Abstract
Thrombus has long been the major contributor of death and disability because it can cause adverse effects to varying degrees on the body, resulting in vascular blockage, embolism, heart valve deformation, widespread bleeding, etc. However, clinically, conventional thrombolytic drug treatments have hemorrhagic complication risks and easy to miss the best time of treatment window. Thus, it is an urgent need to investigate newly alternative treatment strategies that can reduce adverse effects and improve treatment effectiveness. Drugs based on nanomaterials act as a new biomedical strategy and promising tools, and have already been investigated for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in thrombus therapy. Recent studies have some encouraging progress. In the present review, we primarily concern with the latest developments in the areas of nanomedicines targeting thrombosis therapy. We present the thrombus’ formation, characteristics, and biomarkers for diagnosis, overview recent emerging nanomedicine strategies for thrombus therapy, and focus on the future design directions, challenges, and prospects in the nanomedicine application in thrombus therapy.
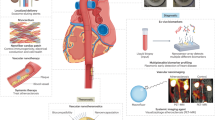
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
No new datasets were collected or generated for the purposes of this review article.
Abbreviations
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular disease
- NPs:
-
Nanoparticles
- US:
-
Ultrasound
- PE:
-
Pulmonary embolism
- FXIIIa:
-
Fibrin and activating factor XIII
- PC:
-
Phosphatidylcholine
- GPIIb/IIIa:
-
Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa
- RGD:
-
Arg–Gly–Asp
- PDI:
-
Protein disulfide isomerase
- ERp57:
-
Endoplasmic Recombinant protein 57
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- PSGL-1:
-
P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1
- RGDS:
-
Arg–Gly–Asp–Ser
- KQAGDV:
-
Lys–Gln–Ala–Gly–Asp–Val
- CREKA:
-
Cysteine–arginine–glutamate–lysine–alanine
- PPACK:
-
Phenylalanine–proline–arginine–chloromethylketone
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- HOCl:
-
Hypochlorous acid
- Nox:
-
NADPH oxidase family
- SS-NPA:
-
Shear-sensitive nanoparticle aggregates
- SK:
-
Streptokinase
- PEG:
-
Polyethylene glycol
- ICCA:
-
1-(4-Isopropylphenyl)-β-carboline-3-carboxylic acid
- THC:
-
1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-β-carbinol
- THCMA:
-
3S-THC-3-methyl aspartyl ester
- LIFU:
-
Low-intensity focused ultrasound
- NPep:
-
Nano emulsion
- EDC/NHS:
-
1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide/N-hydroxysuccinimide
- EPR effect:
-
Enhanced permeability and retention effect
- cRGD:
-
Cyclo(Arg–Gly–Asp–d-Phe–Cys)
- UK:
-
Urokinase
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet light
- UCNPs:
-
Upconversion nanomaterials
- NIR:
-
Near infrared light
- Azo:
-
Azobenzene
- PDA:
-
Polydopamine
- HMSN:
-
Hollow mesoporous silica
- Nets:
-
Networks
- Cur:
-
Curcumin
- HA:
-
Hyaluronic acid
- PVAX:
-
Poly(vanillyl alcohol-oxalate copolymer)
- VA:
-
Vanillyl alcohol
- Oxd:
-
Oxidized dextran
- PM:
-
Platelet membranes
- DTX:
-
Doxorubicin
- PMP:
-
Platelet granules
- PS:
-
Phosphatidylserine
- ECS:
-
Extracellular space
- FDA:
-
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
References
Zenych A, Fournier L, Chauvierre C. Nanomedicine progress in thrombolytic therapy. Biomaterials. 2020;258:120297.
Mathers CD, Loncar D. Projections of global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med. 2006;3(11):e442.
Lutsey PL, Zakai NA. Epidemiology and prevention of venous thromboembolism. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2023;20(4):248–62.
Correa-Paz C, da Silva-Candal A, Polo E, Parcq J, Vivien D, Maysinger D, et al. New approaches in nanomedicine for ischemic stroke. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(5).
