawati, Enggi CK, Isa HT, Wijaya S, Ardika KAR, Asri RM, et al. Validation of spectrophotometric method to quantify cabotegravir in simulated vaginal fluid and porcine vaginal tissue in ex vivo permeation and retention studies from thermosensitive and mucoadhesive gels. Spectrochim Acta - Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc [Internet]. 2022;267:120600. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120600
Rahman L, Lembang RS, Lallo S, Handayani SR, Usmanengsi, Permana AD. Bioadhesive dermal patch as promising approach for improved antibacterial activity of bioactive compound of Zingiber cassumunar Roxb in ex vivo Staphylococcus aureus skin infection model. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol [Internet]. 2021;63:102522. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2021.102522
Permana AD, Utomo E, Pratama MR, Amir MN, Anjani QK, Mardikasari SA, et al. Bioadhesive-thermosensitive in situ vaginal gel of the gel flake-solid dispersion of itraconazole for enhanced antifungal activity in the treatment of vaginal candidiasis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13:18128–41.
Avadi MR, Sadeghi AMM, Mohammadpour N, Abedin S, Atyabi F, Dinarvand R, et al. Preparation and characterization of insulin nanoparticles using chitosan and Arabic gum with ionic gelation method. Nanomedicine Nanotechnology, Biol Med [Internet]. 2010;6:58–63. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2009.04.007
Danaei M, Dehghankhold M, Ataei S, Hasanzadeh Davarani F, Javanmard R, Dokhani A, et al. Impact of particle size and polydispersity index on the clinical applications of lipidic nanocarrier systems. Pharmaceutics. 2018;10:1–17.
Wang D, Wang Y, Zhao G, Zhuang J, Wu W. Improving systemic circulation of paclitaxel nanocrystals by surface hybridization of DSPE-PEG2000. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces [Internet]. 2019;182:110337. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.06.066
Kala SG, Chinni S. Development and characterization of venetoclax nanocrystals for oral bioavailability enhancement. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021;22:1–11.
Moura EA, Correia LP, Pinto MF, Procópio JVV, De Souza FS, MacEdo RO. Thermal characterization of the solid state and raw material fluconazole by thermal analysis and pyrolysis coupled to GC/MS. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;100:289–93.
Reguieg F, Ricci L, Bouyacoub N, Belbachir M, Bertoldo M. Thermal characterization by DSC and TGA analyses of PVA hydrogels with organic and sodium MMT. Polym Bull [Internet]. 2020;77:929–48. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02782-3
Yu M, Yuan W, Li D, Schwendeman A, Schwendeman SP. Predicting drug release kinetics from nanocarriers inside dialysis bags. J Control Release. 2019;315:23–30.
Xing M, Wang X, Zhao L, Zhou Z, Liu H, Wang B, et al. Novel dissolving microneedles preparation for synergistic melasma therapy: Combined effects of tranexamic acid and licorice extract. Int J Pharm [Internet]. 2021;600:120406. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120406
Anderson DJ, Marathe J, Pudney J. The structure of the human vaginal stratum corneum and its role in immune defense. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2014;71:618–23.
Hayashida S, Takada K, Melnikov VG, Komine-Aizawa S, Tsuji NM, Hayakawa S. How were Lactobacillus species selected as single dominant species in the human vaginal microbiota? Coevolution of humans and Lactobacillus. Med Hypotheses [Internet]. 2022;163:110858. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2022.110858
Enggi CK, Isa HT, Sulistiawati S, Ardika KAR, Wijaya S, Asri RM, et al. Development of thermosensitive and mucoadhesive gels of cabotegravir for enhanced permeation and retention profiles in vaginal tissue: A proof of concept study. Int J Pharm [Internet]. 2021;609:121182. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.121182
Sanz R, Clares B, Mallandrich M, Suñer-Carbó J, Montes MJ, Calpena AC. Development of a mucoadhesive delivery system for control release of doxepin with application in vaginal pain relief associated with gynecological surgery. Int J Pharm [Internet]. 2018;535:393–401. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.11.027
Singh A, Bali A. Formulation and characterization of transdermal patches for controlled delivery of duloxetine hydrochloride. J Anal Sci Technol [Internet]. 2016;7. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40543-016-0105-6
Konno H, Taylor LS. Ability of different polymers to inhibit the crystallization of amorphous felodipine in the presence of moisture. Pharm Res. 2008;25:969–78.
Rashid FL, Hashim A. Structural, swelling and water absorption properties of new polymer blends for modern applications. 2021;905–12.
Syafika N, Azis SBA, Enggi CK, Qonita HA, Mahmud TRA, Abizart A, et al. Glucose-responsive microparticle-loaded dissolving microneedles for selective delivery of metformin: A proof-of-concept study. Mol Pharm. 2023;20:1269–84.
Silva-Abreu M, Espinoza LC, Halbaut L, Espina M, García ML, Calpena AC. Comparative study of ex vivo transmucosal permeation of pioglitazone nanoparticles for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Polymers (Basel). 2018;10.
Aung NN, Ngawhirunpat T, Rojanarata T, Patrojanasophon P, Pamornpathomkul B, Opanasopit P. Fabrication, characterization and comparison of α-arbutin loaded dissolving and hydrogel forming microneedles. Int J Pharm. 2020;586.
Funding
This research was supported by Hasanuddin University through “Penelitian Fundamental Kolaboratif” program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.Y.R.A.: conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft, review and editing, and validation; U.M.: investigation and data curation; N.A.S.: investigation and data curation; H.: review and editing and project administration; R.M.A.: methodology, investigation, data curation, and formal analysis; R.Y.: review and editing; R.F.K.: review and editing; Y.W.S.: investigation, data curation, and formal analysis; L.C.: investigation, data curation, and formal analysis; H.H.: investigation, data curation, and formal analysis; A.D.P.: conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft, investigation, data curation, and visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study did not require ethical approval and consent to participate.
Consent for publication
Not available.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aziz, A.Y.R., Mahfufah, U., Syahirah, N.A. et al. Dual delivery systems combining nanocrystals and dissolving microneedles for improved local vaginal delivery of fluconazole. Drug Deliv. and Transl. Res. 14, 1678–1692 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-023-01483-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-023-01483-9