Wang Y, Pisapati AV, Zhang XF, Cheng X. Recent developments in nanomaterial-based shear-sensitive drug delivery systems. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(13):e2002196.
Ma H, Jiang Z, Xu J, Liu J, Guo ZN. Targeted nano-delivery strategies for facilitating thrombolysis treatment in ischemic stroke. Drug Deliv. 2021;28(1):357-71.
Zhu J, Wang J, Li Y. Recent advances in magnetic nanocarriers for tumor treatment. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;159.
Song D, Li C, Zhu M, Chi S, Liu Z. Tracking hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in real time with a reversible NIR-IIb fluorescent redox probe. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022;61(44).
Cabrera D, Eizadi Sharifabad M, Ranjbar JA, Telling ND, Harper AGS. Clot-targeted magnetic hyperthermia permeabilizes blood clots to make them more susceptible to thrombolysis. J Thromb Haemost. 2022;20(11):2556–70.
Yu W, Yin N, Yang Y, Xuan C, Liu X, Liu W, et al. Rescuing ischemic stroke by biomimetic nanovesicles through accelerated thrombolysis and sequential ischemia-reperfusion protection. Acta Biomater. 2022;140:625–40.
Shen M, Wang Y, Hu F, Lv L, Chen K, Xing G. Thrombolytic agents: nanocarriers in targeted release. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). 2021;26(22):6776.
Furie B, Furie BC. Mechanisms of thrombus formation. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(9):938–49.
De Maeseneer MG, Kakkos SK, Aherne T, Baekgaard N, Black S, Blomgren L, et al. Editor's choice - European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2022 clinical practice guidelines on the management of chronic venous disease of the lower limbs. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2022;63(2):184–267.
Manz XD, Bogaard HJ, Aman J. Regulation of VWF (von Willebrand factor) in inflammatory thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2022;42(11):1307–20.
Bettiol A, Alibaz-Oner F, Direskeneli H, Hatemi G, Saadoun D, Seyahi E, et al. Vascular Behcet syndrome: from pathogenesis to treatment. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023;19(2):111–26.
Zhou S, Zhao W, Hu J, Mao C, Zhou M. Application of nanotechnology in thrombus therapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(7).
Dou H, Kotini A, Liu W, Fidler T, Endo-Umeda K, Sun X, et al. Oxidized phospholipids promote netosis and arterial thrombosis in LNK(SH2B3) deficiency. Circulation. 2021;144(24):1940–54.
Alkarithi G, Duval C, Shi Y, Macrae FL, Ariens RAS. Thrombus structural composition in cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021;41(9):2370–83.
Adrover JM, Pellico J, Fernández-Barahona I, Martín-Salamanca S, Ruiz-Cabello J, Hidalgo A, et al. Thrombo-tag, an in vivo formed nanotracer for the detection of thrombi in mice by fast pre-targeted molecular imaging. Nanoscale. 2020;12(45):22978–87.
Klaeske K, Meyer AL, Saeed D, Eifert S, Jawad K, Sieg F, et al. Decreased platelet specific receptor expression of P-selectin and GPIIb/IIIa predict future non-surgical bleeding in patients after left ventricular assist device implantation. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(18).
Bachelet L, Bertholon I, Lavigne D, Vassy R, Jandrot-Perrus M, Chaubet F, et al. Affinity of low molecular weight fucoidan for p-selectin triggers its binding to activated human platelets. Biochem Biophys Acta. 2009;1790(2):141–6.
Nayak L, Sweet DR, Thomas A, Lapping SD, Kalikasingh K, Madera A, et al. A targetable pathway in neutrophils mitigates both arterial and venous thrombosis. Sci Transl Med. 2022;14(660):eabj7465.
Hajtuch J, Iwicka E, Szczoczarz A, Flis D, Megiel E, Cieciorski P, et al. The pharmacological effects of silver nanoparticles functionalized with eptifibatide on platelets and endothelial cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:4383–400.
Yin R, Zhou L, Gao N, Lin L, Sun H, Chen D, et al. Unveiling the disaccharide-branched glycosaminoglycan and anticoagulant potential of its derivatives. Biomacromol. 2021;22(3):1244–55.
Zhou XH, Cheng ZP, Lu M, Lin WY, Luo LL, Ming ZY, et al. Adiponectin receptor agonist adiporon modulates human and mouse platelet function. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023;44(2):356–66.
Souri M, Yokoyama C, Osaki T, Ichinose A. Antibodies against noncatalytic b subunit of factor XIII inhibit activation of factor XIII and fibrin crosslinking. Thromb Haemost. 2023;123(9):841–54.
Pasternack R, Buchold C, Jahnig R, Pelzer C, Sommer M, Heil A, et al. Novel inhibitor ZED3197 as potential drug candidate in anticoagulation targeting coagulation FXIIIa (F13a). J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18(1):191–200.
Zhang N, Ru B, Hu J, Xu L, Wan Q, Liu W, et al. Recent advances of creka peptide-based nanoplatforms in biomedical applications. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):77.
Arjmand S, Pardakhty A, Forootanfar H, Khazaeli P. A road to bring Brij52 back to attention: shear stress sensitive Brij52 niosomal carriers for targeted drug delivery to obstructed blood vessels. Med Hypotheses. 2018;121:137–41.
Behera SS, Pramanik K, Nayak MK. Recent advancement in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases: conventional therapy to nanotechnology. Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(30):4479–97.
Mohri H, Ohkubo T. How vitronectin binds to activated glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex and its function in platelet aggregation. Am J Clin Pathol. 1991;96(5):605–9.
Huang J, Li X, Shi X, Zhu M, Wang J, Huang S, et al. Platelet integrin alphaIIbbeta3: signal transduction, regulation, and its therapeutic targeting. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12(1):26.
Xiong B, Jha V, Min JK, Cho J. Protein disulfide isomerase in cardiovascular disease. Exp Mol Med. 2020;52(3):390–9.
Juenet M, Aid-Launais R, Li B, Berger A, Aerts J, Ollivier V, et al. Thrombolytic therapy based on fucoidan-functionalized polymer nanoparticles targeting p-selectin. Biomaterials. 2018;156:204–16.
Setiadi H, Yago T, Liu Z, McEver RP. Endothelial signaling by neutrophil-released oncostatin m enhances P-selectin-dependent inflammation and thrombosis. Blood Adv. 2019;3(2):168–83.
Libby P. The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nature. 2021;592(7855):524–33.
Wei Z, Xin G, Wang H, Zheng H, Ji C, Gu J, et al. The diosgenin prodrug nanoparticles with pH-responsive as a drug delivery system uniquely prevents thrombosis without increased bleeding risk. Nanomedicine. 2018;14(3):673–84.
Mitchell JL, Little G, Bye AP, Gaspar RS, Unsworth AJ, Kriek N, et al. Platelet factor XIII-a regulates platelet function and promotes clot retraction and stability. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2023;7(5).
Poon C, Gallo J, Joo J, Chang T, Bañobre-López M, Chung EJ. Hybrid, metal oxide-peptide amphiphile micelles for molecular magnetic resonance imaging of atherosclerosis. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018;16(1):92.
Peters D, Kastantin M, Kotamraju VR, Karmali PP, Gujraty K, Tirrell M, et al. Targeting atherosclerosis by using modular, multifunctional micelles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106(24):9815–9.
Davie EW, Kulman JD. An overview of the structure and function of thrombin. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2006;32(Suppl 1):3–15.
Gunawan ST, Kempe K, Bonnard T, Cui J, Alt K, Law LS, et al. Multifunctional thrombin-activatable polymer capsules for specific targeting to activated platelets. Adv Mater (Deerfield Beach, Fla). 2015;27(35):5153–7.
Lin KY, Lo JH, Consul N, Kwong GA, Bhatia SN. Self-titrating anticoagulant nanocomplexes that restore homeostatic regulation of the coagulation cascade. ACS Nano. 2014;8(9):8776–85.
Chen J, Vemuri C, Palekar RU, Gaut JP, Goette M, Hu L, et al. Antithrombin nanoparticles improve kidney reperfusion and protect kidney function after ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015;308(7):F765–73.
Tintelnot J, Xu Y, Lesker TR, Schonlein M, Konczalla L, Giannou AD, et al. Microbiota-derived 3-IAA influences chemotherapy efficacy in pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2023;615(7950):168–74.
Bettiol A, Galora S, Argento FR, Fini E, Emmi G, Mattioli I, et al. Erythrocyte oxidative stress and thrombosis. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2022;24.
Braunersreuther V, Montecucco F, Asrih M, Pelli G, Galan K, Frias M, et al. Role of nadph oxidase isoforms Nox1, Nox2 and Nox4 in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013;64:99–107.
Nabeebaccus AA, Reumiller CM, Shen J, Zoccarato A, Santos CXC, Shah AM. The regulation of cardiac intermediary metabolism by NADPH oxidases. Cardiovasc Res. 2023;118(17):3305–19.
Xu H, She P, Ma B, Zhao Z, Li G, Wang Y. Ros responsive nanoparticles loaded with lipid-specific aiegen for atherosclerosis-targeted diagnosis and bifunctional therapy. Biomaterials. 2022;288.
Wang D, Wang X. Diosgenin and its analogs: potential protective agents against atherosclerosis. Drug Des Dev Ther. 2022;16:2305–23.
Li B, Chen R, Zhang Y, Zhao L, Liang H, Yan Y, et al. Rgd modified protein-polymer conjugates for pH-triggered targeted thrombolysis. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2019;2(1):437–46.
Ferrero JM, Gonzalez-Ascaso A, Matas JFR. The mechanisms of potassium loss in acute myocardial ischemia: new insights from computational simulations. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1074160.
Broersma RJ, Bullemer GD, Mammen EF. Acidosis induced disseminated intravascular microthrombosis and its dissolution by streptokinase. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1970;24(1):55–67.
Zhang G, Qin Q, Zhang C, Sun X, Kazama K, Yi B, et al. Ndrg1 signaling is essential for endothelial inflammation and vascular remodeling. Circ Res. 2023;132(3):306–19.
Ku DN. Blood flow in arteries. Annu Rev Fluid Mech. 1997;29(1):399–434.
Molloy CP, Yao Y, Kammoun H, Bonnard T, Hoefer T, Alt K, et al. Shear-sensitive nanocapsule drug release for site-specific inhibition of occlusive thrombus formation. J Thromb Haemost : JTH. 2017;15(5):972–82.
Torchilin VP, Papisov MI, Orekhova NM, Belyaev AA, Petrov AD, Ragimov SE. Magnetically driven thrombolytic preparation containing immobilized streptokinase-targeted transport and action. Haemostasis. 1988;18(2):113–6.
Nguyen PD, O’Rear EA, Johnson AE, Patterson E, Whitsett TL, Bhakta R. Accelerated thrombolysis and reperfusion in a canine model of myocardial infarction by liposomal encapsulation of streptokinase. Circ Res. 1990;66(3):875–8.
Igor A, Tatyana V, Irina L, Katsiaryna D, Vladimir A. Efficiency of targeted delivery of streptokinase based on fibrin-specific liposomes in the in vivo experiment. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023;13(3):811–21.
Sun N, Ye Z, Hao T, Zheng S, Sun Y, Zhang Y, et al. Inhibition of arterial thrombus formation by blocking exposed collagen surface using lwwnsyy-poly(l-glutamic acid) nanoconjugate. Langmuir : The ACS Journal of Surfaces and Colloids. 2021;37(22):6792–9.
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Wu J, Chen H, Zhao M, et al. Modifying ICCA with Trp-Phe-Phe to enhance in vivo activity and form nano-medicine. Int J Nanomed. 2020;15:465–81.
Feng Q, Wang M, Muhtar E, Wang Y, Zhu H. Nanoparticles of a new small-molecule P-selectin inhibitor attenuate thrombosis, inflammation, and tumor growth in two animal models. Int J Nanomed. 2021;16:5777–95.
Liu Y, Yang Z, Huang X, Yu G, Wang S, Zhou Z, et al. Glutathione-responsive self-assembled magnetic gold nanowreath for enhanced tumor imaging and imaging-guided photothermal therapy. ACS Nano. 2018;12(8):8129–37.
Ji W, Zhang Y, Deng Y, Li C, Kankala RK, Chen A. Nature-inspired nanocarriers for improving drug therapy of atherosclerosis. Regen Biomater. 2023;10:rbad069.
Deng Q, Zhang L, Lv W, Liu X, Ren J, Qu X. Biological mediator-propelled nanosweeper for nonpharmaceutical thrombus therapy. ACS Nano. 2021;15(4):6604–13.
Sloand JN, Rokni E, Watson CT, Miller MA, Manning KB, Simon JC, et al. Ultrasound-responsive nanopeptisomes enable synchronous spatial imaging and inhibition of clot growth in deep vein thrombosis. Adv Healthcare Mater. 2021;10(16).
Nan D, Jin H, Yang D, Yu W, Jia J, Yu Z, et al. Combination of polyethylene glycol-conjugated urokinase nanogels and urokinase for acute ischemic stroke therapeutic implications. Transl Stroke Res. 2021;12(5):844–57.
Cui W, Liu R, Jin H, Huang Y, Liu W, He M. The protective effect of polyethylene glycol-conjugated urokinase nanogels in rat models of ischemic stroke when administrated outside the usual time window. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;523(4):887–93.
Chavan YR, Tambe SM, Jain DD, Khairnar SV, Amin PD. Redefining the importance of polylactide-co-glycolide acid (PLGA) in drug delivery. Ann Pharm Fr. 2022;80(5):603–16.
Chen K, Wang Y, Liang H, Xia S, Liang W, Kong J, et al. Intrinsic biotaxi solution based on blood cell membrane cloaking enables fullerenol thrombolysis in vivo. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(13):14958–70.
Wang Y, Zhang K, Qin X, Li T, Qiu J, Yin T, et al. Biomimetic nanotherapies: red blood cell based core-shell structured nanocomplexes for atherosclerosis management. Adv Sci (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany). 2019;6(12):1900172.
Huang Y, Gu B, Salles C, II, Taylor KA, Yu L, Ren J, et al. Fibrinogen-mimicking, multiarm nanovesicles for human thrombus-specific delivery of tissue plasminogen activator and targeted thrombolytic therapy. Sci Adv. 2021;7(23).
Fang RH, Kroll AV, Gao W, Zhang L. Cell membrane coating nanotechnology. Adv Mater (Deerfield Beach, Fla). 2018;30(23).
Huang M, Zhang SF, Lü S, Qi T, Yan J, Gao C, et al. Synthesis of mesoporous silica/polyglutamic acid peptide dendrimer with dual targeting and its application in dissolving thrombus. J Biomed Mater Res, Part A. 2019;107(8):1824–31.
Marcano L, Orue I, Gandia D, Gandarias L, Weigand M, Abrudan RM, et al. Magnetic anisotropy of individual nanomagnets embedded in biological systems determined by axi-asymmetric x-ray transmission microscopy. ACS Nano. 2022;16(5):7398–408.
Lv J, Zhang L, Du W, Ling G, Zhang P. Functional gold nanoparticles for diagnosis, treatment and prevention of thrombus. J Controlled Release. 2022;345:572–85.
Sha X, Dai Y, Song X, Liu S, Zhang S, Li J. The opportunities and challenges of silica nanomaterial for atherosclerosis. Int J Nanomed. 2021;16:701–14.
Chen D, Zhu T, Fu W, Zhang H. Electrospun polycaprolactone/collagen nanofibers cross-linked with 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide/n-hydroxysuccinimide and genipin facilitate endothelial cell regeneration and may be a promising candidate for vascular scaffolds. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:2127–44.
Chen JP, Yang PC, Ma YH, Lu YJ. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for delivery of tissue plasminogen activator. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2011;11(12):11089–94.
Xu J, Zhou Y, Nie H, Xiong Z, OuYang H, Huang L, et al. Hyperthermia-triggered uk release nanovectors for deep venous thrombosis therapy. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(4):787–93.
Liu S, Sun Y, Zhang T, Cao L, Zhong Z, Cheng H, et al. Upconversion nanoparticles regulated drug & gas dual-effective nanoplatform for the targeting cooperated therapy of thrombus and anticoagulation. Bioact Mater. 2022;18:91–103.
Zhang Z, Chen Y, Zhang Y. Self-assembly of upconversion nanoparticles based materials and their emerging applications. Small. 2022;18(9).
Morya VK, Kim J, Kim EK. Algal fucoidan: Structural and size-dependent bioactivities and their perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012;93(1):71–82.
Falahati M, Sharifi M, Hagen T. Explaining chemical clues of metal organic framework-nanozyme nano-/micro-motors in targeted treatment of cancers: Benchmarks and challenges. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):153.
Zheng J, Qi R, Dai C, Li G, Sang M. Enzyme catalysis biomotor engineering of neutrophils for nanodrug delivery and cell-based thrombolytic therapy. ACS Nano. 2022;16(2):2330–44.
Nelson CE, Kintzing JR, Hanna A, Shannon JM, Gupta MK, Duvall CL. Balancing cationic and hydrophobic content of pegylated siRNA polyplexes enhances endosome escape, stability, blood circulation time, and bioactivity in vivo. ACS Nano. 2013;7(10):8870–80.
Ma B, Xu H, Wang Y, Yang L, Zhuang W, Li G, et al. Biomimetic-coated nanoplatform with lipid-specific imaging and ROS responsiveness for atherosclerosis-targeted theranostics. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(30):35410–21.
Sun W, Xu Y, Yao Y, Yue J, Wu Z, Li H, et al. Self-oxygenation mesoporous MnO2 nanoparticles with ultra-high drug loading capacity for targeted arteriosclerosis therapy. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):88.
Xu C, Lei C, Yu C. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for protein protection and delivery. Front Chem. 2019;7:290.
Zhang X, Liu J, Yang X, He G, Li B, Qin J, et al. CuCo2S4 nanocrystals as a nanoplatform for photothermal therapy of arterial inflammation. Nanoscale. 2019;11(19):9733–42.
Li S, Zhang K, Ma Z, Zhang W, Song Z, Wang W, et al. Biomimetic nanoplatelets to target delivery hirudin for site-specific photothermal/photodynamic thrombolysis and preventing venous thrombus formation. Small. 2022;18(51):e2203184.
Wu X, Liu K, Wang R, Yang G, Lin J, Liu X. Multifunctional CuBiS2 nanoparticles for computed tomography guided photothermal therapy in preventing arterial restenosis after endovascular treatment. Front Bioeng Biotech. 2020;8.
Liu J, Wang P, Zhang X, Wang L, Wang D, Gu Z, et al. Rapid degradation and high renal clearance of Cu3BiS3 nanodots for efficient cancer diagnosis and photothermal therapy in vivo. ACS Nano. 2016;10(4):4587–98.
Fu D, Fang Q, Yuan F, Liu J, Ding H, Chen X, et al. Thrombolysis combined therapy using CuS@SiO2-PEG/uPA nanoparticles. Front Chem. 2021;9.
Bhatia SN, Chen X, Dobrovolskaia MA, Lammers T. Cancer nanomedicine. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22(10):550–6.
Zhang H, Qu H, He Q, Gao L, Zhang H, Wang Y, et al. Thrombus-targeted nanoparticles for thrombin-triggered thrombolysis and local inflammatory microenvironment regulation. J Control Release. 2021;339:195–207.
Zhang H, Pei Y, Gao L, He Q, Zhang H, Zhu L, et al. Shear force responsive and fixed-point separated system for targeted treatment of arterial thrombus. Nano Today. 2021;38.
Guan Q, Dou H. Thrombus-targeting polymeric nanocarriers and their biomedical applications in thrombolytic therapy. Front Physiol. 2021;12.
Zhao Y, Xie R, Yodsanit N, Ye M, Wang Y, Gong S. Biomimetic fibrin-targeted and H2O2-responsive nanocarriers for thrombus therapy. Nano Today. 2020;35.
Jung E, Noh J, Kang C, Yoo D, Song C, Lee D. Ultrasound imaging and on-demand therapy of peripheral arterial diseases using H2O2-activated bubble generating anti-inflammatory polymer particles. Biomaterials. 2018;179:175–85.
Kang C, Cho W, Park M, Kim J, Park S, Shin D, et al. H2O2-triggered bubble generating antioxidant polymeric nanoparticles as ischemia/reperfusion targeted nanotheranostics. Biomaterials. 2016;85:195–203.
Zhao Y, Xie R, Yodsanit N, Ye M, Wang Y, Wang B, et al. Hydrogen peroxide-responsive platelet membrane-coated nanoparticles for thrombus therapy. Biomaterials science. 2021;9(7):2696–708.
Russell P, Hagemeyer CE, Esser L, Voelcker NH. Theranostic nanoparticles for the management of thrombosis. Theranostics. 2022;12(6):2773–800.
Ma Y, Ma Y, Gao M, Han Z, Jiang W, Gu Y, et al. Platelet-mimicking therapeutic system for noninvasive mitigation of the progression of atherosclerotic plaques. Adv Sci (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany). 2021;8(8):2004128.
Hu CM, Fang RH, Wang KC, Luk BT, Thamphiwatana S, Dehaini D, et al. Nanoparticle biointerfacing by platelet membrane cloaking. Nature. 2015;526(7571):118–21.
Mohale S, Kunde SS, Wairkar S. Biomimetic fabrication of nanotherapeutics by leukocyte membrane cloaking for targeted therapy. Colloids Surf, B. 2022;219.
Wang Y, Zhang K, Li T, Maruf A, Qin X, Luo L, et al. Macrophage membrane functionalized biomimetic nanoparticles for targeted anti-atherosclerosis applications. Theranostics. 2021;11(1):164–80.
Lee NH, You S, Taghizadeh A, Taghizadeh M, Kim HS. Cell membrane-cloaked nanotherapeutics for targeted drug delivery. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(4).
Xu WJ, Cai JX, Li YJ, Wu JY, Xiang D. Recent progress of macrophage vesicle-based drug delivery systems. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022;12(10):2287–302.
Zhong Y, Gong WJ, Gao XH, Li YN, Liu K, Hu YG, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of a novel nanoparticle carrying urokinase used in targeted thrombolysis. J Biomed Mater Res, Part A. 2020;108(2):193–200.
Luo X, Xie J, Zhou Z, Ma S, Wang L, Li M, et al. Virus-inspired gold nanorod-mesoporous silica core-shell nanoparticles integrated with TTF-EG3287 for synergetic tumor photothermal therapy and selective therapy for vascular thrombosis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(37):44013–27.
Zhong Y, Qin X, Wang Y, Qu K, Luo L, Zhang K, et al. "Plug and play" functionalized erythrocyte nanoplatform for target atherosclerosis management. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(29):33862–73.
Thompson W, Papoutsakis ET. Similar but distinct: The impact of biomechanical forces and culture age on the production, cargo loading, and biological efficacy of human megakaryocytic extracellular vesicles for applications in cell and gene therapies. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023;8(5).
De Matteis V, Rinaldi R. Toxicity assessment in the nanoparticle era. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1048:1–19.
Wingard CJ, Walters DM, Cathey BL, Hilderbrand SC, Katwa P, Lin S, et al. Mast cells contribute to altered vascular reactivity and ischemia-reperfusion injury following cerium oxide nanoparticle instillation. Nanotoxicology. 2011;5(4):531–45.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21605161), Shenyang High-level Innovative Talent Program (RC180167), and Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (2021-BS-105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to conceptualizing and writing this manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
No animal or human studies were performed to generate data for this article.
Consent for publication
All authors have reviewed this manuscript and approve of its publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Y., Yu, Y., Zhang, X. et al. Progress of nanomaterials in the treatment of thrombus. Drug Deliv. and Transl. Res. 14, 1154–1172 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-023-01478-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-023-01478-6